This document outlines quick test methods for determining the concentrations of chromium and chloride in water samples. It describes:
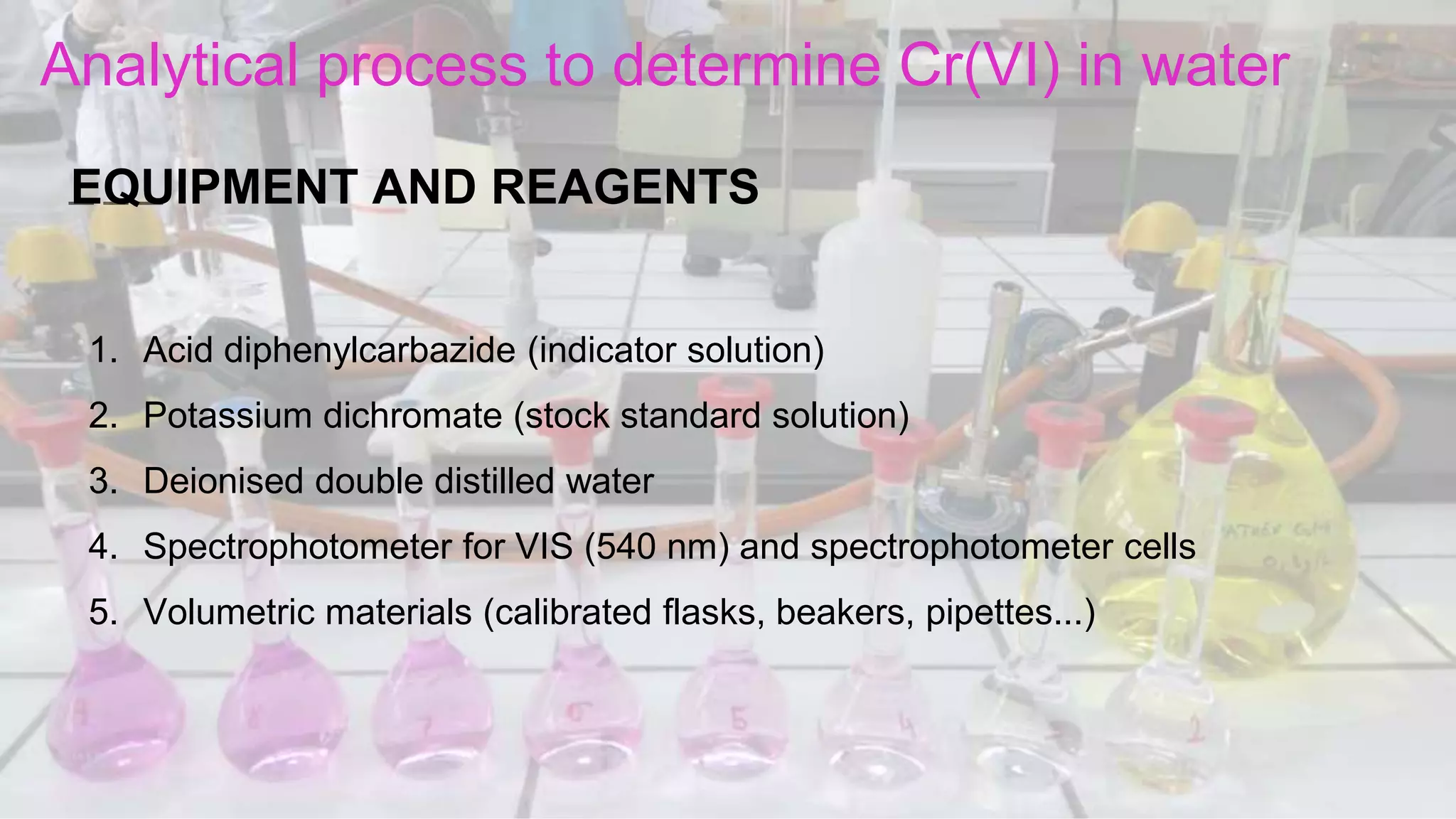
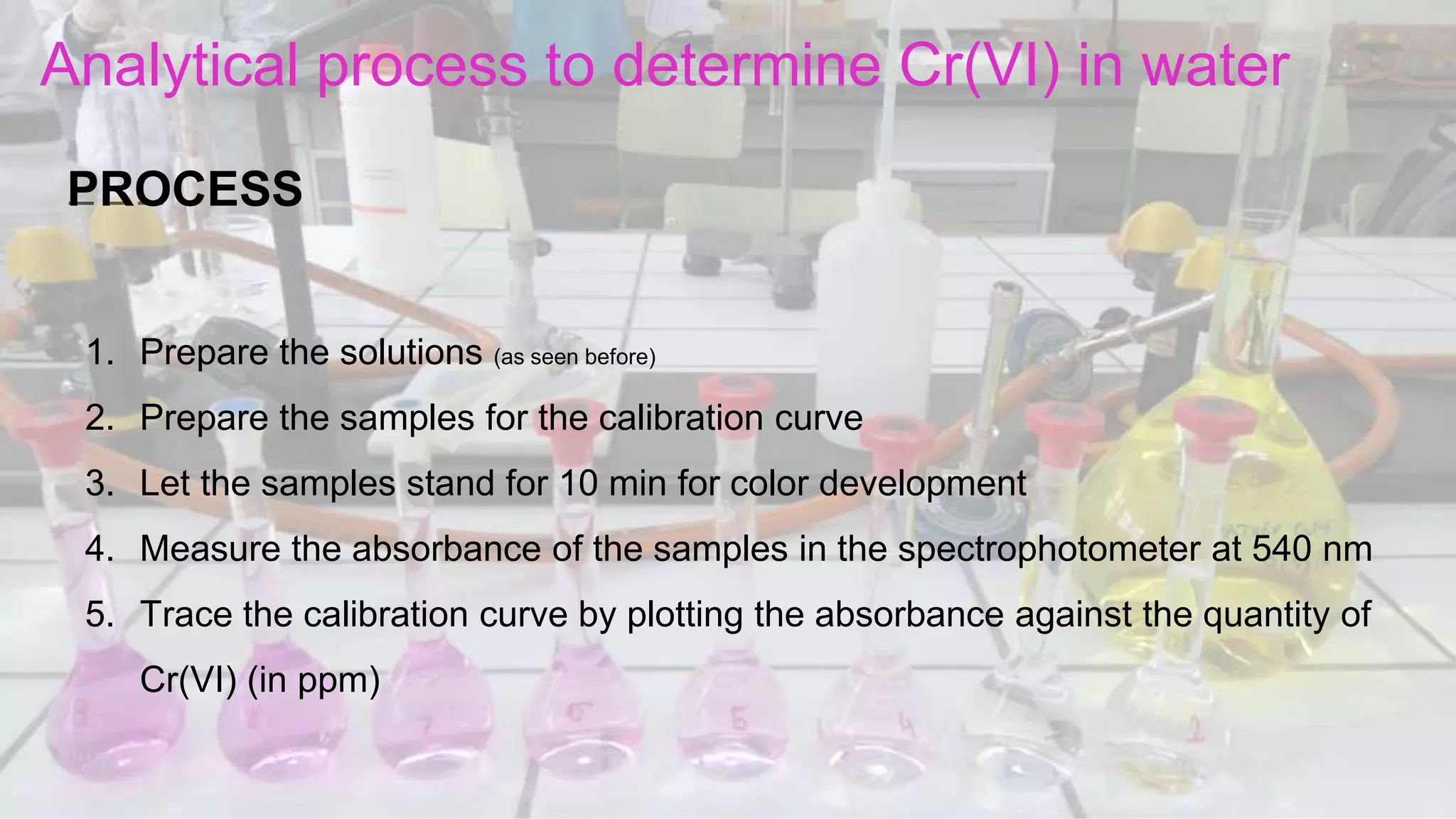
