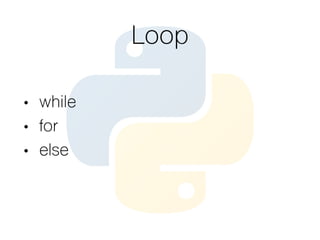
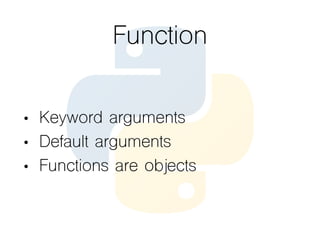
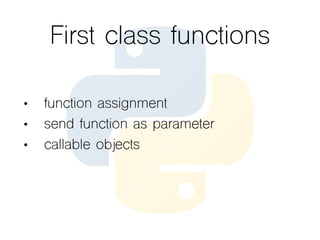
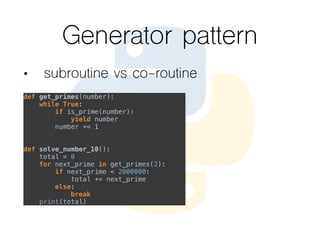
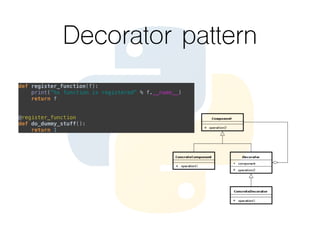
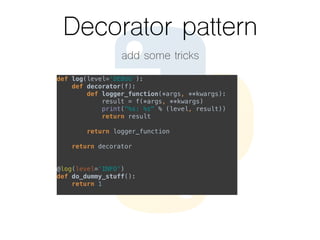
This document provides an overview of the Python programming language. It discusses what Python is, its key features like being multi-purpose, readable, and productive. It then demonstrates Hello World programs in Python, C++, Java, and PHP. The rest of the document covers Python concepts like operators, variables, strings, lists, conditions, loops, functions, object oriented programming, and design patterns like strategy, closure, generator, and decorator patterns.




![Hello, world!
public class Program {
public static main(string[] argus){
System.out.println(“Hello, world!”);
}
}
Java](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/python-160514111628/85/Python-in-90-minutes-6-320.jpg)


![Variables
•int i = 1
•float f = 2.1
•bool b = False
•str s = ‘hi’
•list l = [1, 2, “hello again”, 4]
•tuple t = (True, 2.1)
•dict d = {1:”One”, 2:”Two”}
•set s = {“some”, “unique”, “objects”}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/python-160514111628/85/Python-in-90-minutes-10-320.jpg)
![Variables - Casting
>>> float(1)
1.0
>>> str(1)
‘1’
>>> int(‘1’)
1
>>> list(1)
[1, ]
>>> list(‘hello’)
['h', 'e', 'l', 'l', ‘o']
>>> set([1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0])
set([1, 0])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/python-160514111628/85/Python-in-90-minutes-12-320.jpg)






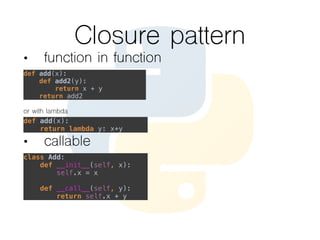

![Complex syntax
One-line if:
print('even' if i % 2 == 0 else 'odd')
One line for:
l = [num ** 2 for num in numbers]
None or … :
value = dummy_function_may_return_none() or 0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/python-160514111628/85/Python-in-90-minutes-28-320.jpg)
