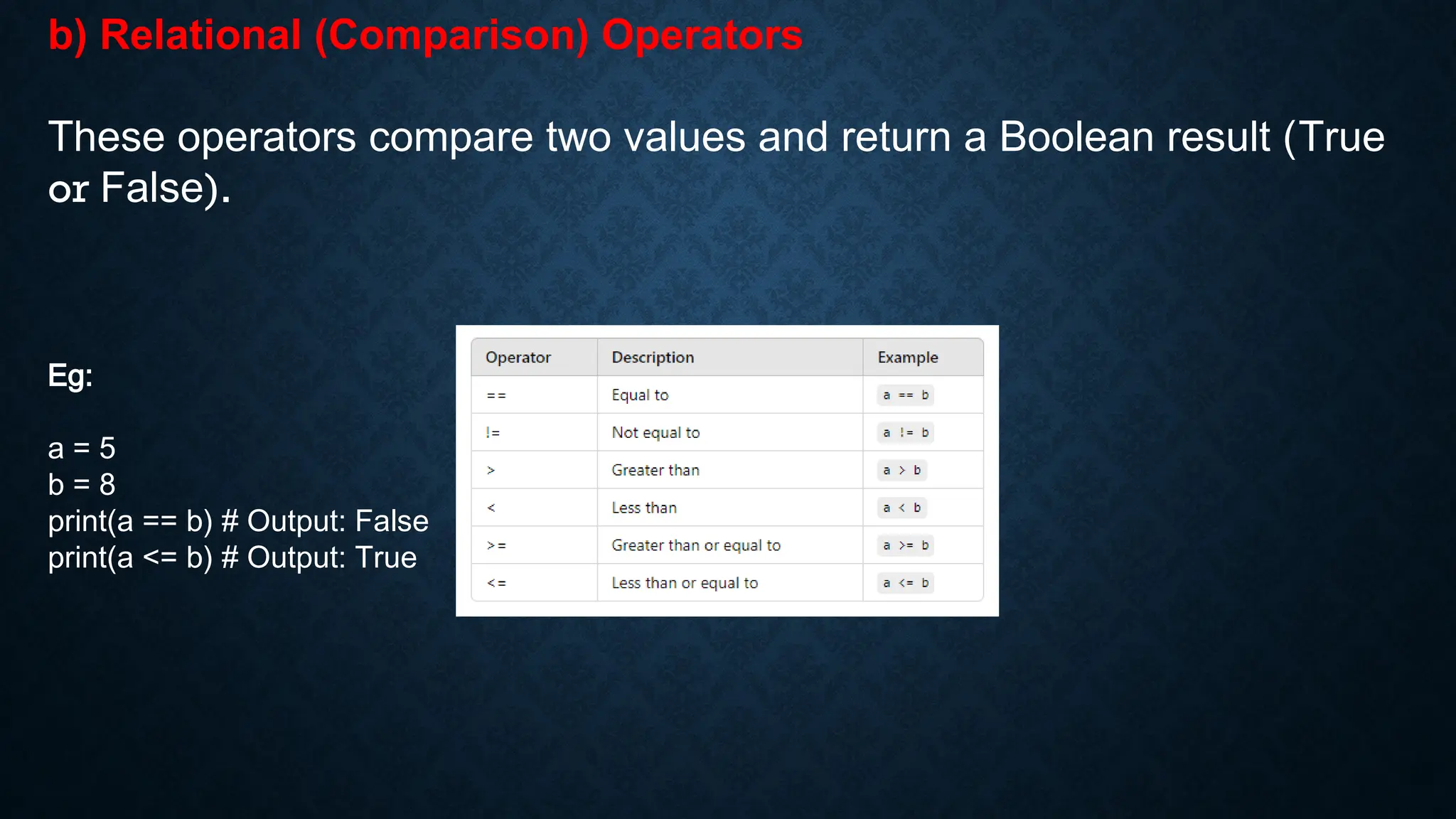
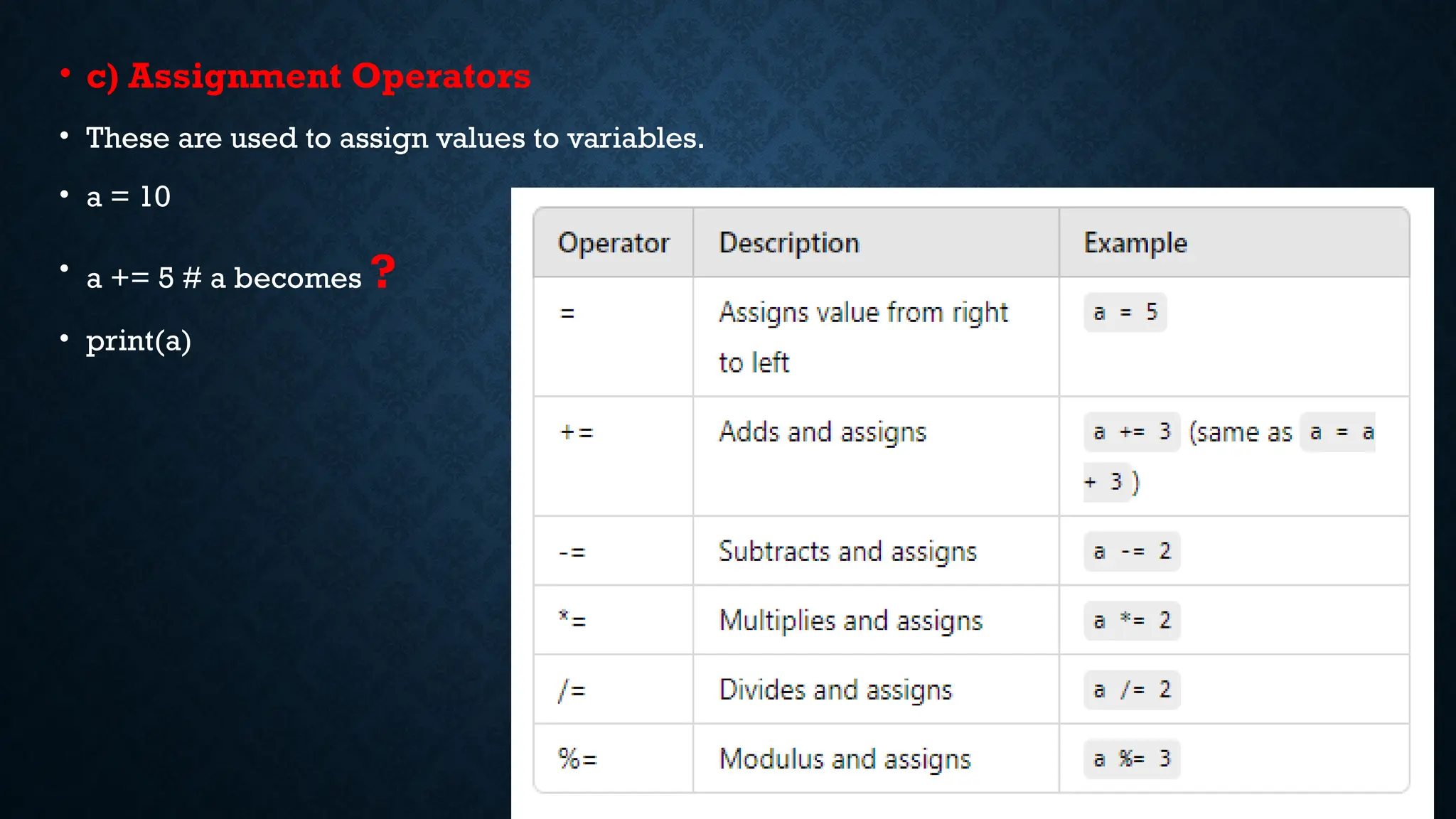
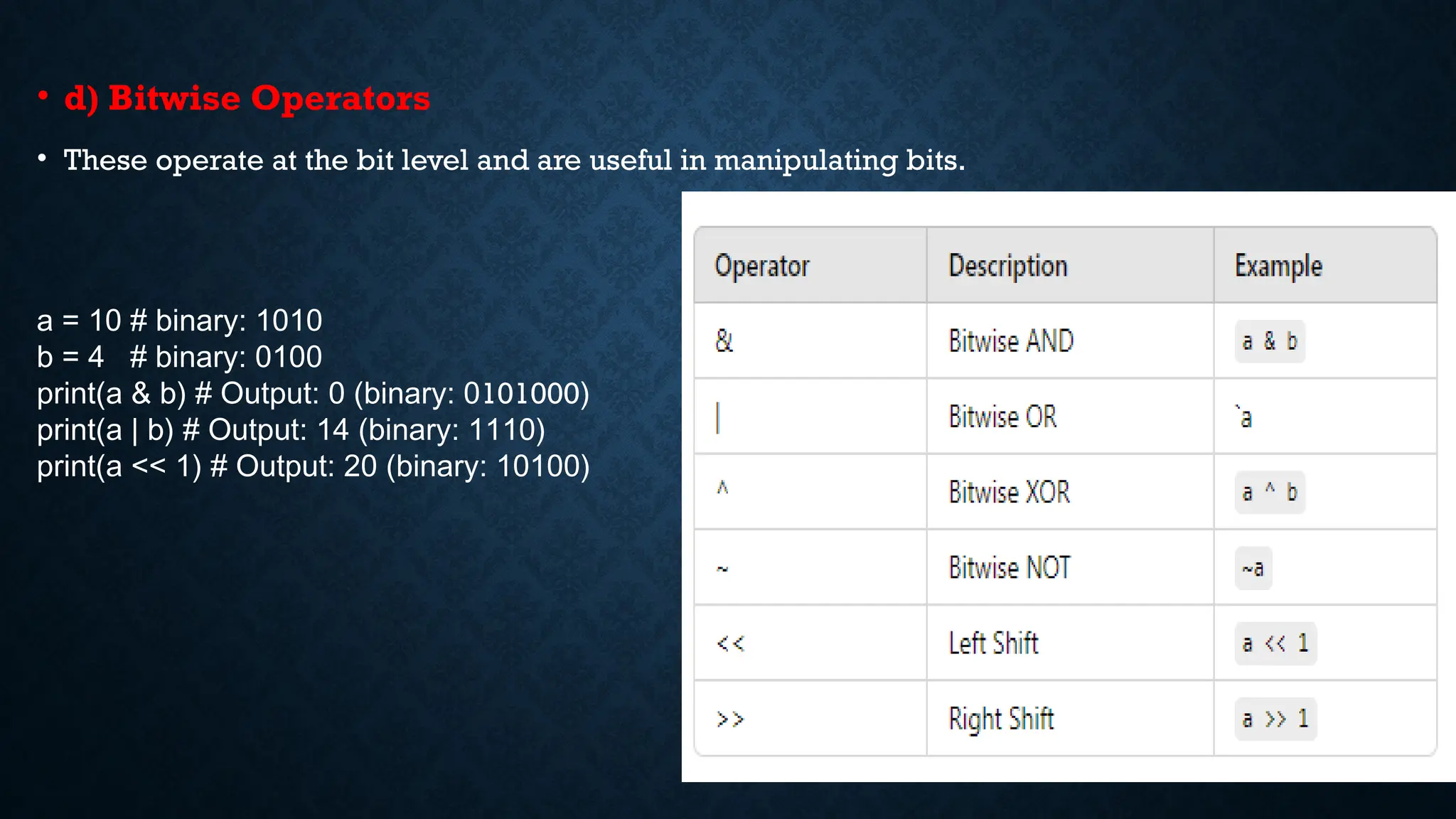
The document explains basic Python programming concepts, including statements, expressions, and operators. It categorizes operators into arithmetic, relational, assignment, bitwise, logical, and membership operators, providing examples for each. Additionally, it covers how these operators perform operations on variables and values, including comparisons and conditions.





![f) Membership Operators
• Membership operators are used to test whether a value or variable exists in a
sequence (such as a string, list, tuple, or dictionary).
• in: Returns True if a value is found in the sequence.
• not in: Returns True if a value is not found in the sequence.
• my_list = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
• # IN Operator
• if 3 in my_list: print("3 is in the list") # Output: 3 is in the list
• # NOT IN Operator
• if 6 not in my_list: print("6 is not in the list") # Output: 6 is not in the list](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonstatementexpressionsandoperators-241127073139-4e21c6f6/75/python-statement-expressions-and-operators-pptx-9-2048.jpg)