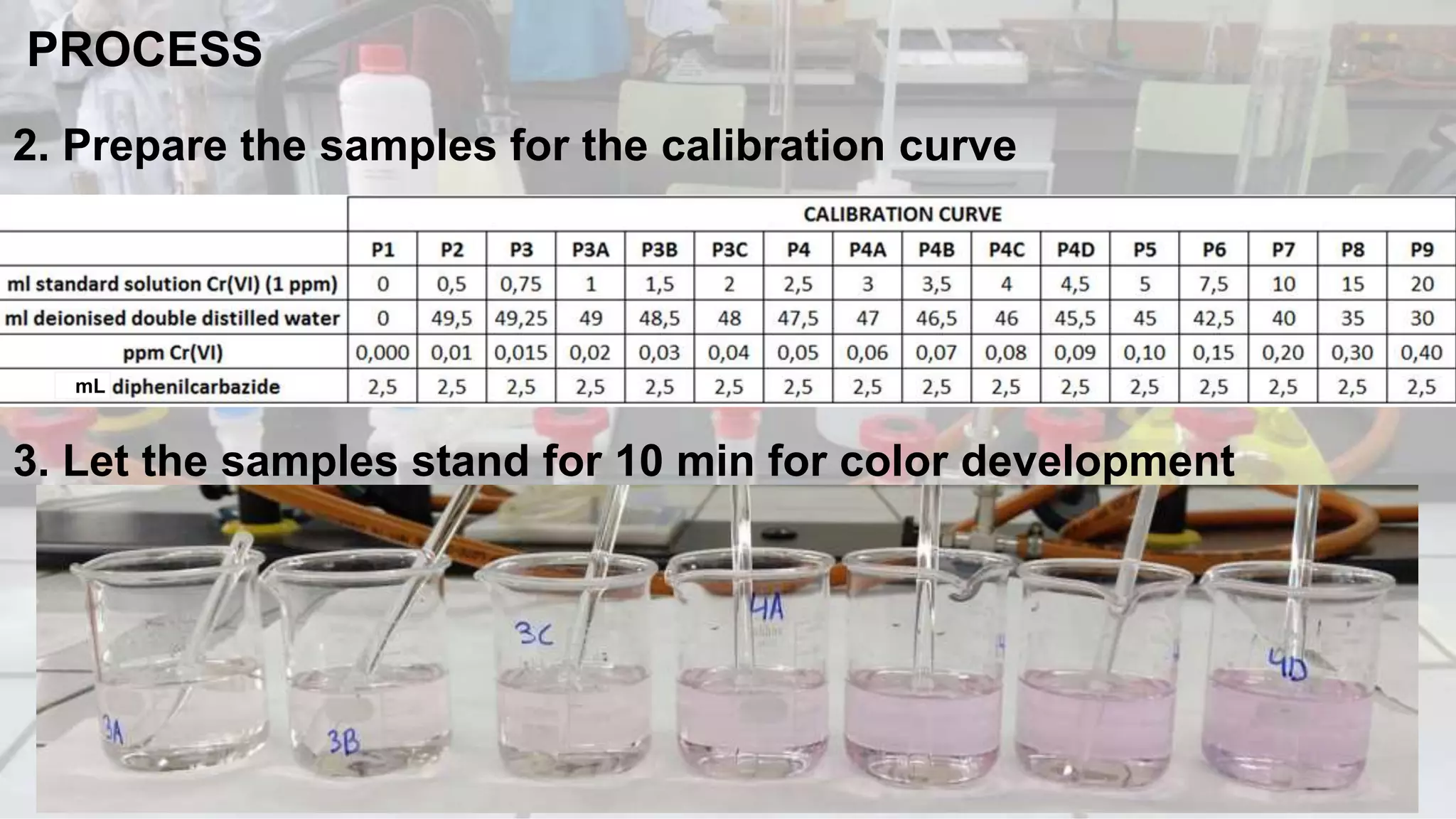
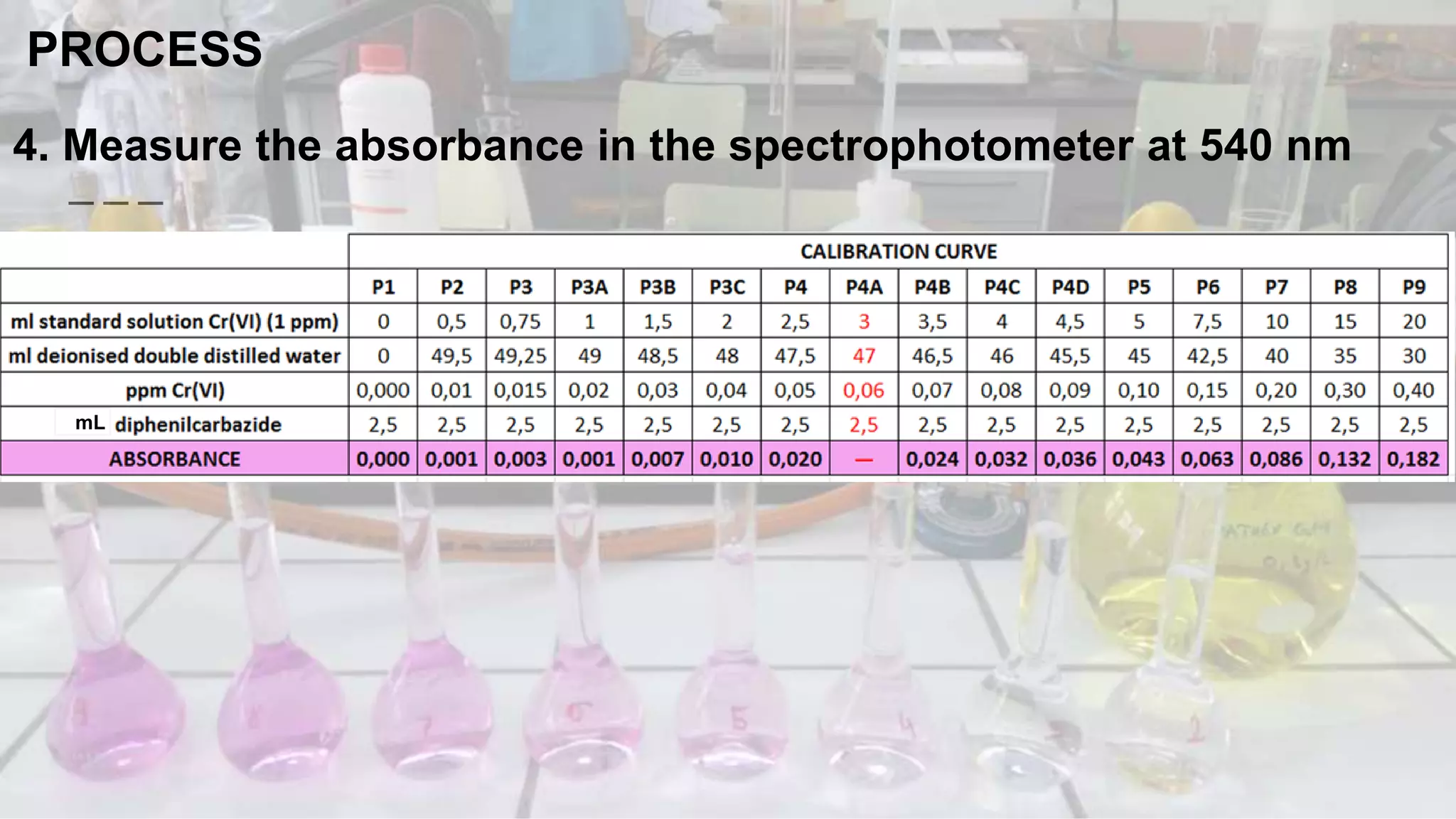
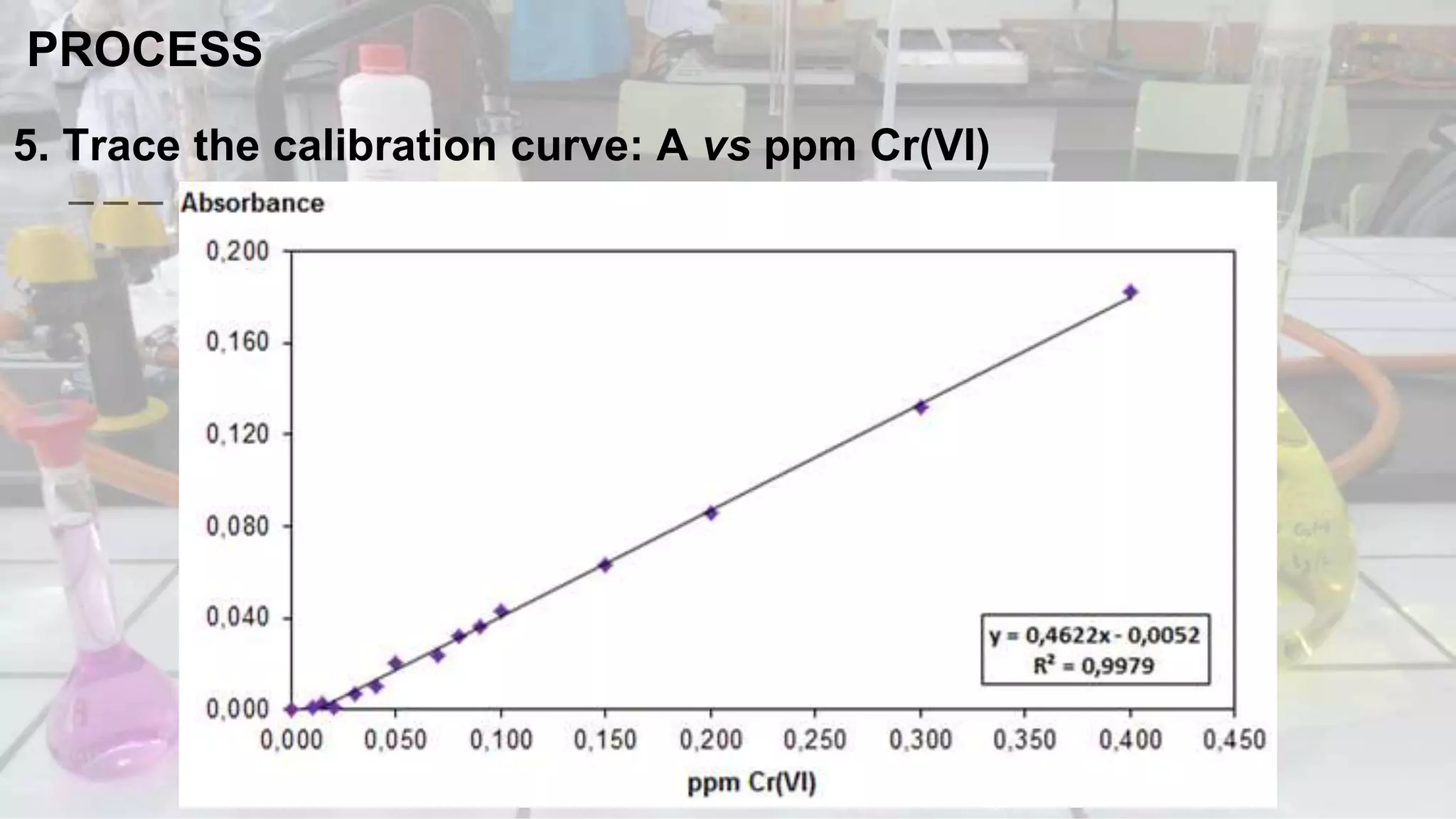
1. The analytical process to determine chromium using acid diphenylcarbazide indicator solution and