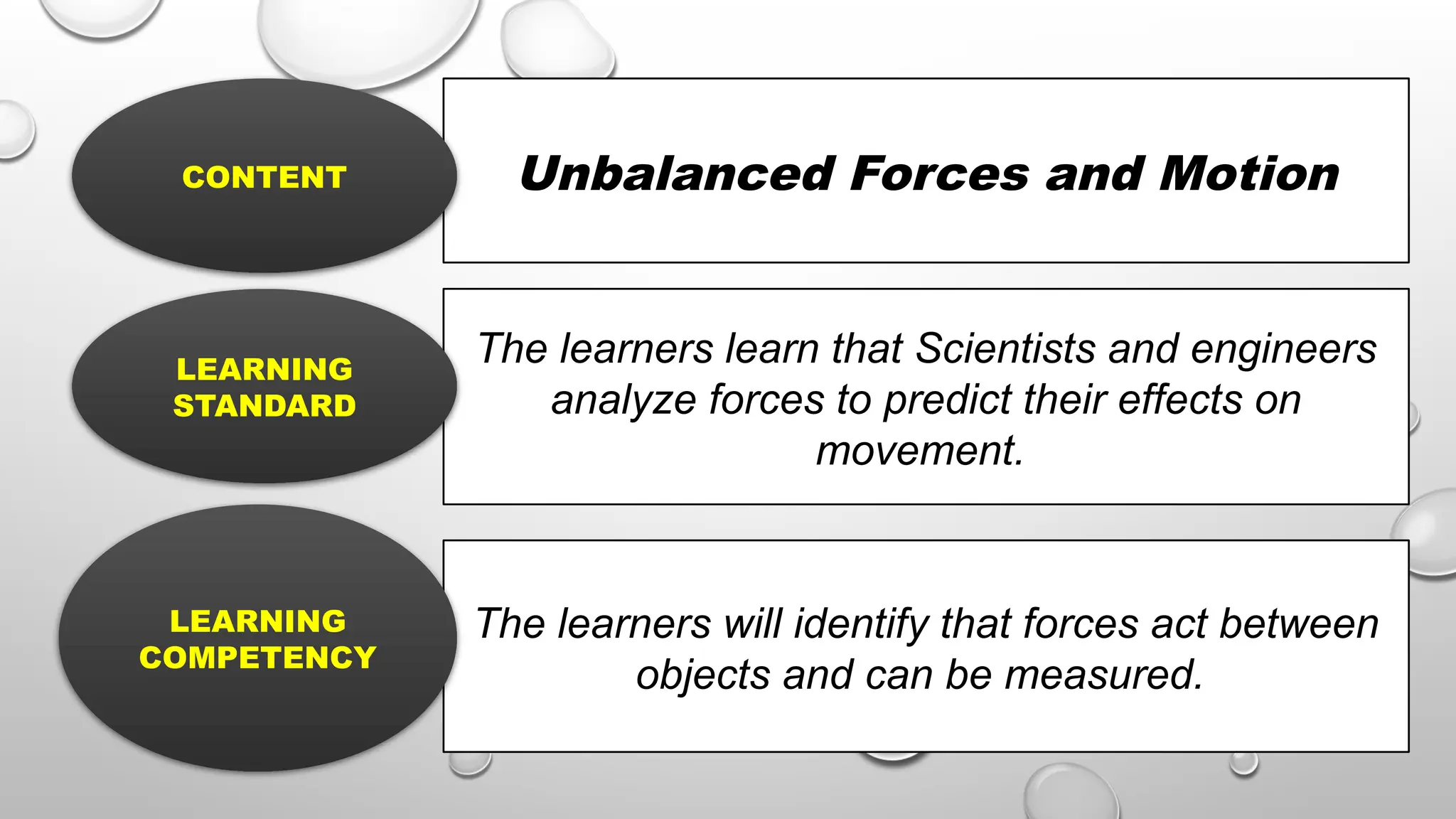
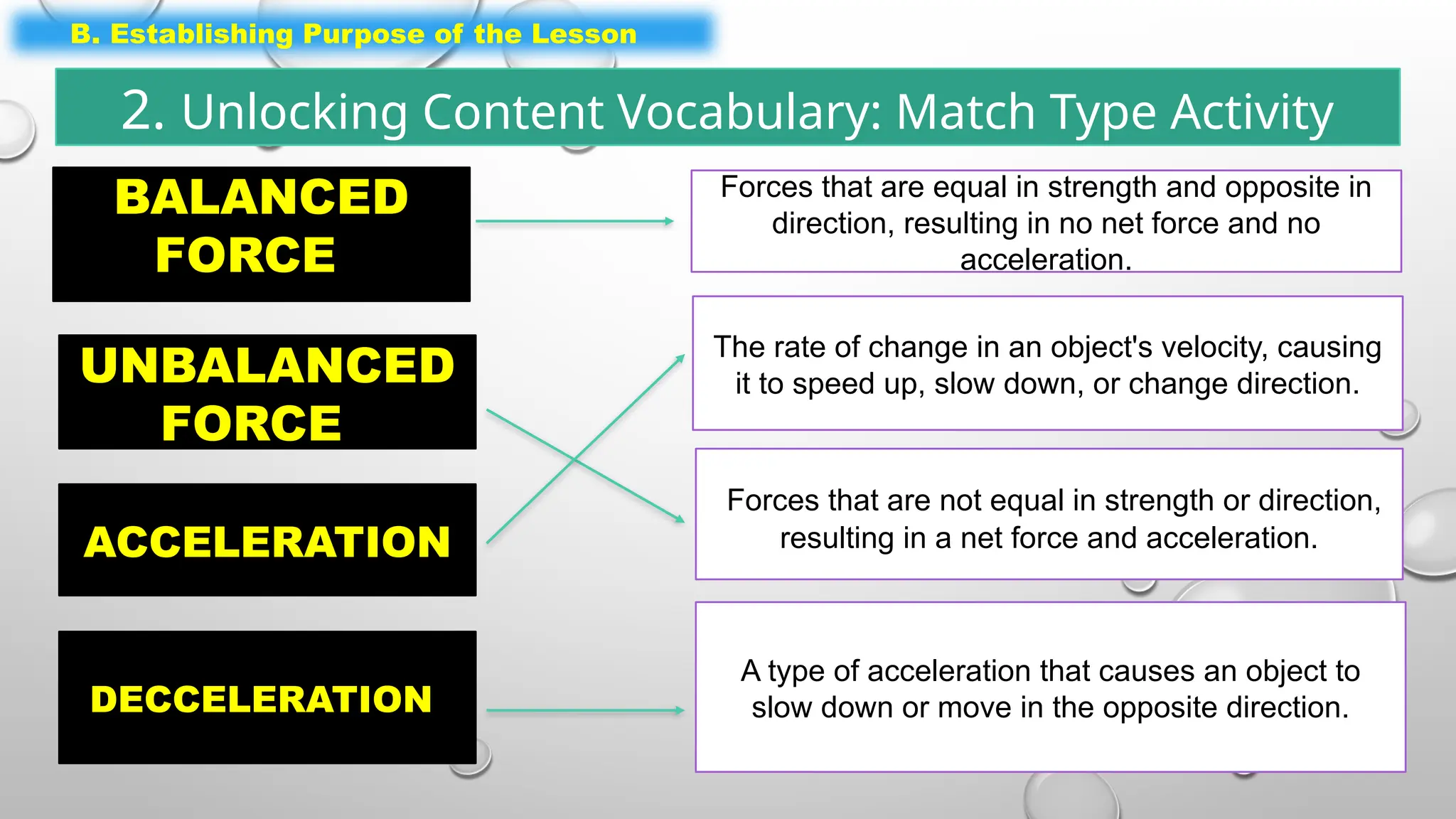
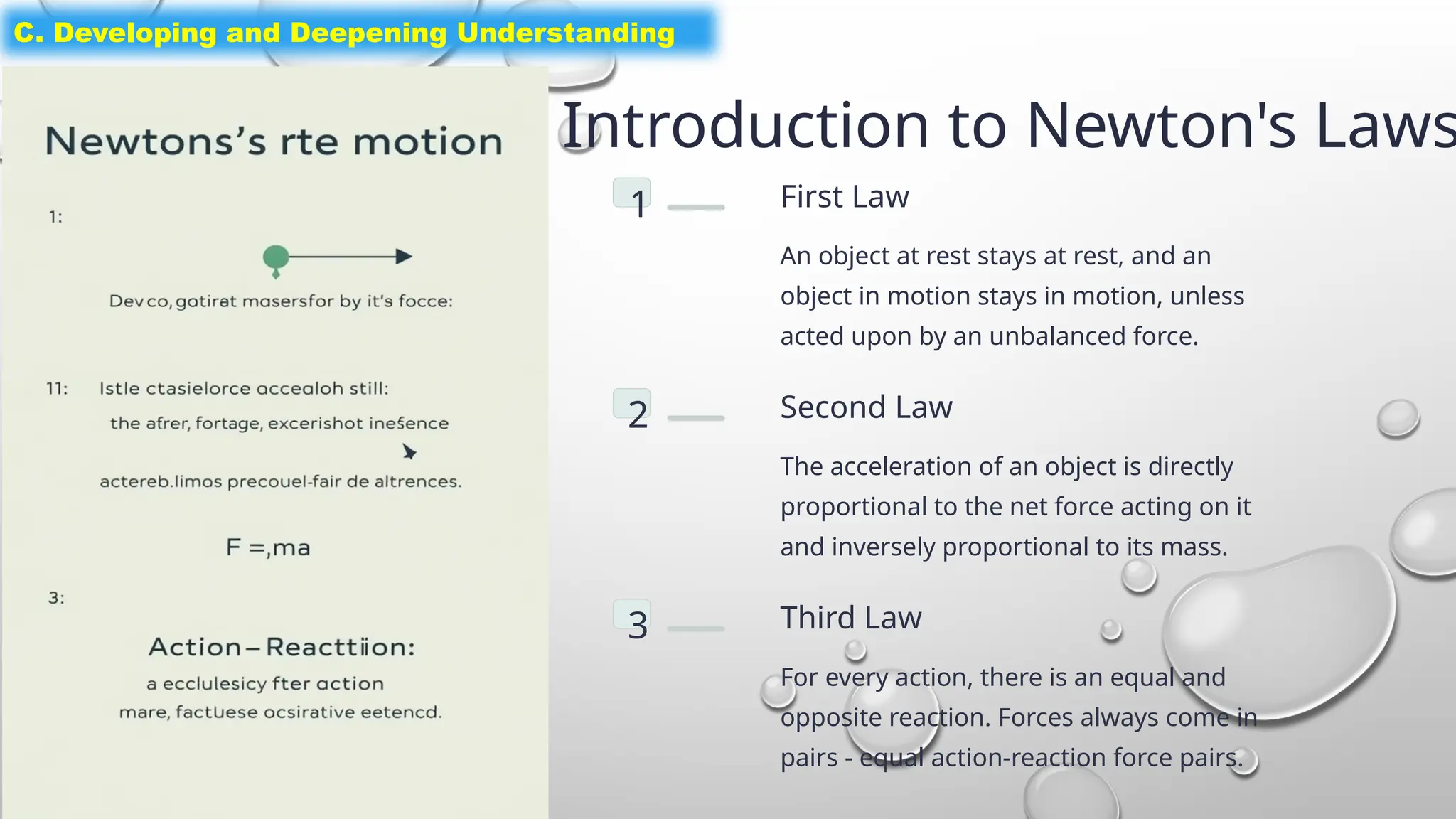
