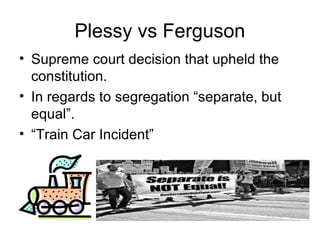
This document provides a review of key concepts for an upcoming quiz. It summarizes information about the president, legislative branch, and several important Supreme Court cases. The president has authority over the military, executes laws, and controls the nuclear arsenal. Congress is made up of the Senate and House of Representatives. Key Supreme Court cases discussed include Brown v. Board of Education, Roe v. Wade, and Miranda v. Arizona. Links are also provided to additional review materials on slideshare and blogger.