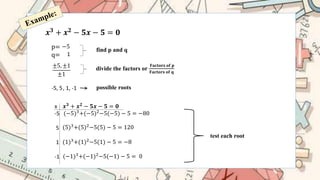
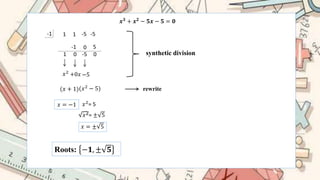
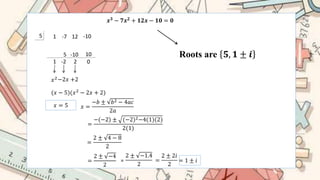
This document provides information about solving polynomials with irrational and imaginary roots. It begins with an introduction to irrational roots, noting that the polynomial coefficients must be rational. It then defines imaginary roots as occurring when the discriminant of a quadratic equation is negative. The document goes on to show examples of solving polynomials with rational number factorization and the quadratic formula to find irrational or imaginary roots. Roots found include irrational numbers like ±5 and imaginary numbers like 1±i. In all, the document demonstrates the process of finding all types of roots of polynomials.