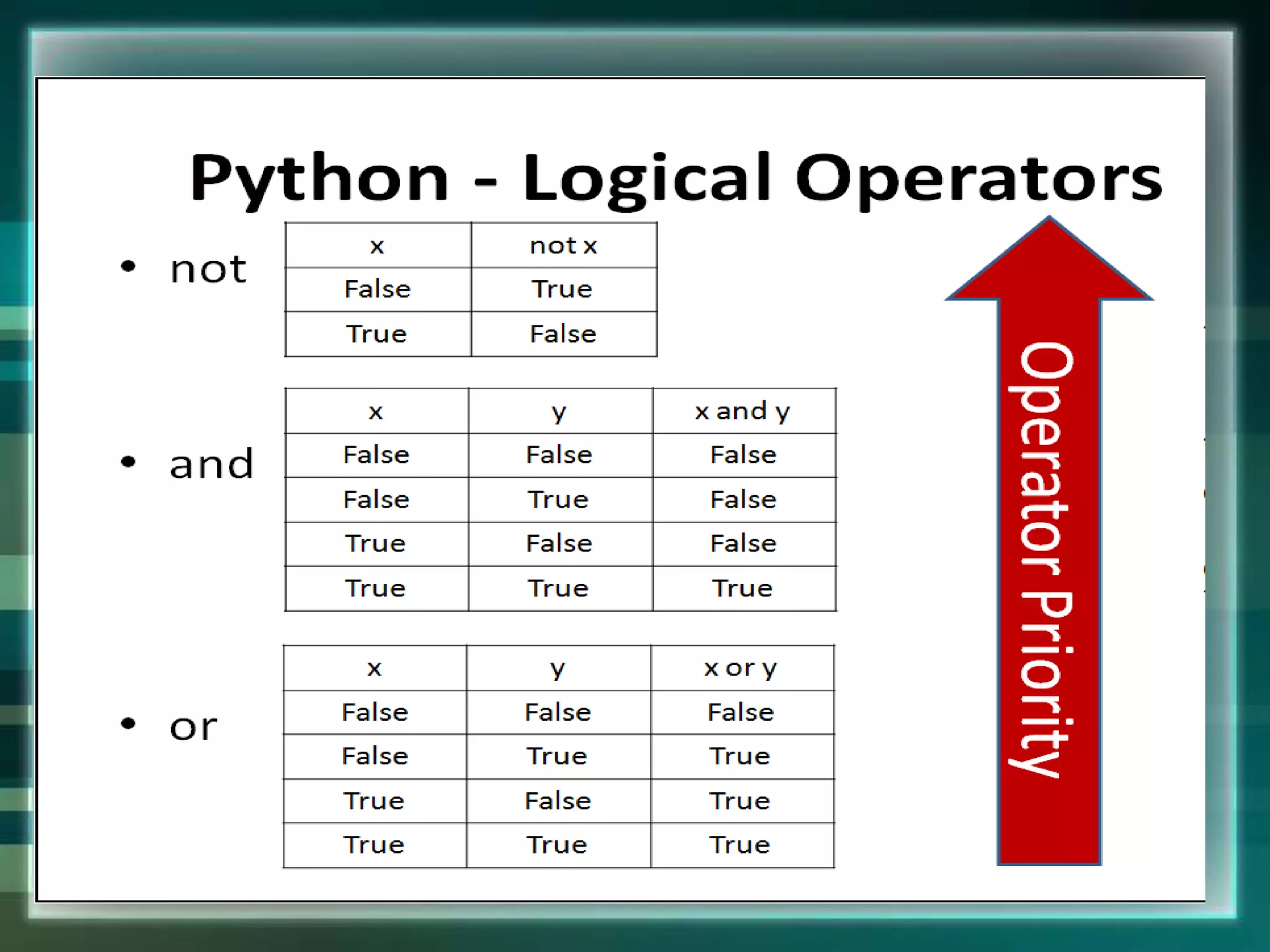
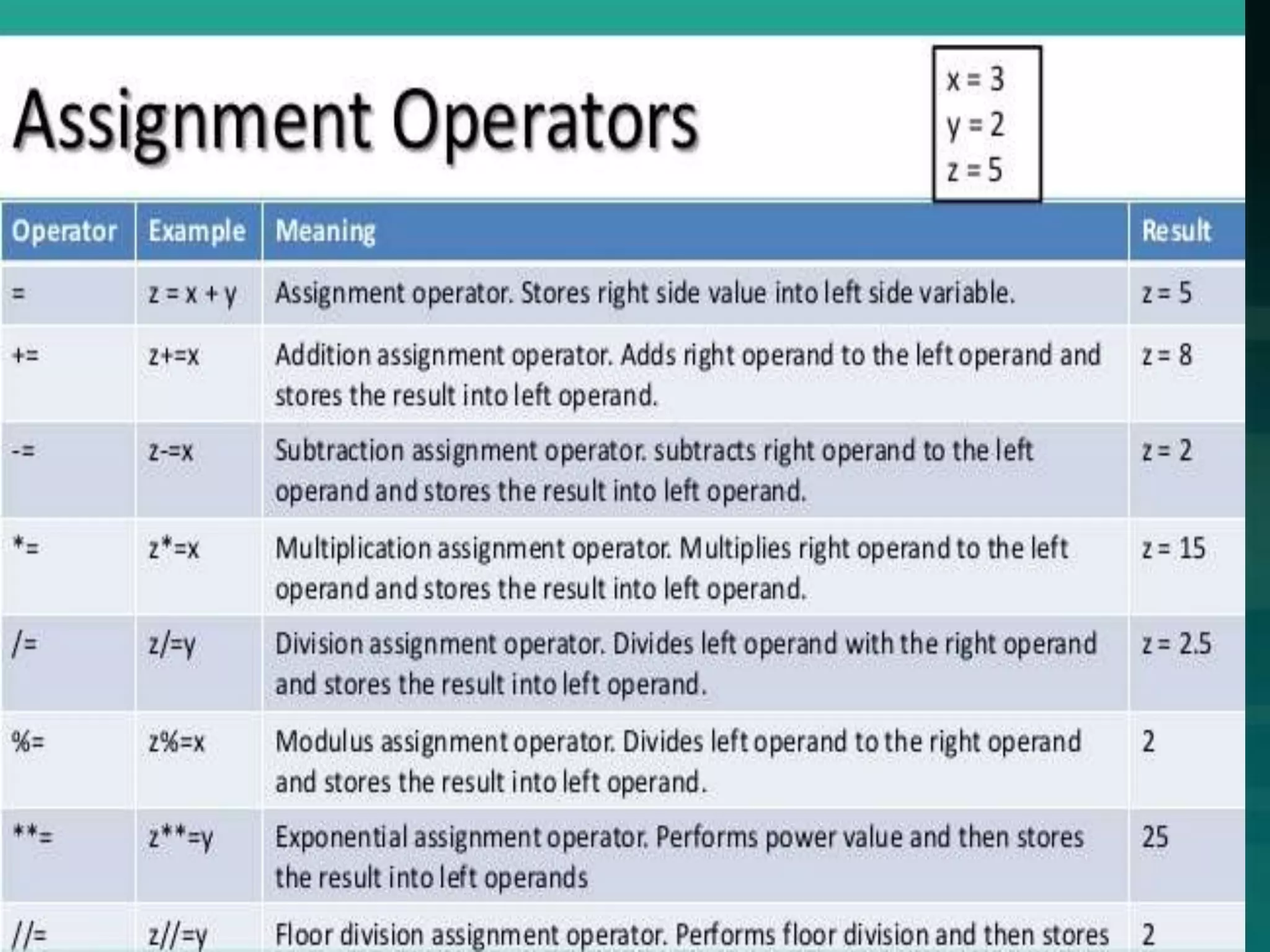
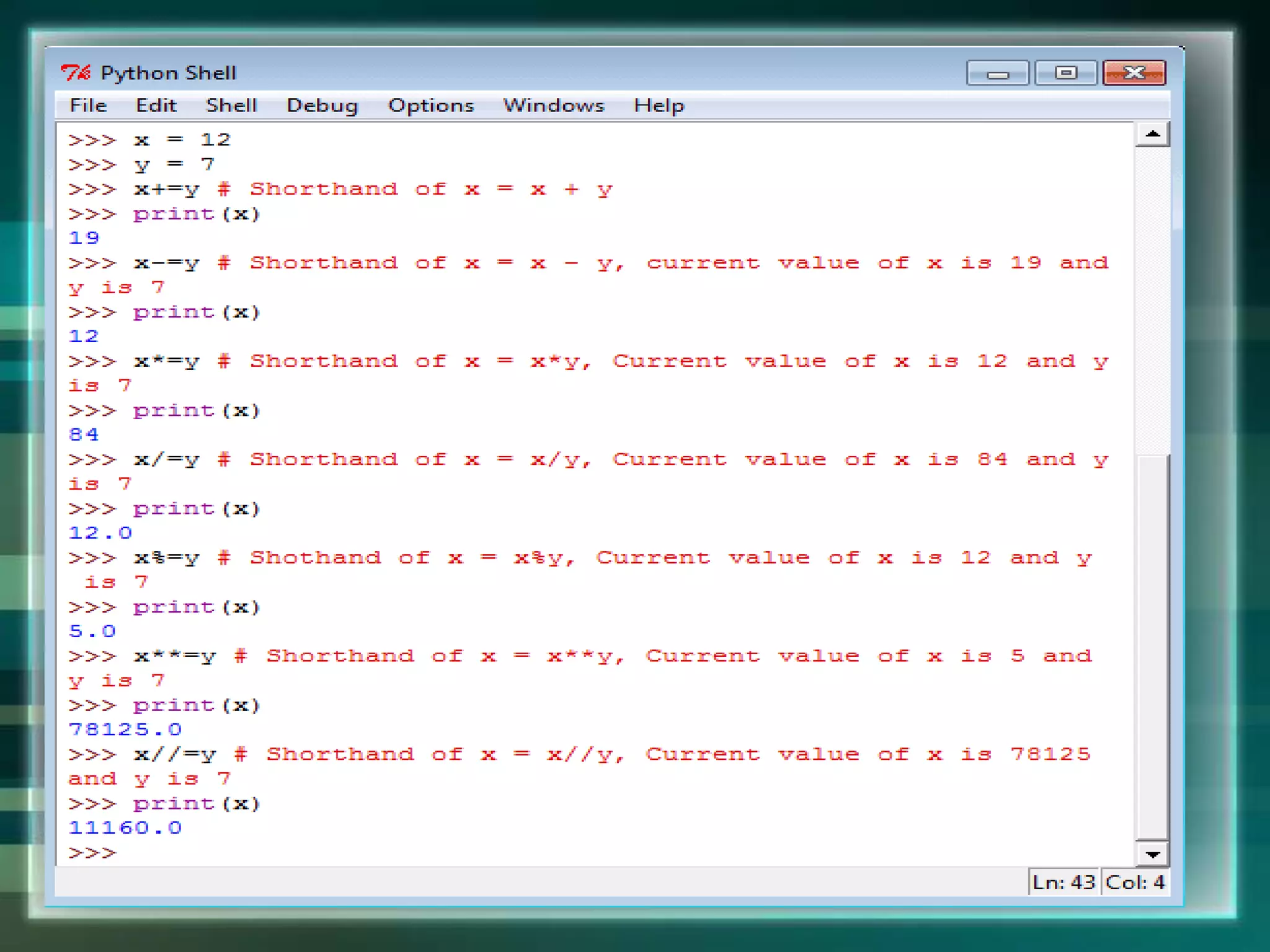
Python is an open source programming language created by Guido van Rossum in 1991. It is named after the comedy group Monty Python and is based on the ABC language. Python supports both procedural and object-oriented programming and can be used for web development, data analysis, artificial intelligence, and more. It has a simple syntax and large standard library that make it easy to learn and use for various applications.






