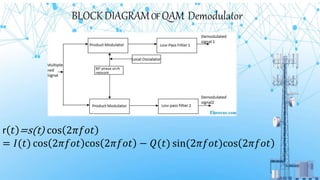
Quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM) is a modulation technique that encodes data by changing both the amplitude and phase of carrier waves. It offers higher bandwidth efficiency than other modulation techniques like PSK. In QAM, two carriers shifted in phase by 90 degrees are modulated such that the output signal exhibits both amplitude and phase variations. Common types of QAM include 16QAM, 32QAM, 64QAM, and 256QAM. QAM is widely used in digital cable television, digital terrestrial television, wireless networks, and other communication systems due to its transmission efficiency. However, QAM signals are more susceptible to noise and require linear power amplifiers, which are less efficient than non-linear amplifiers used for phase-only modulations.