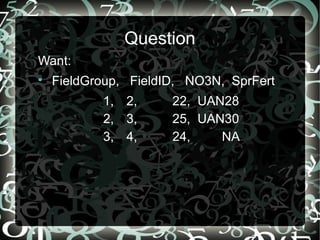
This document discusses using the merge() function in R to perform SQL joins. It shows how merge() can be used to join two datasets (A and B) on the common field "FieldGroup" to get a full outer join, equivalent to a LEFT JOIN in SQL. The default behavior of merge() performs an inner join, but specifying all.y=TRUE ensures all records from the second dataset (B) are kept, even if they don't match the first dataset (A). It also demonstrates how the output can be larger than the inputs if duplicate keys are present.