![Python Character Set:
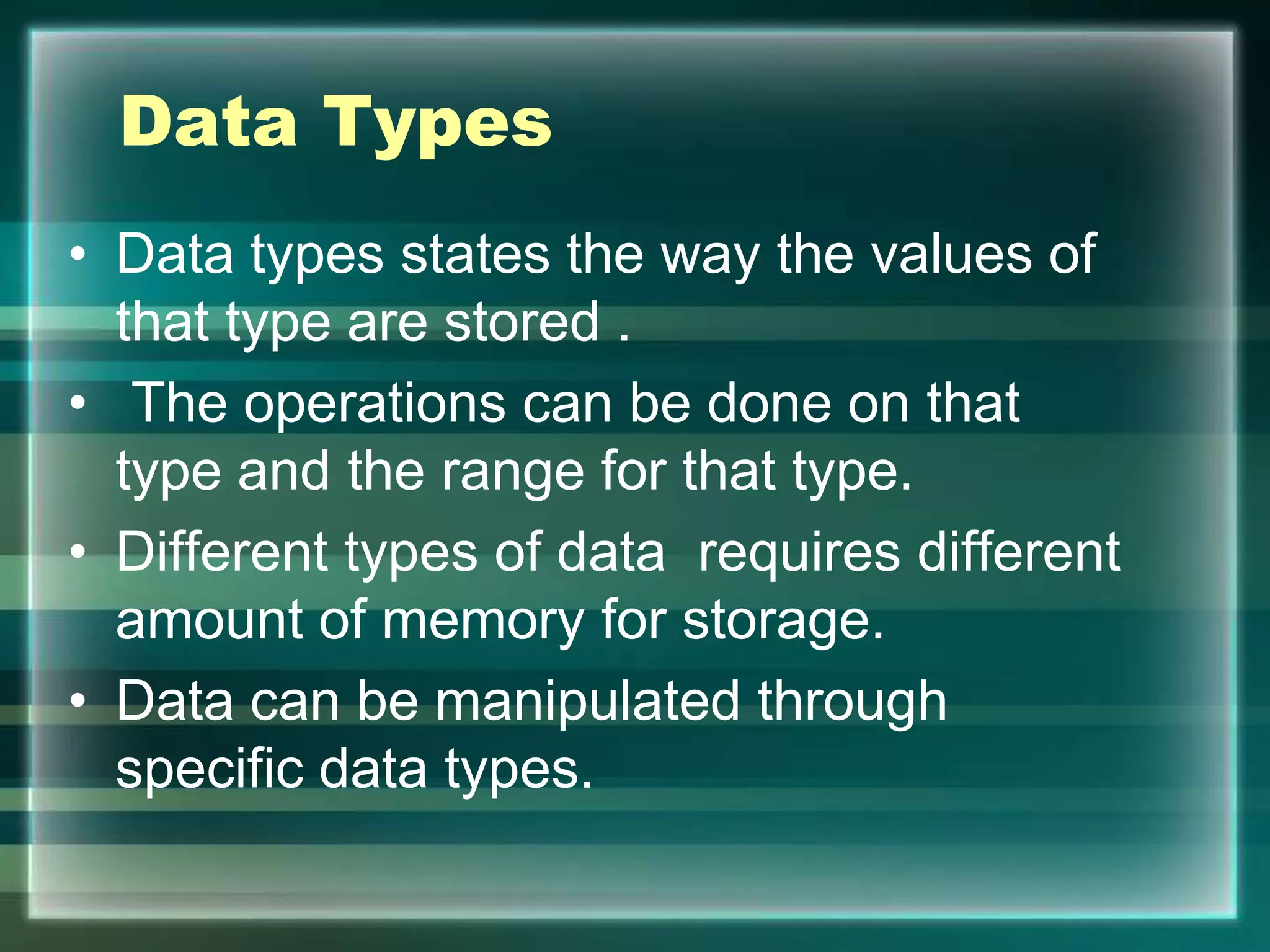
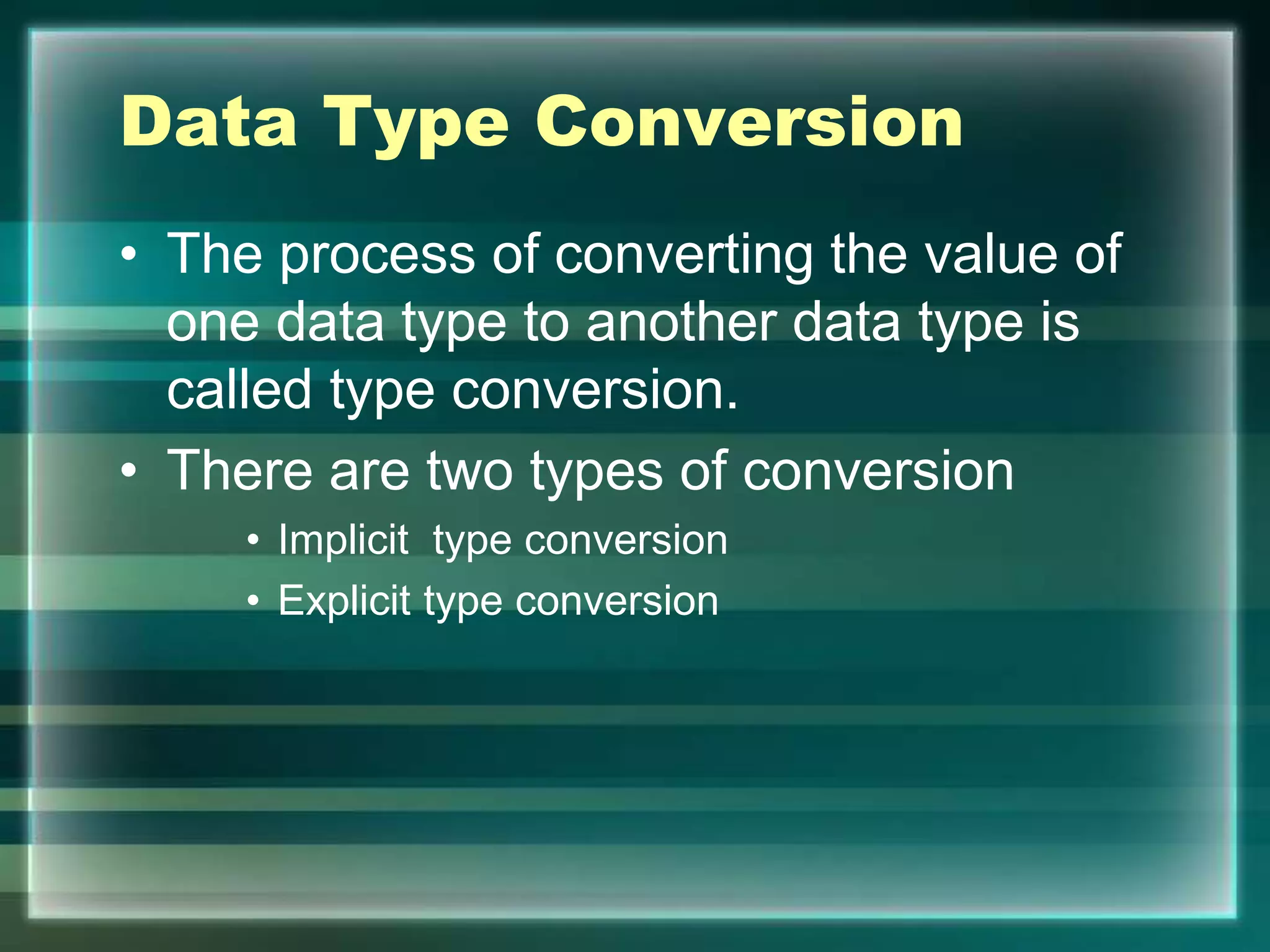
• A set of Valid characters that a language can recognize.
• A character set includes:
Letters : A-Z , a-z.
Digits : 0-9
Special Symbols :Space + -*/**(){}[]//!= ==<,>.’’ “”;:%!
White spaces : Blank space ,tabs carriage return ,new
line , form feed.
