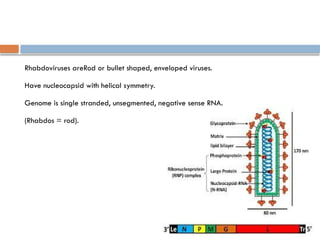
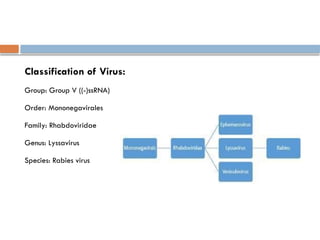
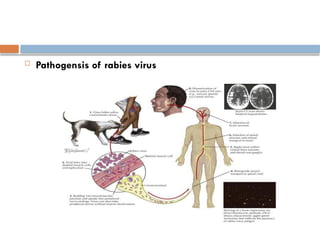
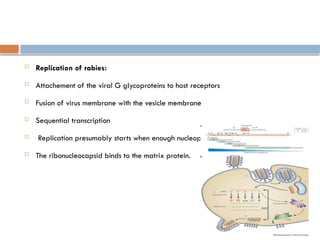
Rabies virus is a bullet-shaped, enveloped virus classified under the family Rhabdoviridae and genus Lyssavirus, with a single-stranded, negative sense RNA genome. It primarily affects the central nervous system and initial symptoms can include malaise, fever, and anxiety, leading to severe neurological manifestations. Treatment involves wound washing, application of disinfectants, and administration of rabies immunoglobulin.