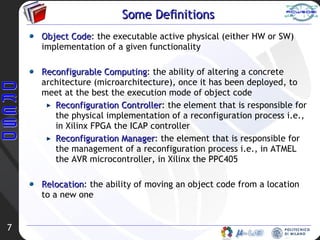
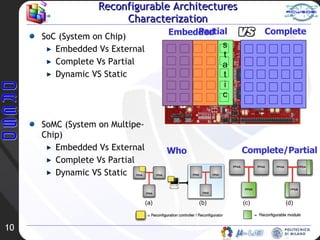
The document discusses concepts related to partial dynamic reconfiguration. It defines key terms like reconfigurable computing, object code, reconfiguration controller, and reconfiguration manager. It also discusses the 5 Ws of reconfiguration - who controls it, where the controller is located, when configurations are generated, which is the granularity, and in what dimension it operates. Examples of reconfiguration in everyday life like sports are provided. Reconfigurable architectures are characterized based on factors like embedded vs external, complete vs partial, and dynamic vs static. Finally, more definitions related to cores, IP cores, and reconfigurable functional units and regions are given.
![Reconfiguration: basic concepts P artial D ynamic R econfiguration W orkshop DRESD Team [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/basicconcepts-1225470702210871-9/75/RCW-DEI-Basic-Concepts-1-2048.jpg)