Other Characters : process all ASCII](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter7-introductiontopython-210207052027/75/introduction-to-python-7-2048.jpg)







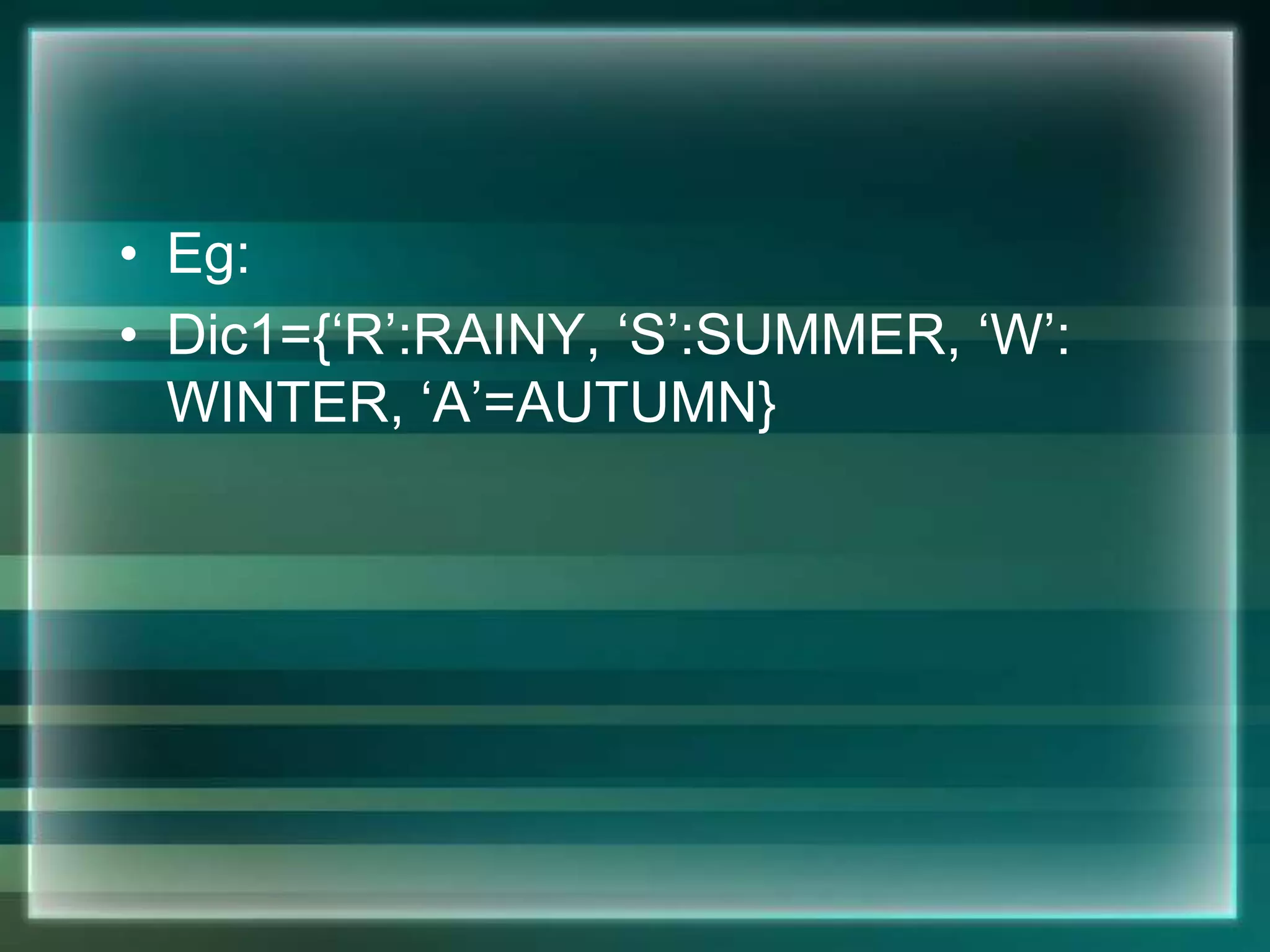
![Eg:
• List1=[1,56,84,5]
• List2=[45,98,48,65,0,23]
• List3=[‘anna’,’aby’,’riya’,’diya’]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter7-introductiontopython-210207052027/75/introduction-to-python-16-2048.jpg)



