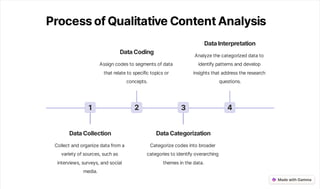
Qualitative content analysis is a research method for systematically analyzing both text and non-text data to derive deeper insights. It consists of several key steps including data collection, coding, categorization, and interpretation, with applications in marketing research, social science, and media analysis. Challenges include interpretation bias and resource intensiveness, yet it remains a flexible tool for uncovering complex meanings.