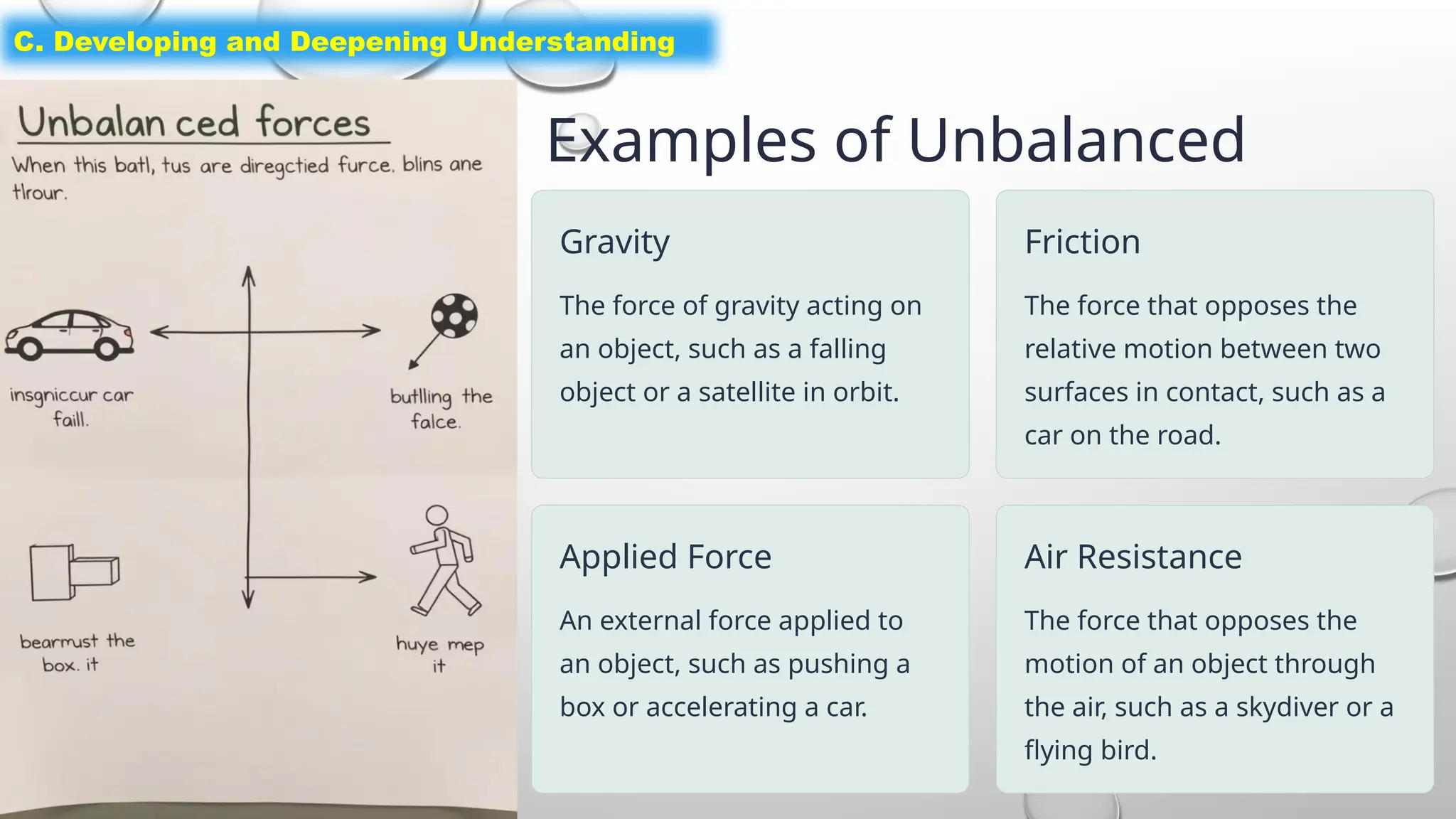
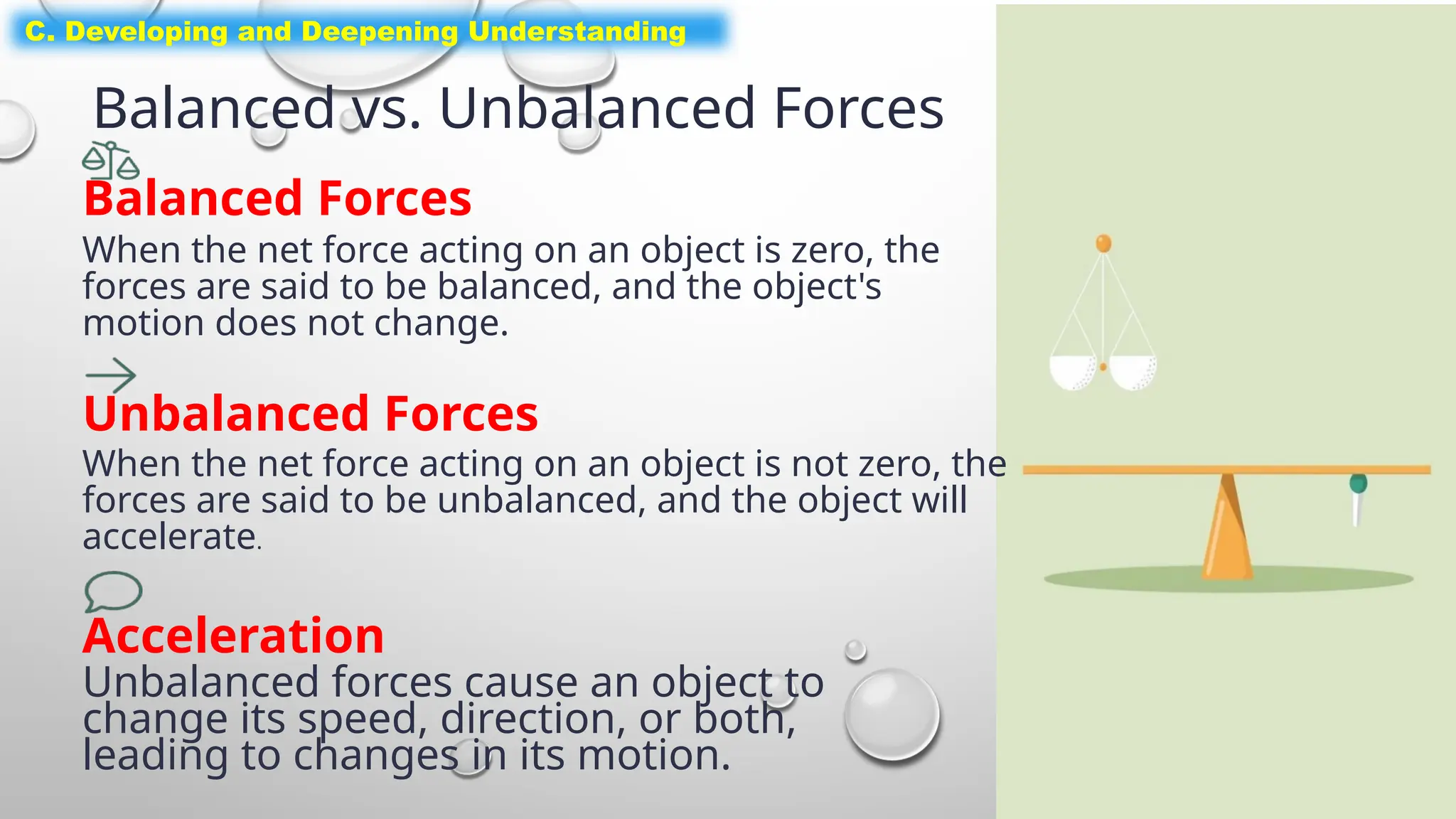
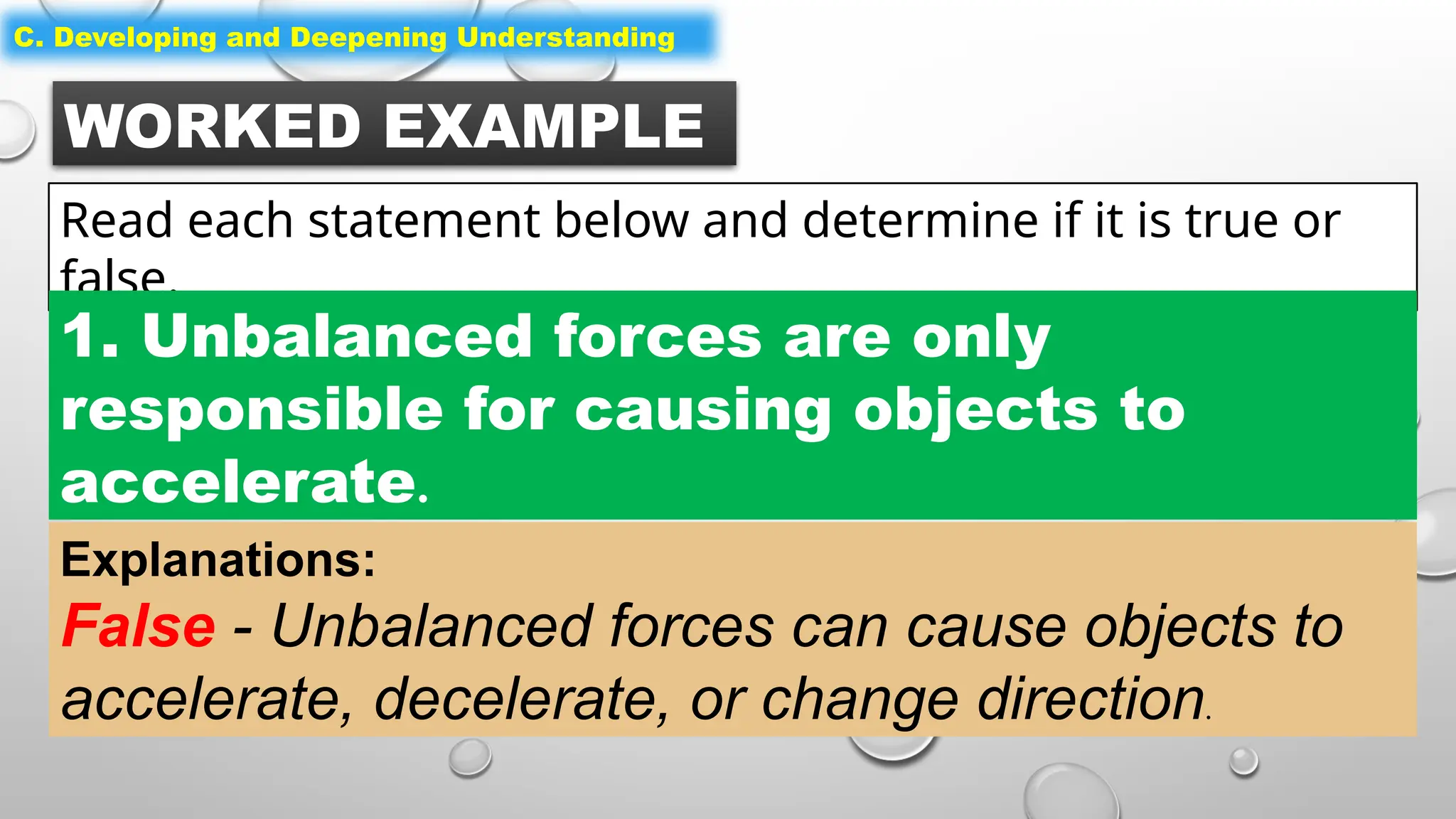
