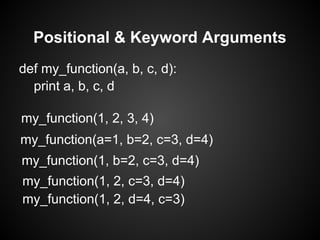
The document provides a side-by-side comparison of Python and Java, highlighting key features and differences in syntax and functionality. It covers various programming constructs such as lists, arrays, hashtables, and classes, as well as Python's special features like introspection and enhanced data structures. Additionally, it discusses the strengths and weaknesses of Python in different applications, including string processing and operating system interfaces.




![Hello World
Java Python 2.7
public class Main { print "Hello World"
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Hello World");
}
}
Python 3.x
print("Hello World")](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythontour-120601183334-phpapp01/85/Python-tour-5-320.jpg)
![Lists
Java Python
import java.util.Vector x = ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd']
public class Main { for item in x:
public static void main(String[] args) { print item
Vector x = new Vector();
x.addElement("a")
x.addElement("b")
x.addElement("c")
x.addElement("d")
for (int i = 0 ; i < x.length; i++) {
System.out.println(x.elementAt(i));
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythontour-120601183334-phpapp01/85/Python-tour-6-320.jpg)
![Lists vs Arrays
Java Python
Array Array
int[] a = {1, 2, 3}; import array
System.out.println(a[0]) a = array.array('i',
a[0] = 55 [1,2,3])
print a[0]
List
a[0] = 55
List<Integer> a = new
ArrayList<Integer>(); List
a.add(new Integer(1)) a = [1,2,3]
System.out.println(a.get(0)) print a[0]
a[0] = 55](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythontour-120601183334-phpapp01/85/Python-tour-7-320.jpg)
![Hashtables
Java Python
import java.util.Hashtable x = {}
public class Main { x['a'] = 1
public static void main(String[] args) { print x['a']
Hashtable x = new Hashtable();
x.put("a", new Integer(1))
System.out.println(x.get("a"));
OR
}
x = {'a' : 1}
}
print x['a']](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythontour-120601183334-phpapp01/85/Python-tour-8-320.jpg)
![IO
Java Python
public class Main { f = open('file.txt', 'w')
public static void main(String[] args) { f.write('Hello World')
try { f.close()
File f = new File('file.txt');
PrintWriter ps = new PrintWriter(
new OutputStreamWriter(
new File OutputStream(f)));
OR
ps.print("Hello World")
}
catch (IOException e) {
with open('file.txt, 'w') as f:
e.printStackTrace();
f.write('Hello World')
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythontour-120601183334-phpapp01/85/Python-tour-9-320.jpg)
![Classes
Java Python
public class Point { class Point():
public int x; def __init__(self, x, y) {
public int y; self.x = x
public MyClass(int x, int y) { self.y = y
this.x = x }
this.y = y p = Point(1, 2)
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
p = new Point(1, 2)
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythontour-120601183334-phpapp01/85/Python-tour-10-320.jpg)


![Syntactic Sugar for very high level
data structures
Lists Tuples
l = ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd'] t = ('a', 'b', 'c', 'd')
print l[0] print t[0]
l[0] = 'z'
Strings
Hashtables s = 'abcd'
d = {0:'a', 100:'b', 5:'c'} print s[0]
print d[0]
d['strings_too'] = 'z' Sets
s = {0, 1, 2, 3}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythontour-120601183334-phpapp01/85/Python-tour-13-320.jpg)