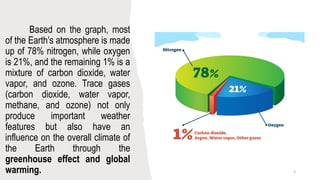
The document outlines the Earth's atmosphere, detailing its five layers: the troposphere, stratosphere, mesosphere, thermosphere, and exosphere, along with their characteristics and roles in weather and climate. It explains the greenhouse effect, the sources of greenhouse gases, and the impact of human activities on global warming. Additionally, the document includes an activity section with true/false statements and questions related to the content.