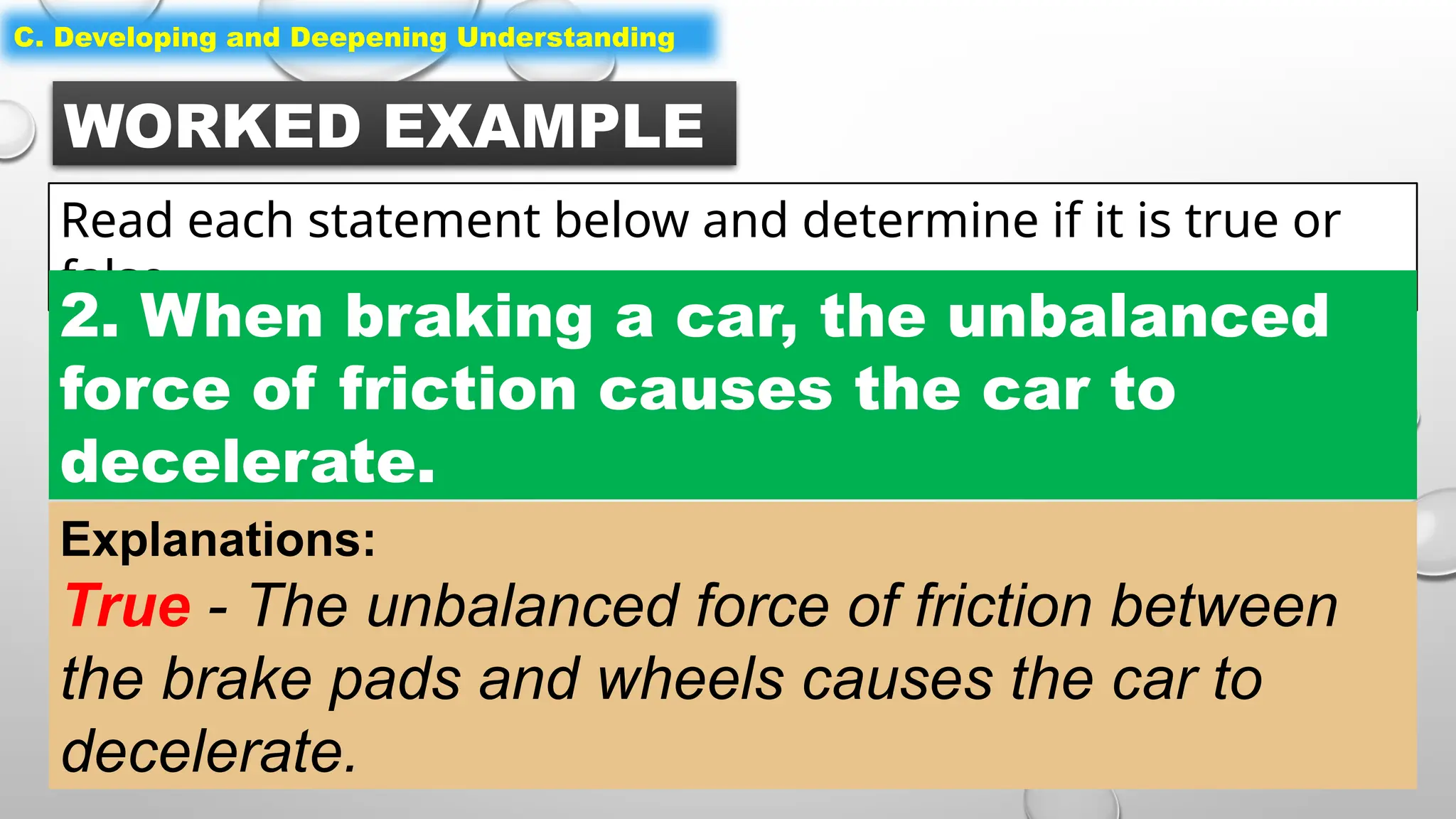
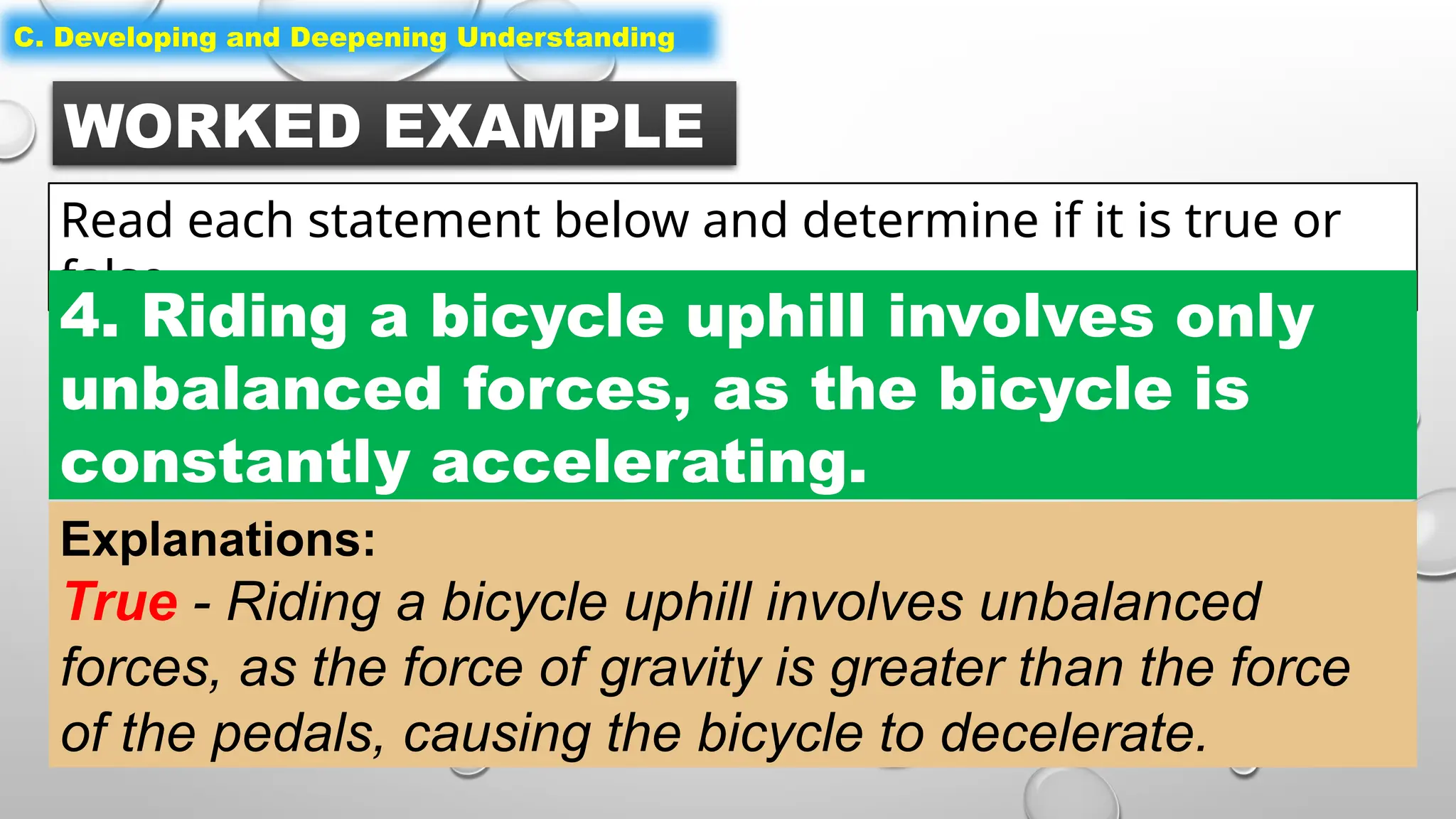
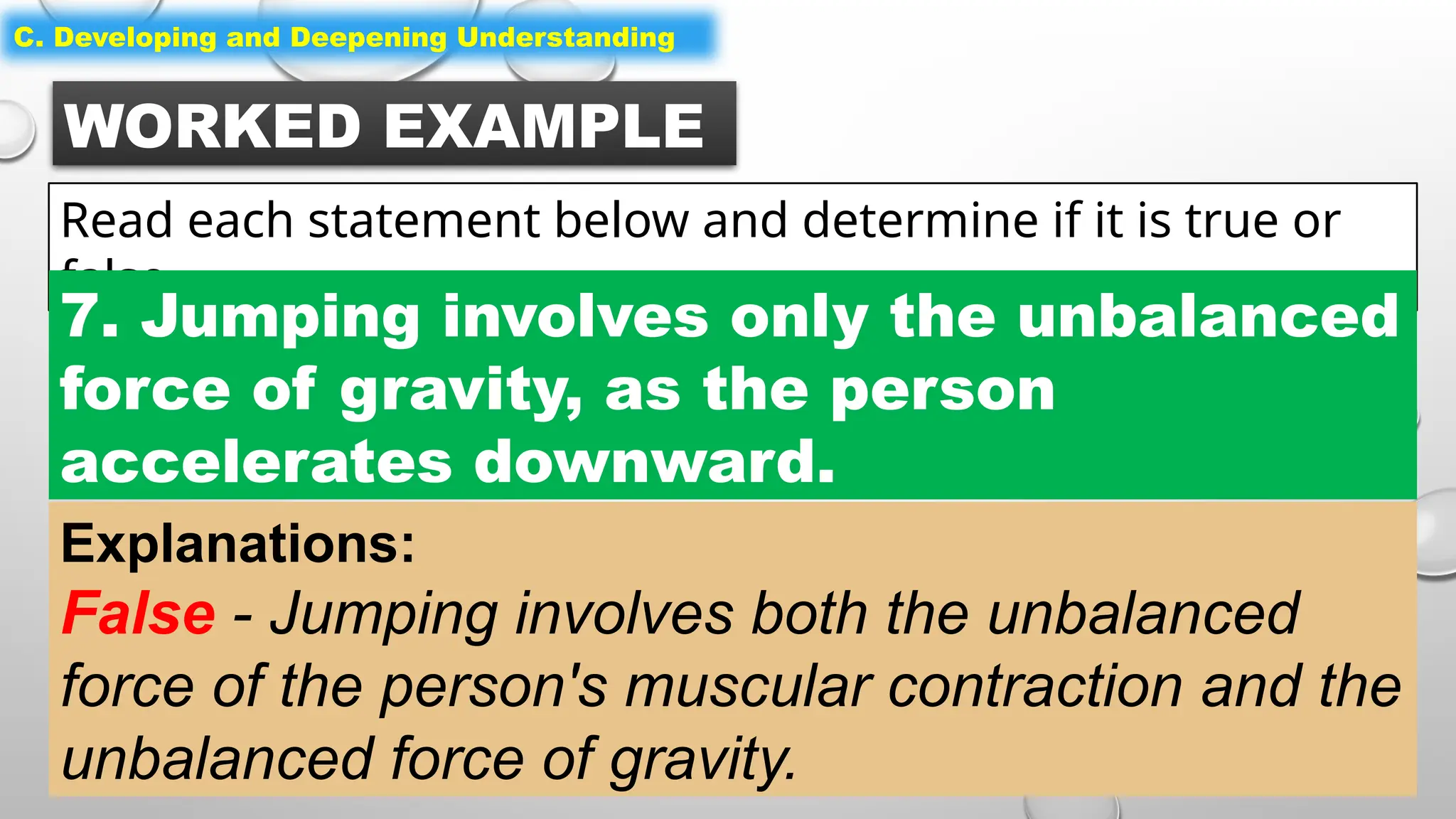