spectrophotometry. Standards and samples are prepared and their absorbance measured to create a calibration curve relating absorbance to chromium concentration.
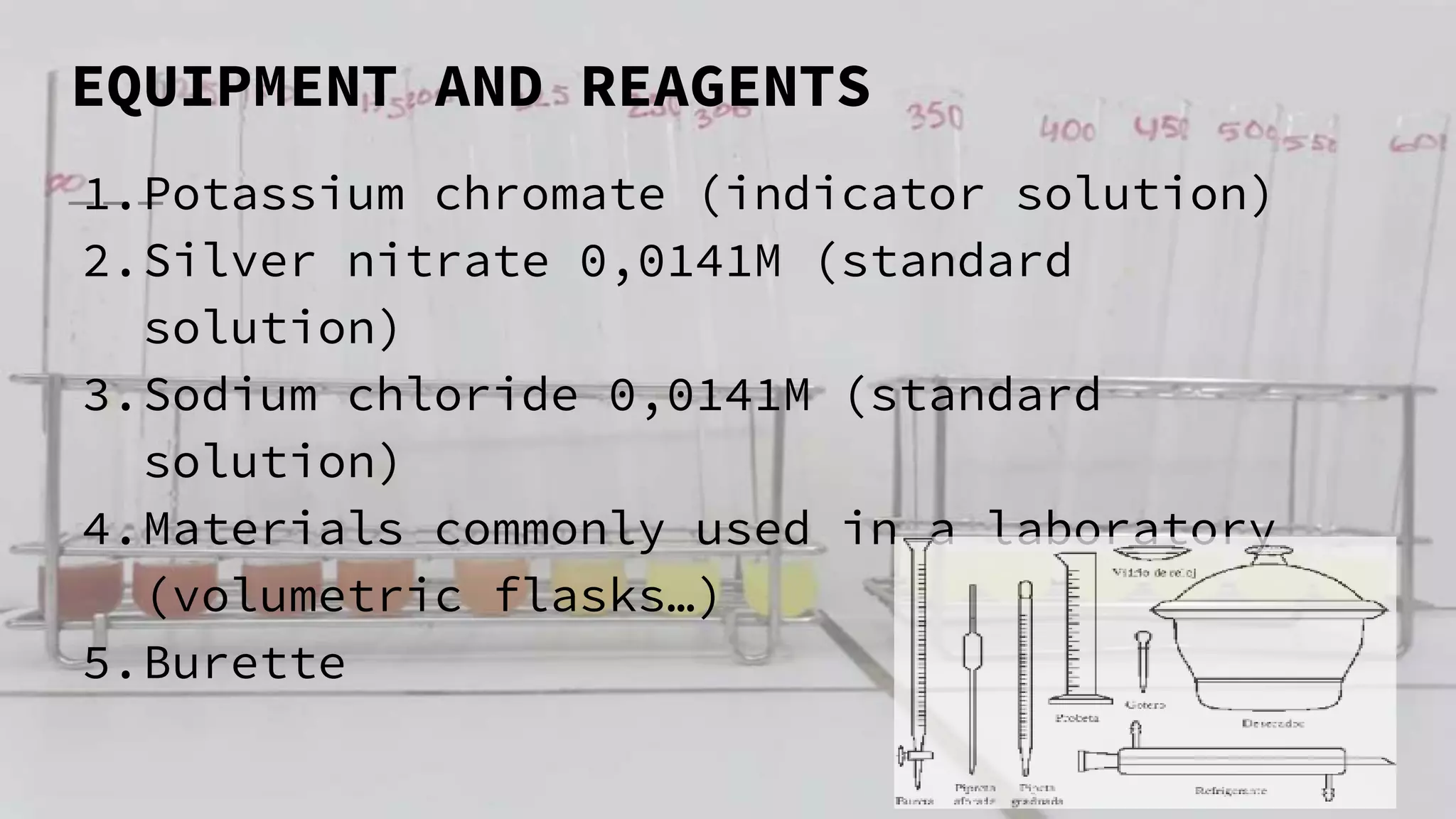
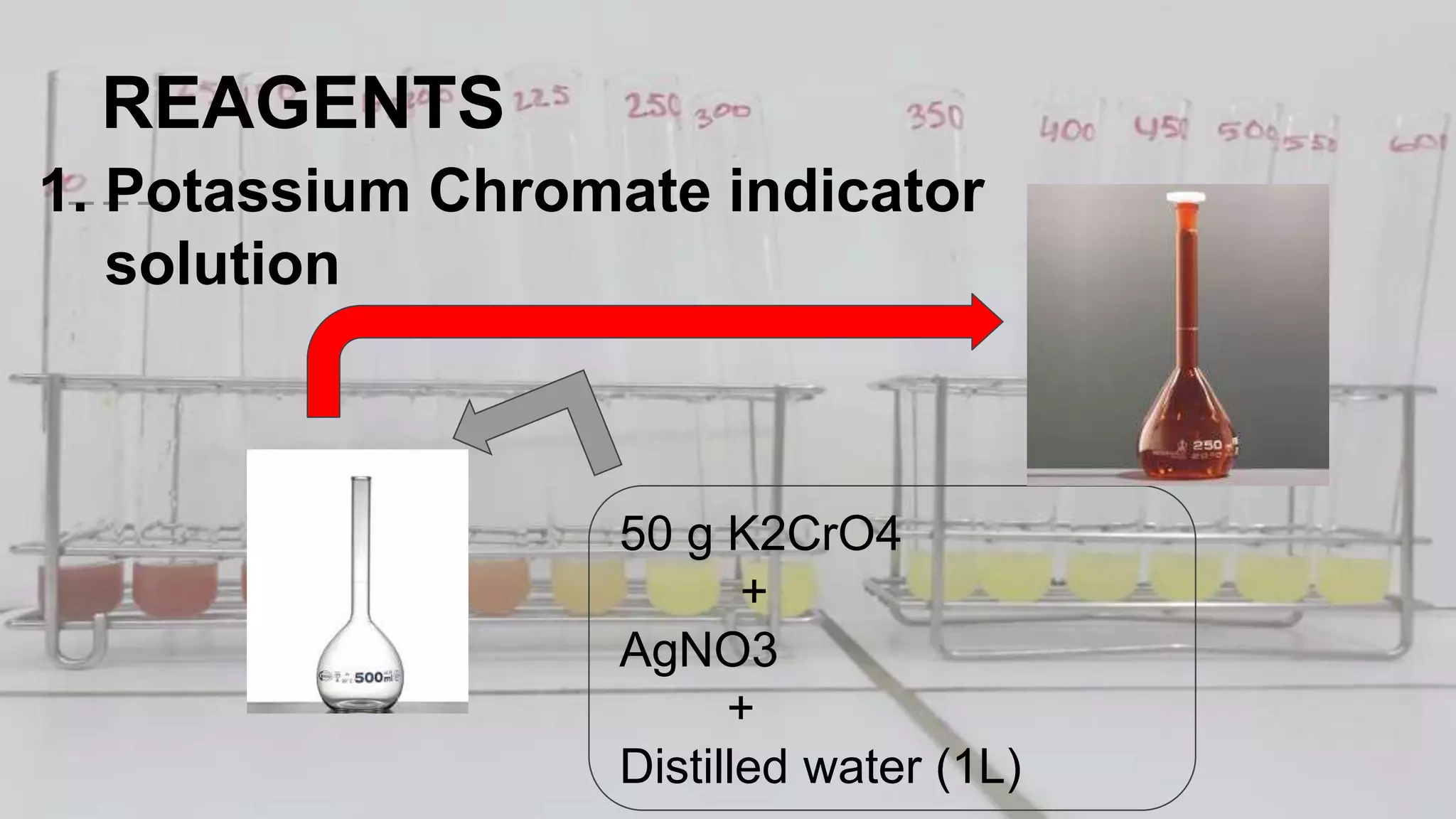
