The document discusses QR codes, including:
- QR codes were created in 1994 by Denso Wave to track vehicle parts and became widely used in Japan in 2002 with mobile phones.
- QR codes can store various data types and are read by smartphones. They consist of black square modules arranged in a pattern on a white background.
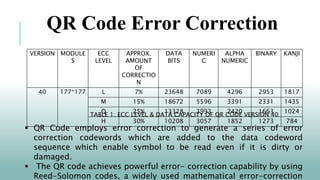
- The error correction capability allows QR codes to be read even if dirty or damaged. It employs Reed-Solomon codes to generate error correction codewords.
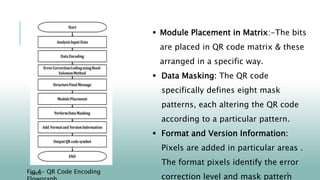
- QR code versions range from 1 to 40, with higher versions having larger matrix sizes and storage capacity. Structure includes data, error correction codewords, and format/version information.


![Introduction
Contents Here
• A QR code is a type of matrix bar code or
two-dimensional code that can store data
information and designed to be read by
smartphones.
• QR stands for “Quick Response”
indicating that the code contents should
be decoded very quickly at high speed.
• The code consists of black modules
arranged in a square pattern on a white
background. The information encoded
may be text, a URL and other data. [1,2]
01](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/qrcodescanningpowerpointtemplates-231001132602-c053d1f1/85/QR-Code-Scanning-PowerPoint-Templates-pptx-3-320.jpg)
![Evolution
1994
1960
s
2002
QR Codes are created
by the Toyota
subsidiary Denso
Wave in 1994, and
was initially used for
tracking inventory in
vehicle parts
manufacturing.[1,2]
Traditional
barcodes and the
POS system, where
a cash register
displays the price
of an item after
the barcode was
scanned by an
optical sensor.[3]
In 2002, mobile
phones in Japan
were equipped with
a QR code-reading
prompting
widespread public
usage, so people
could access
websites and obtain
a coupon by](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/qrcodescanningpowerpointtemplates-231001132602-c053d1f1/85/QR-Code-Scanning-PowerPoint-Templates-pptx-4-320.jpg)
![Versions Of QR Code
"Module configuration" refers to the number of modules
contained in a symbol, commencing with Version 1 (21 × 21
modules) up to Version 40 (177 × 177 modules) [4].
Figure 2:- Module configuration of the basic QR
codes.
The symbol versions of the QR Code range from Version 1
to Version 40. Each version has a different module
configuration or number of modules. (The module refers to the
black and white dots that make up QR Code).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/qrcodescanningpowerpointtemplates-231001132602-c053d1f1/85/QR-Code-Scanning-PowerPoint-Templates-pptx-5-320.jpg)
![Structure Of QR Code
Fig.3- Structure Of a QR Code[5]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/qrcodescanningpowerpointtemplates-231001132602-c053d1f1/85/QR-Code-Scanning-PowerPoint-Templates-pptx-6-320.jpg)

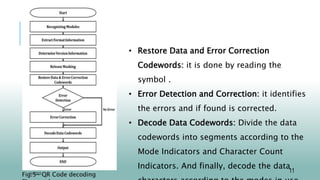
![ Recognizing Modules: Recognize dark and light
modules as an array of “1" and “0" .
• Extract Format Information: It identifies the
masking pattern and ECC level used in the QR
Code.
• Determine Version Information: It determines the
Specific version of QR Code which is used.
• Release Masking: XOR the encoding region bit
pattern with the Mask Pattern.[5,6]
Decoding
Fig.5- QR Code decoding](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/qrcodescanningpowerpointtemplates-231001132602-c053d1f1/85/QR-Code-Scanning-PowerPoint-Templates-pptx-10-320.jpg)