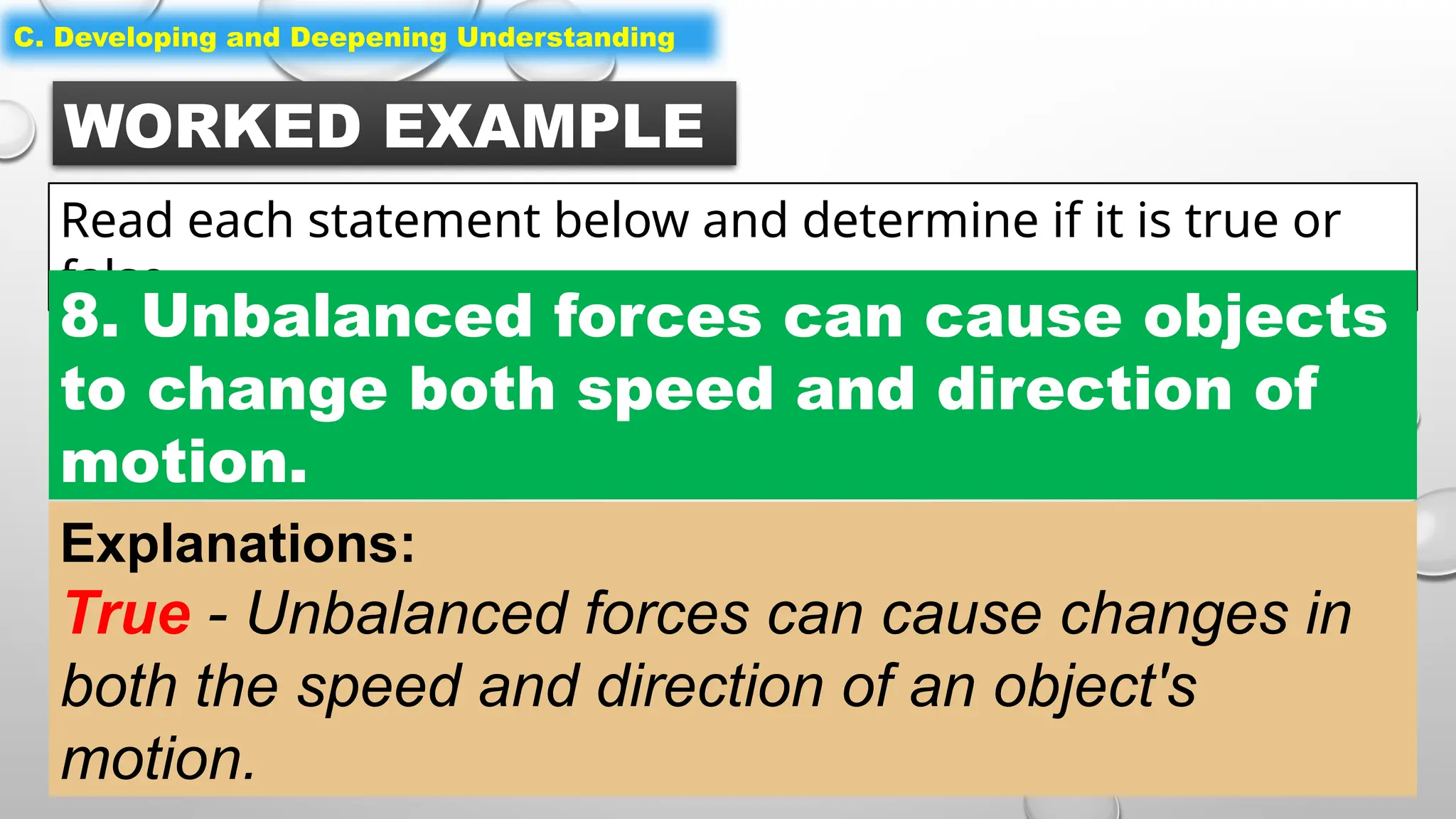
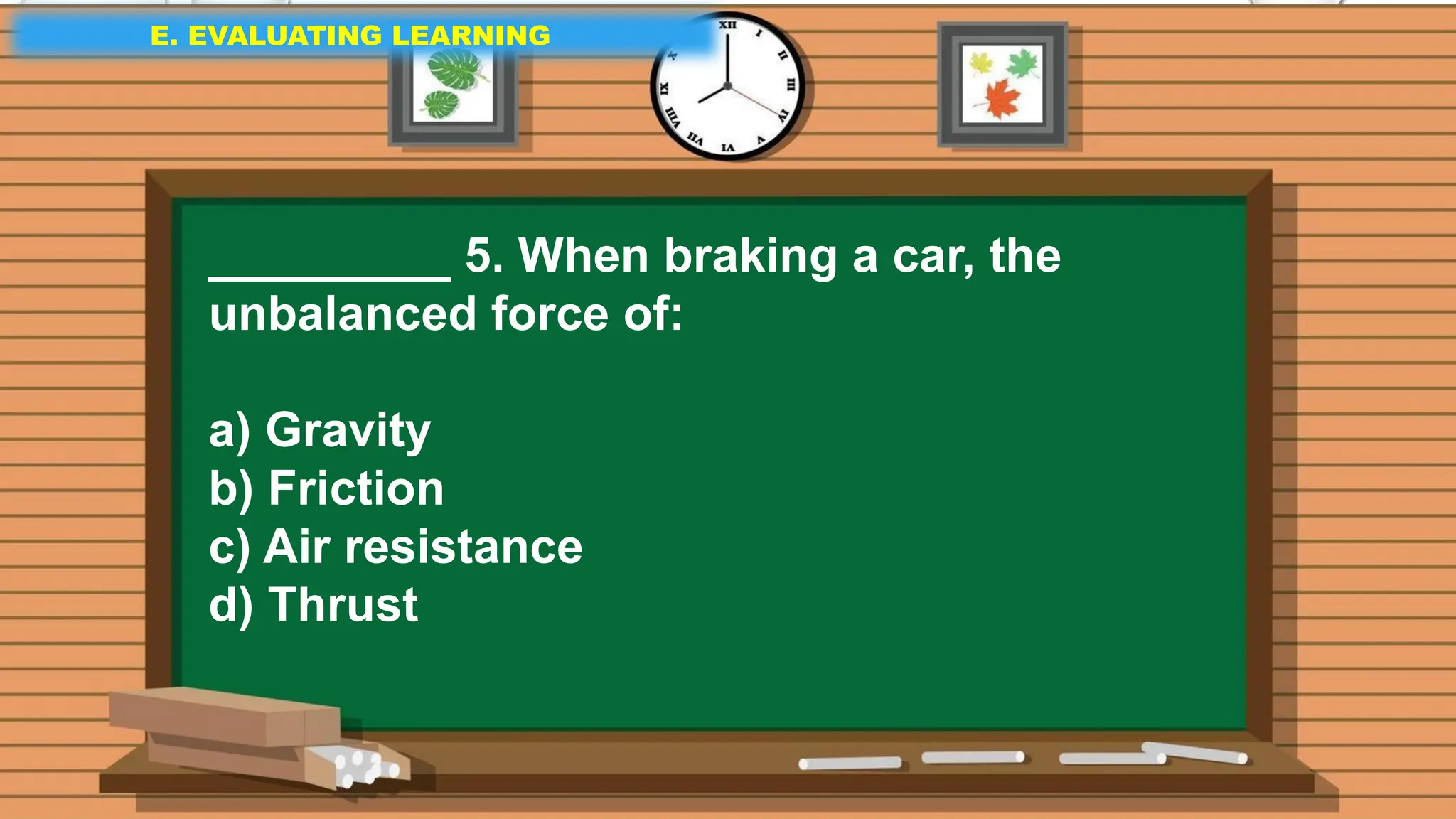
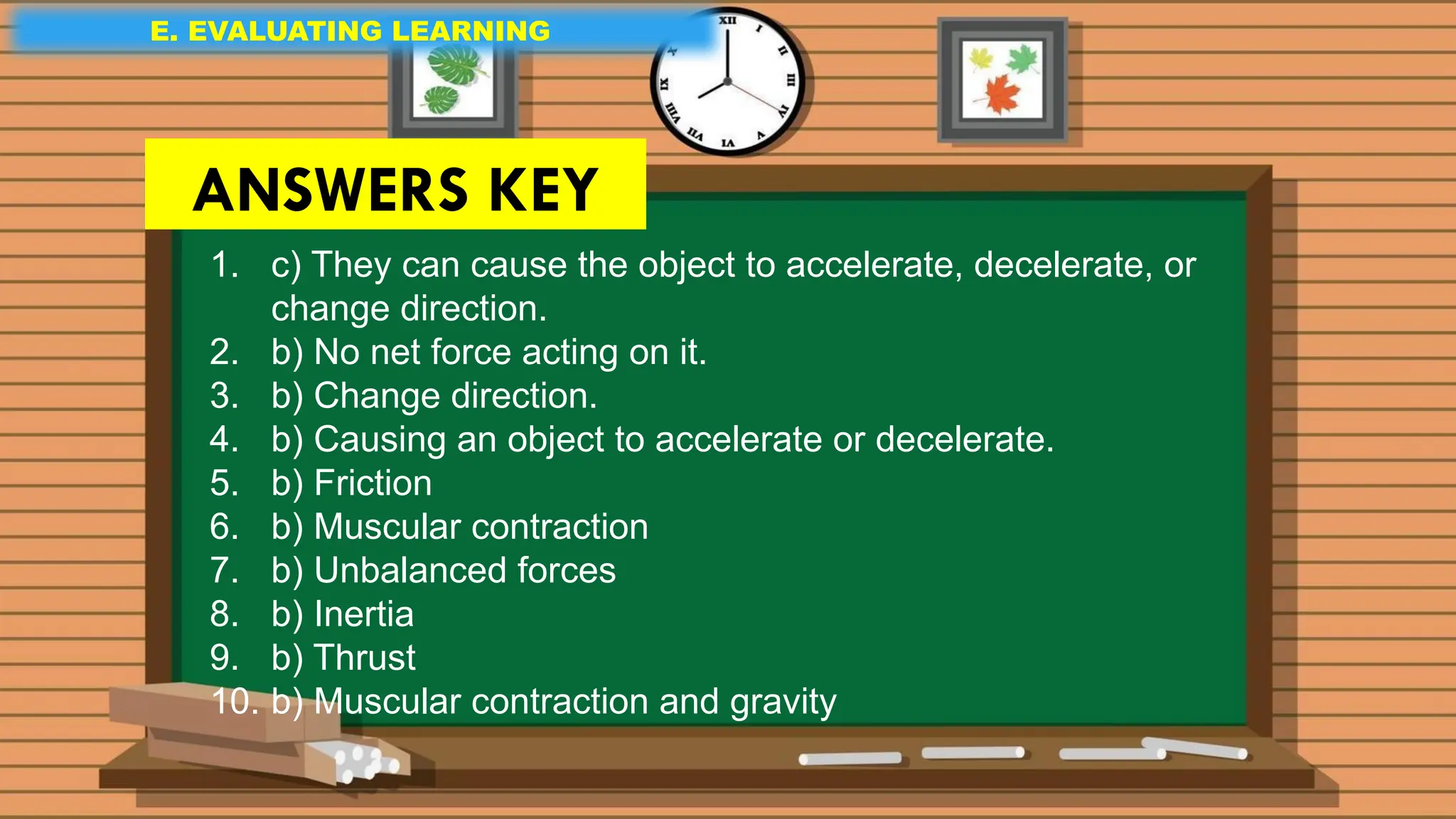
The document outlines a science lesson on unbalanced forces and their effects on motion, focusing on identifying balanced and unbalanced forces, measuring changes in speed and direction, and understanding the role of these forces in various scenarios. Key topics include Newton's laws, examples of unbalanced forces, and practical applications in real-world situations. The lesson aims to enhance learners' understanding through activation of prior knowledge, problem-solving, and reflection on the impact of forces on motion.