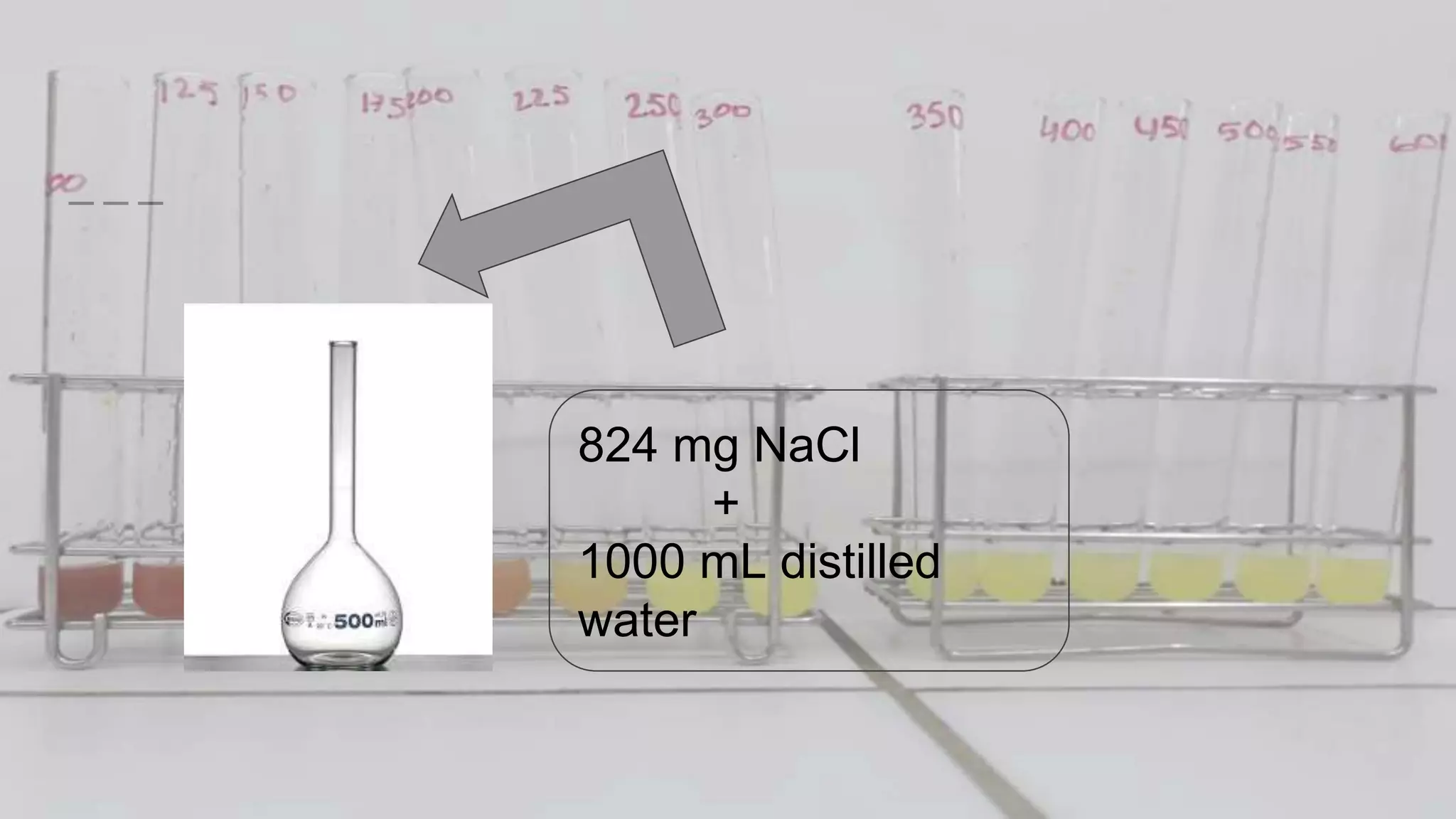
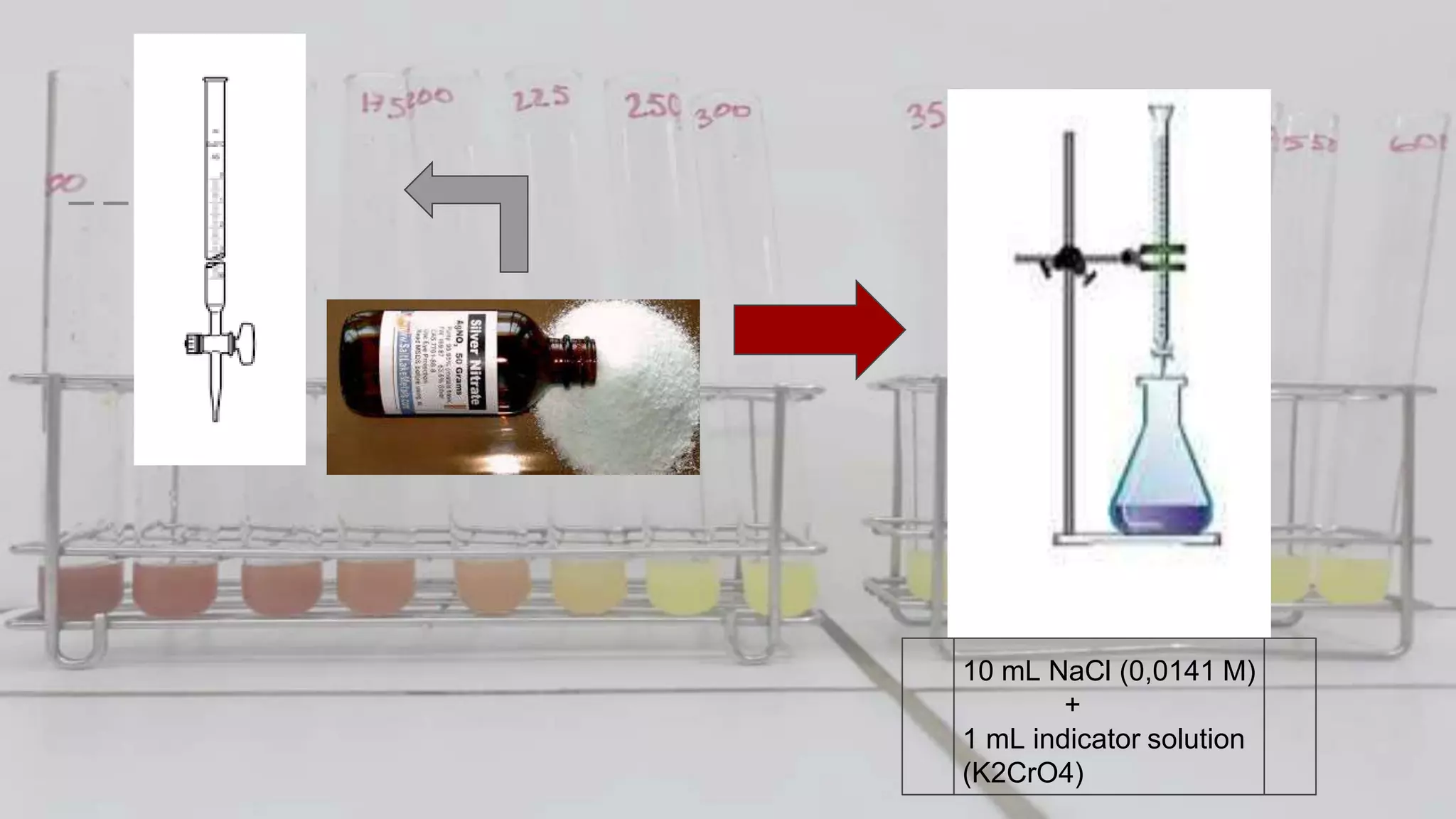
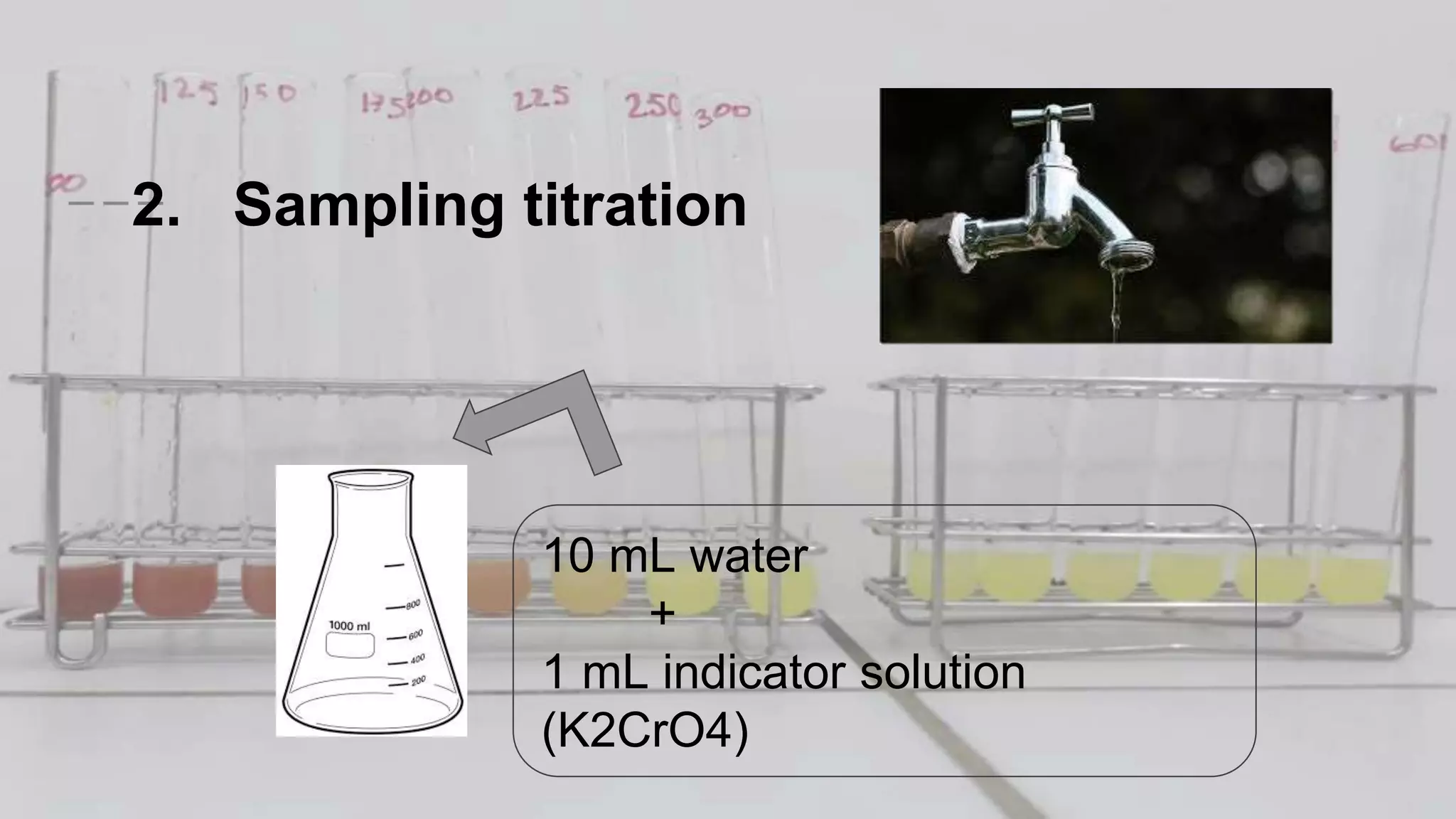
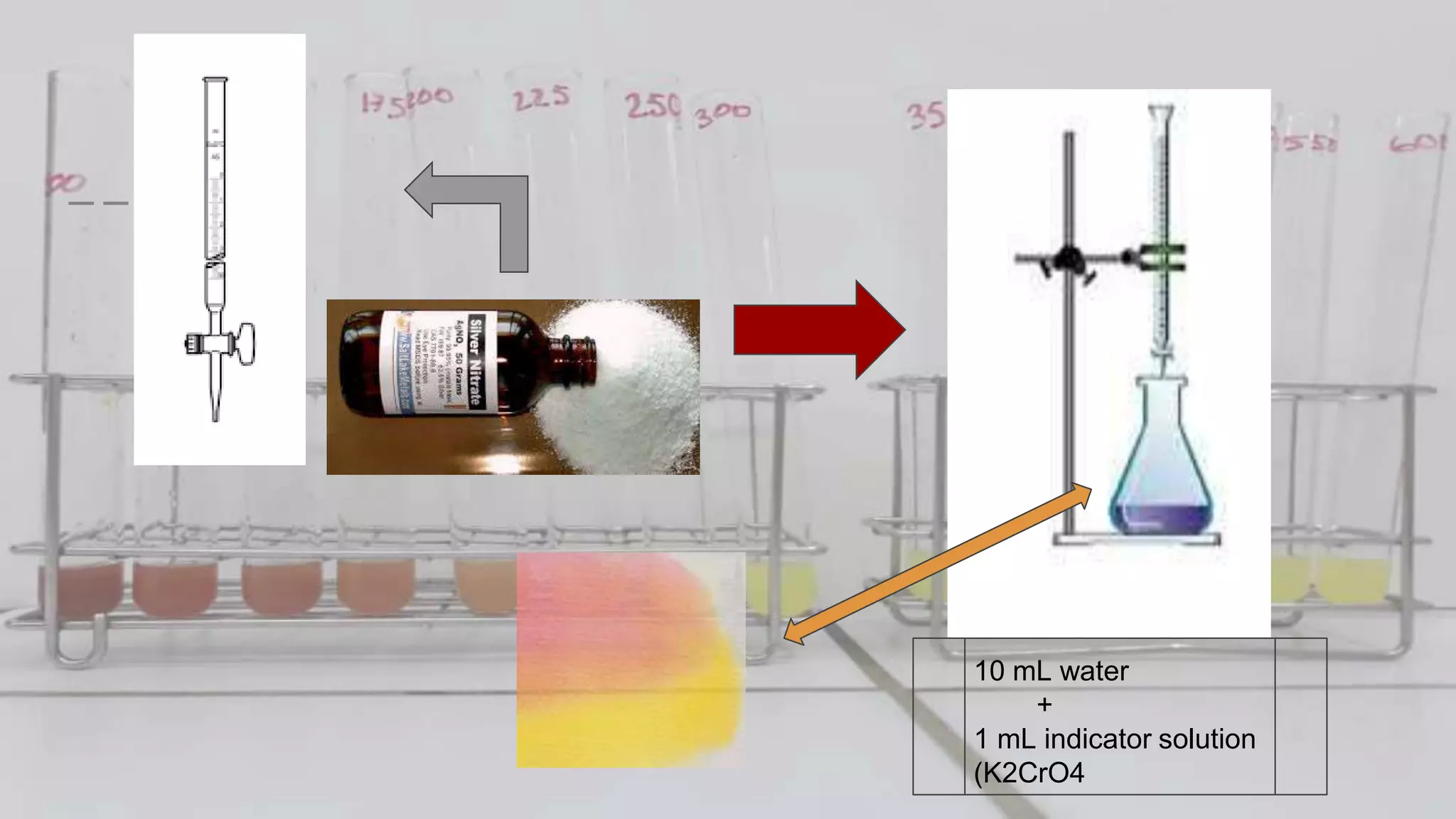
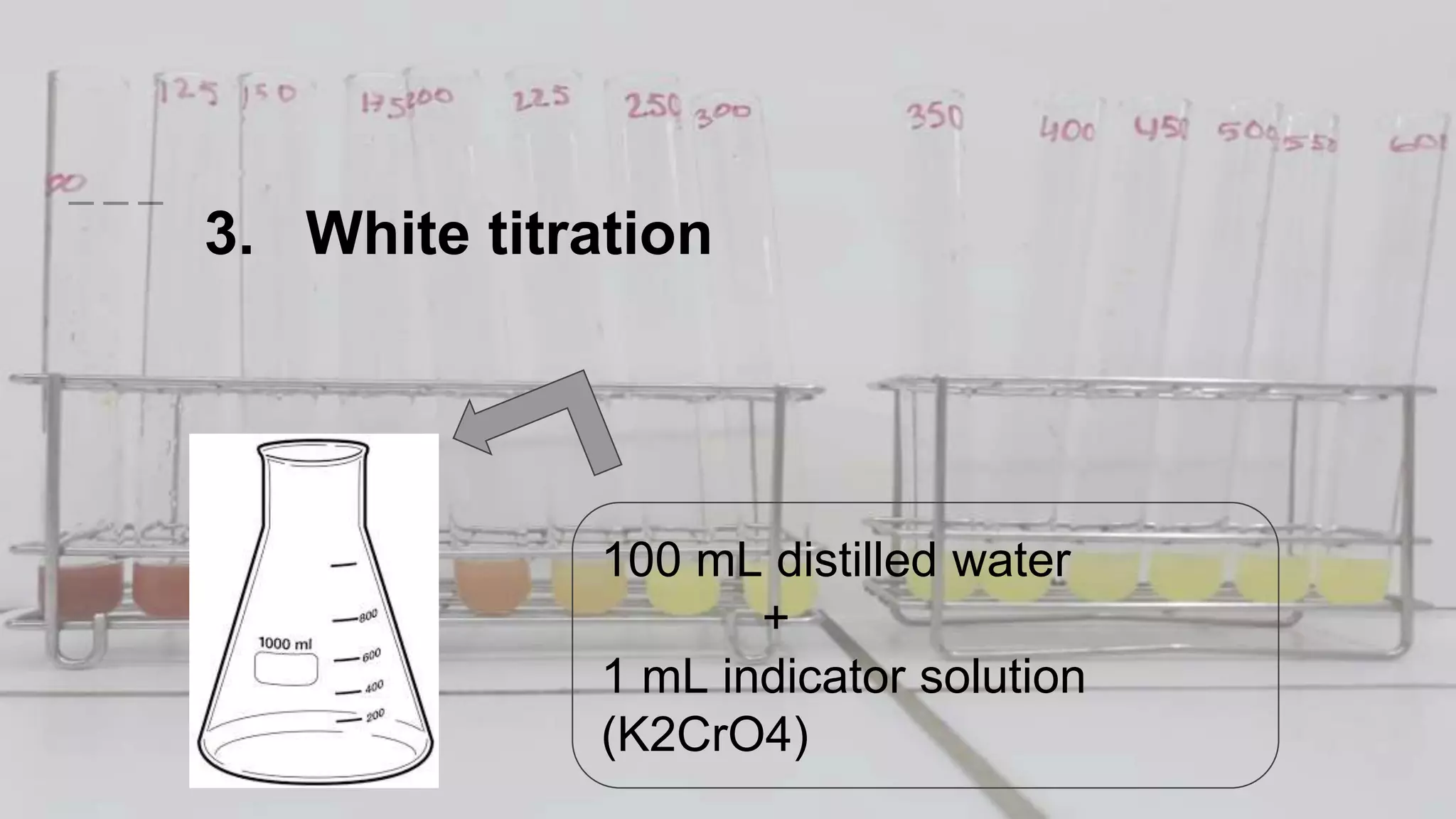
