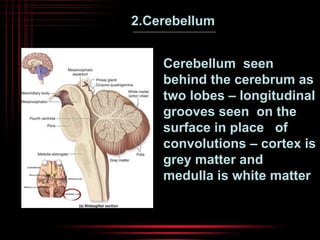
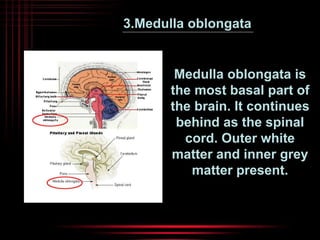
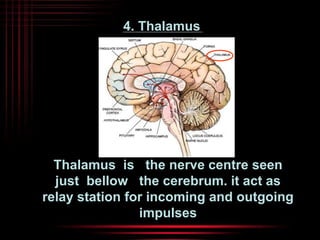
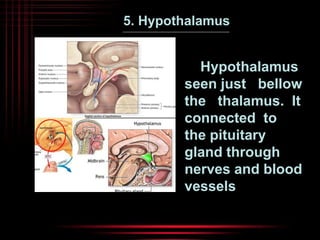
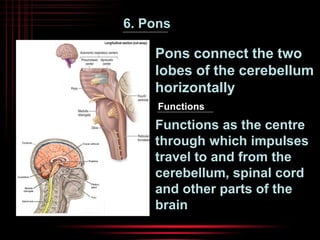
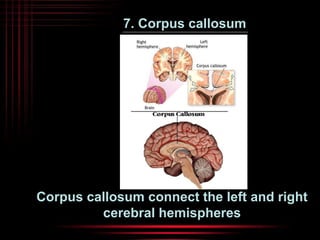
The brain and spinal cord make up the central nervous system. The brain is protected by three layers of meninges and situated within the cranium. It is divided into several parts that each have distinct functions. The cerebrum is the largest part and controls conscious thought and voluntary movement. The cerebellum coordinates balance and muscle activity. The medulla oblongata regulates involuntary functions like breathing and heart rate. Other key parts include the thalamus, which relays signals, and the hypothalamus, which helps maintain homeostasis.