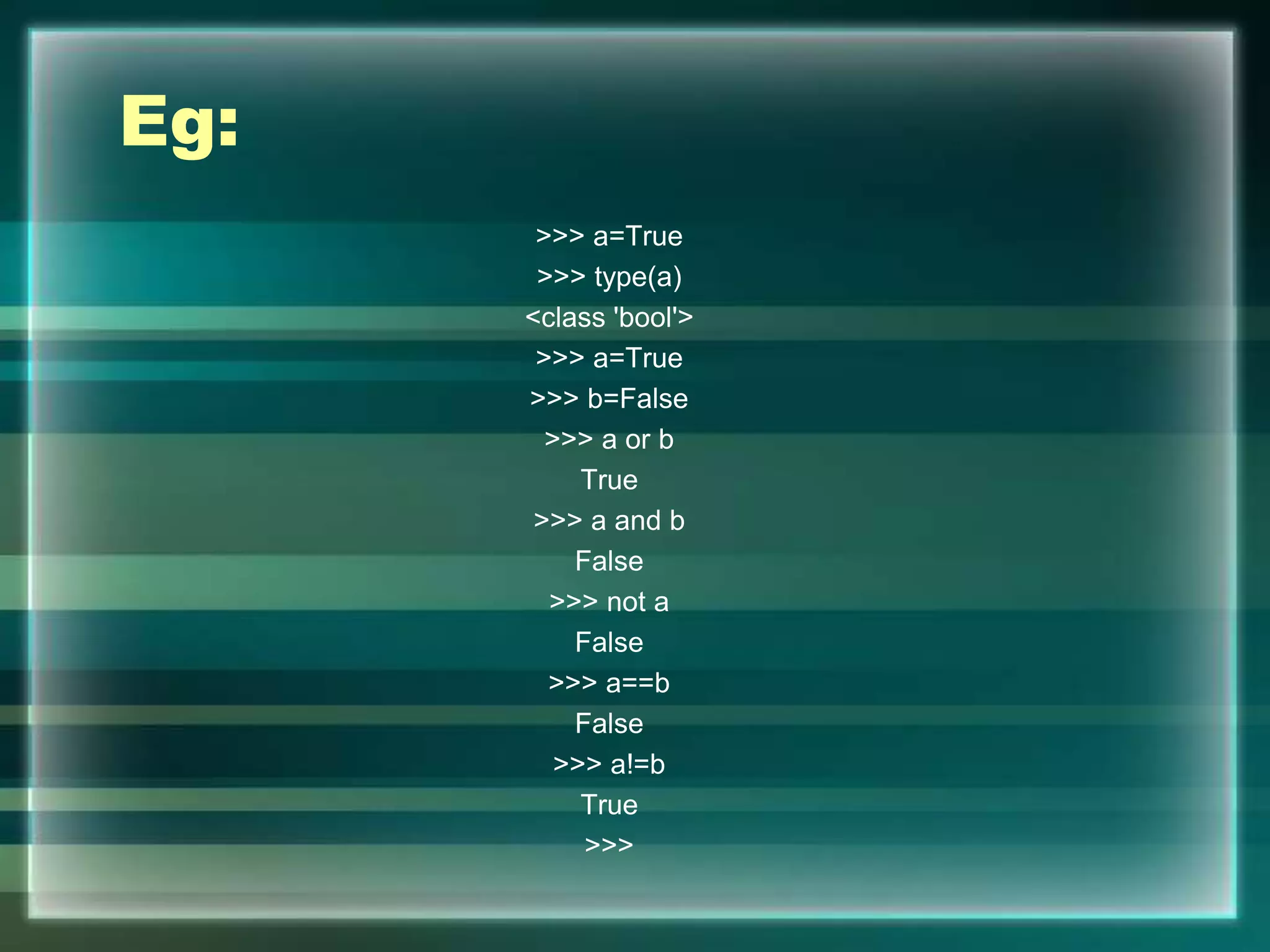

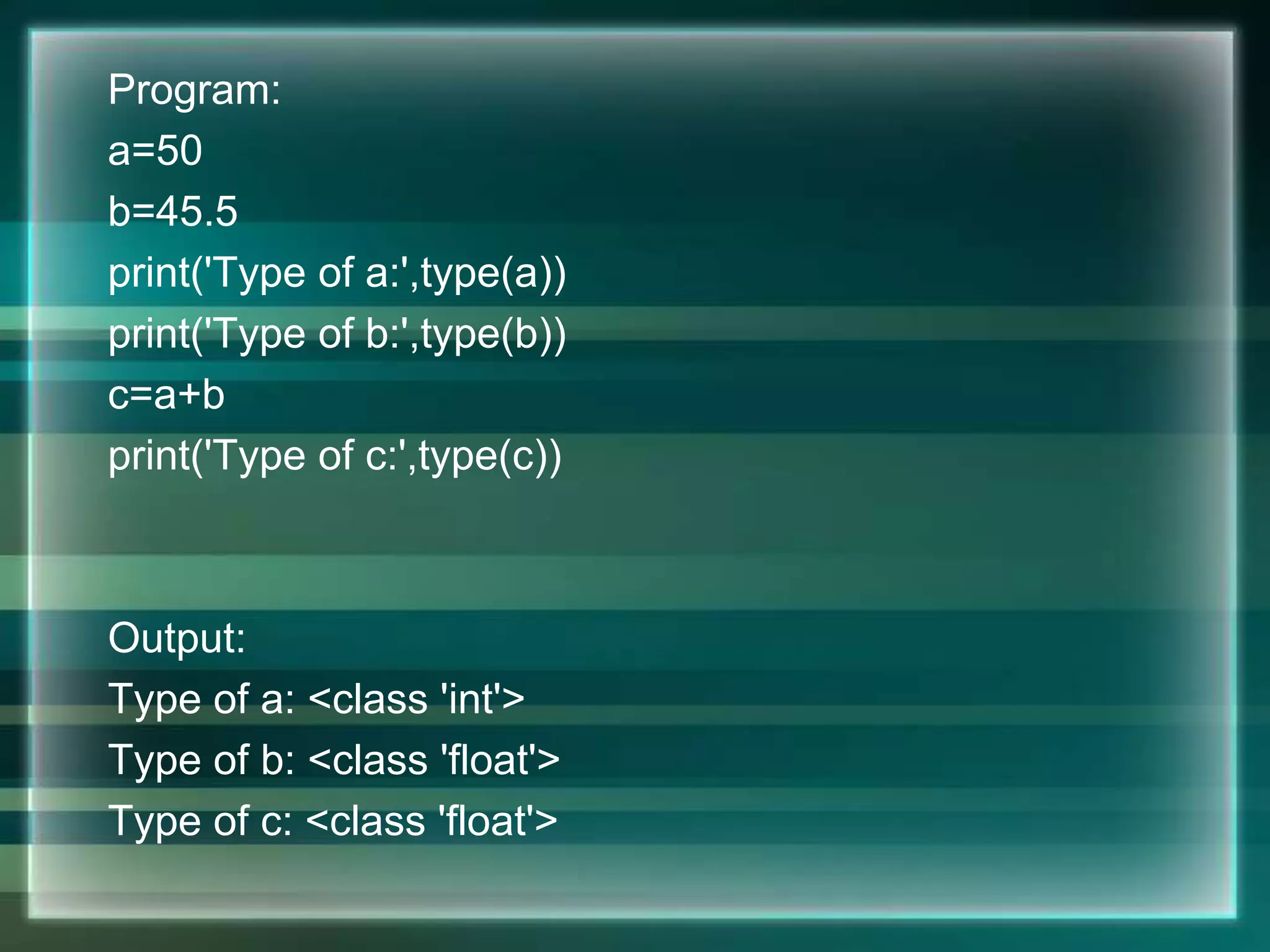
![Input
a=100
b=20.50
c='567'
print('Variable a converted into string:',str(a))
print('Variable a converted into float:',float(a))
print('Variable b converted into integer:',int(b))
print('Variable b converted into string:',str(b))
print('Variable c converted into integer:',int(c))
print('Variable c converted into float:',float(c))
print('Variable a converted into list:',list(c))
OUTPUT
Variable a converted into string: 100
Variable a converted into float: 100.0
Variable b converted into integer: 20
Variable b converted into string: 20.5
Variable c converted into integer: 567
Variable c converted into float: 567.0
Variable a converted into list: ['5', '6', '7']](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter7-introductiontopython-210207052027/75/introduction-to-python-27-2048.jpg)