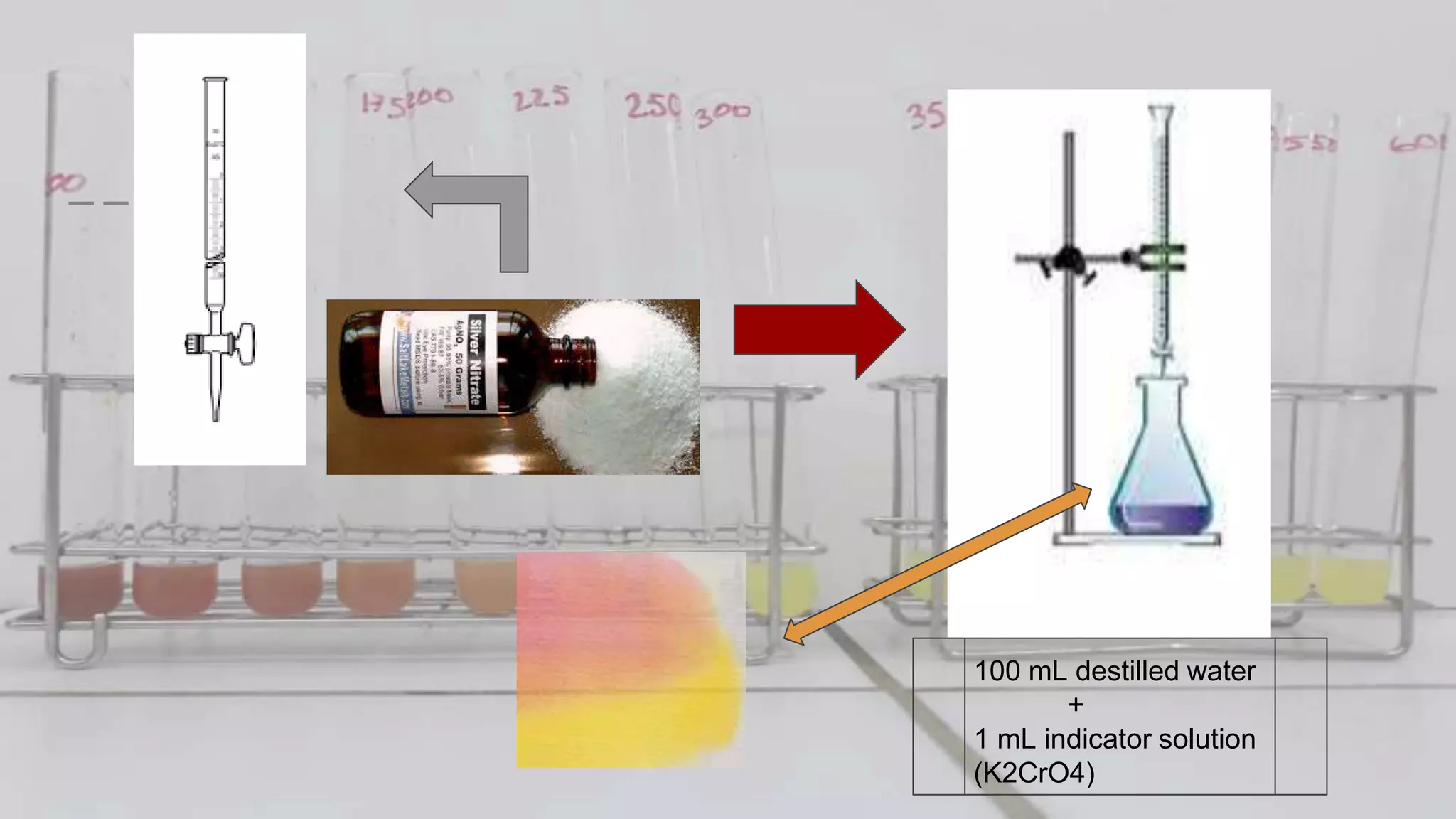
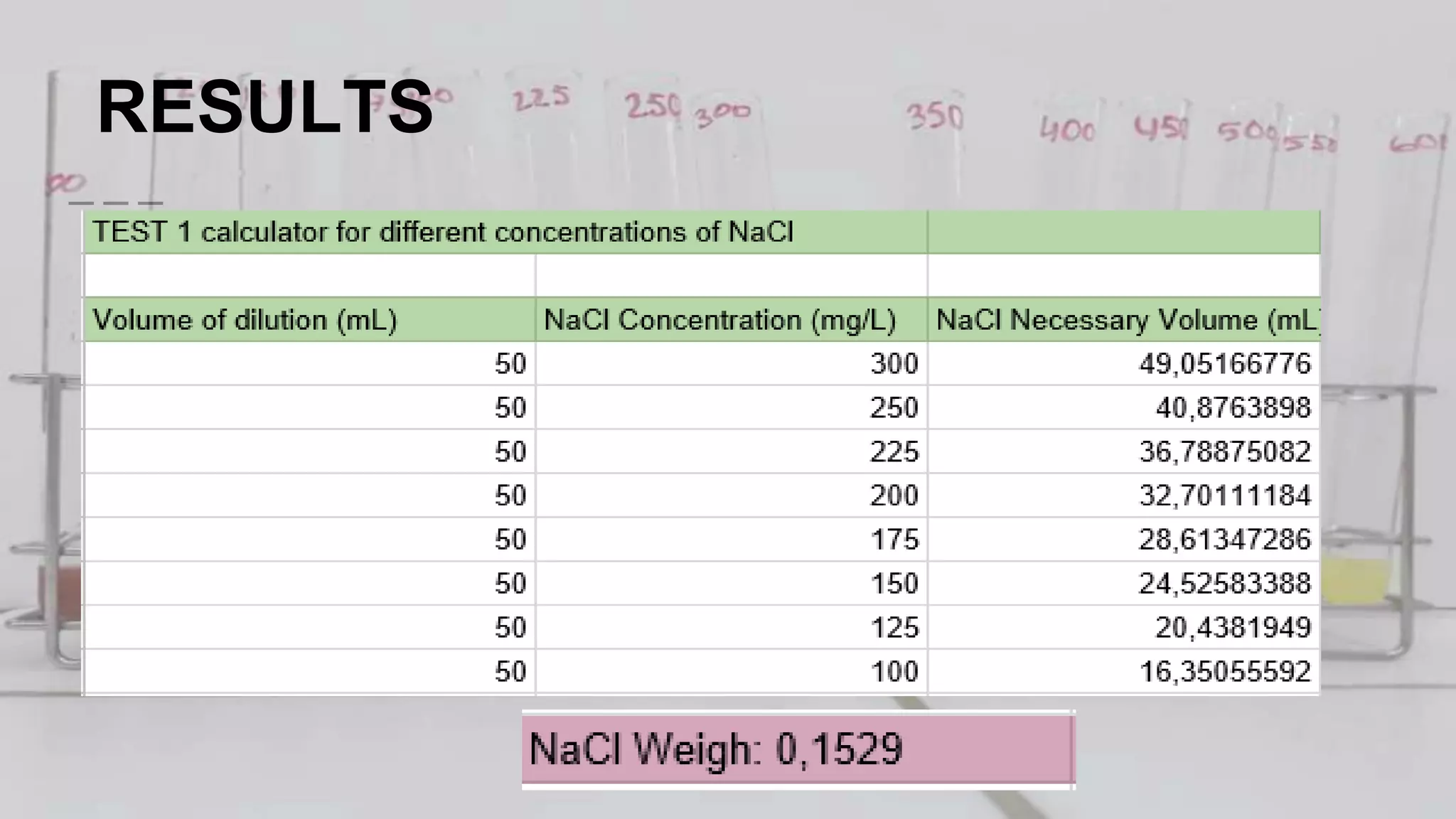
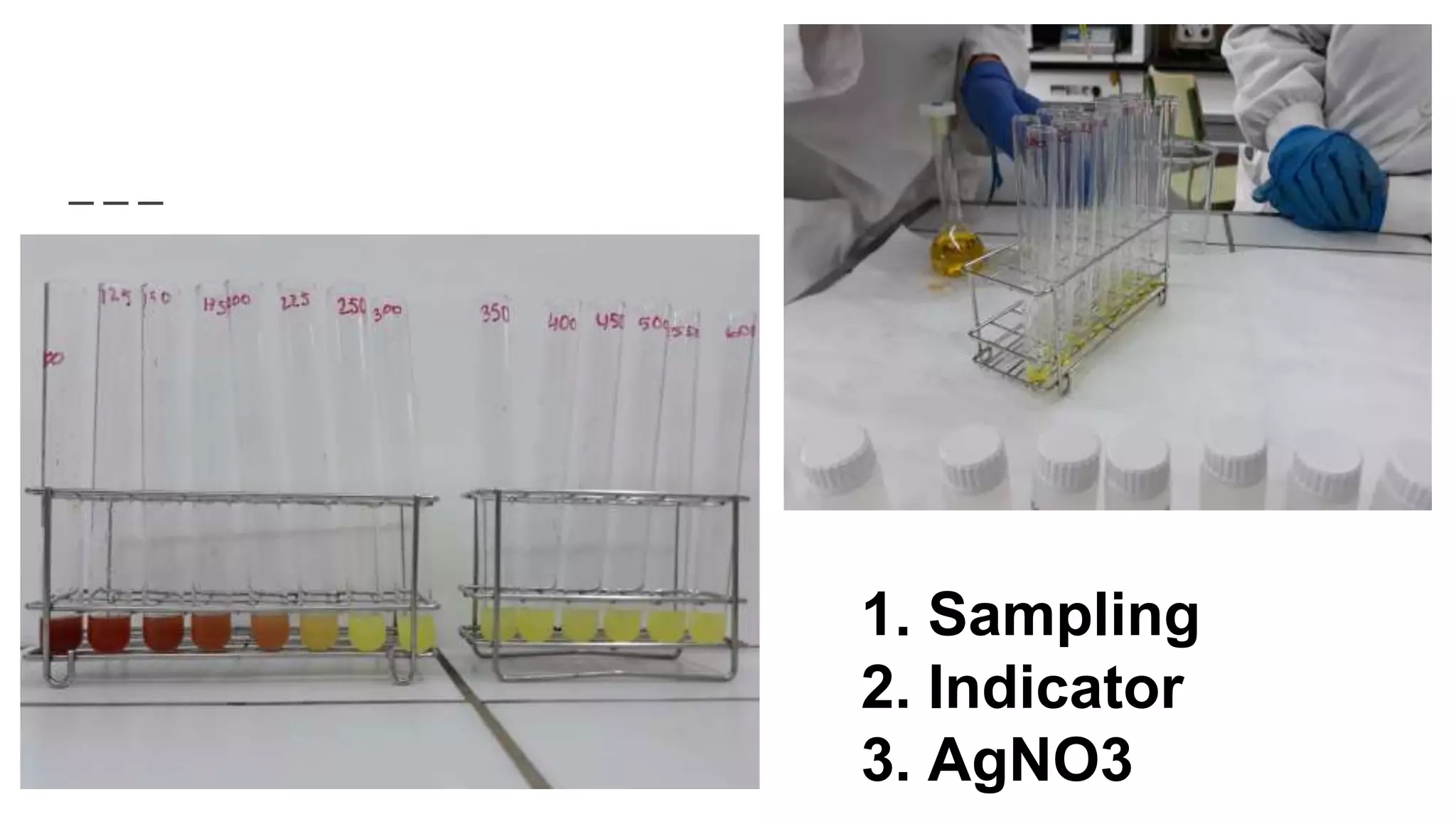
2. The analytical process to determine chloride using potassium chromate indicator solution and silver nitrate titration. Sodium chloride and water samples are titrated with silver nitrate and the volumes recorded.
3. Potential ways to package the reagents for portability, including using pill containers and glass ampoules. It also discusses the possibility of developing a smartphone app using the camera


















![[Cl-]
mg/L
R G B
100 63 7 3
125 81 18 3
150 83 25 13
175 94 40 12
200 109 63 30
225 139 117 60
250 146 146 58
300 151 146 61
350 136 144 51
400 147 146 62
450 144 142 65
500 148 146 63
550 148 146 61
600 152 146 58](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/quicktestsfordeterminingcrycl-180909185830/75/Quick-tests-for-determining-Cr-VI-y-Cl-34-2048.jpg)