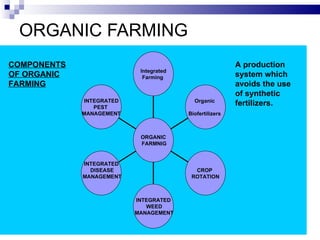
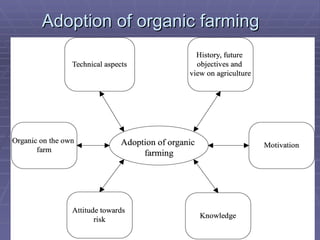
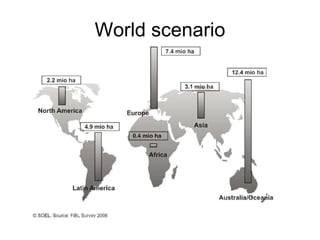
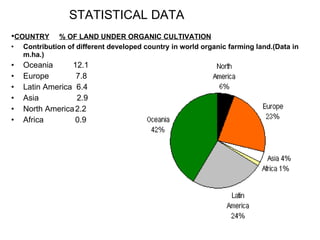
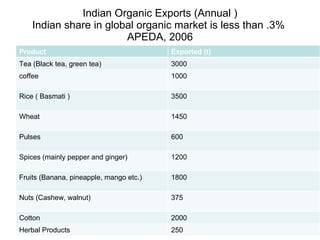
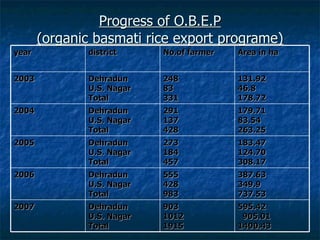
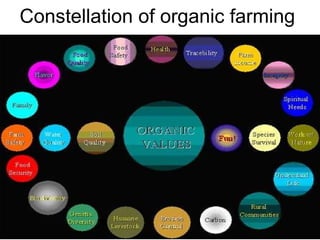
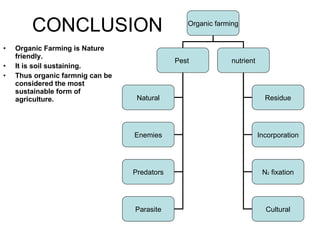
The document discusses the principles, advantages, and components of organic farming compared to chemical farming, emphasizing its sustainability and environmental benefits. It includes statistical data on organic farming in India and globally, highlighting challenges and opportunities for organic cultivation and exports. Organic farming aims to improve food security, enhance soil fertility, and promote eco-friendly practices within agricultural systems.