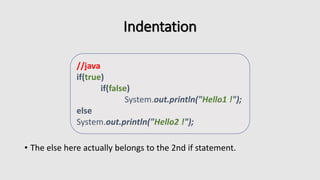
The document is an introductory tutorial on Python, covering fundamental concepts such as syntax, indentation, comments, data types (strings, numbers, lists, dictionaries), and control flow structures (conditionals, loops). It emphasizes Python's unique features like significant indentation and details how to manipulate strings and perform arithmetic operations. Additionally, it includes examples of functions and list comprehensions, providing practical programming insights.













![Lists
# Lists can be heterogenous
favorites = []
# Appending
favorites.append(42)
# Extending
favorites.extend(['Python' , True])
# Equivalent to
favorites = [42 , 'Python' , True]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonintroduction-1-180321095455/85/Python-introduction-1-15-320.jpg)
![Lists
numbers = [ 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 ]
len(numbers)
# 5
numbers[0]
# 1
numbers[0:2]
# [1 ,2]
numbers[2:]
# [3, 4, 5]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonintroduction-1-180321095455/85/Python-introduction-1-16-320.jpg)
![Dictionaries
person = {}
# Set by key / Get by key
person['name'] = 'Ahmad Hussein'
# Update
person.update({
'favorites' : [42 , 'food'] ,
'gender' : 'male'
})
# Any immutable object can be a dictionary key
person[42] = 'favorite number'
person[(44.47 , -73.21)] = 'coordinates'](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonintroduction-1-180321095455/85/Python-introduction-1-17-320.jpg)
![Dictionary Methods
person = { 'name' : 'karim' , 'gender' : 'Male'}
person['name']
person.get('name')
# 'karim'
person.keys()
# ['name' , 'gender']
person.values()
# ['karim' , 'Male']
person.items()
# [['name' , 'karim'] , ['gender' , 'Male']]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonintroduction-1-180321095455/85/Python-introduction-1-18-320.jpg)
![Booleans
Is_python = True
# Everything in python can be cast to Boolean
Is_pyhton = bool('any object’)
# All of these things are equivalent to False
These_are_false = False or 0 or "" or {} or [] or None
# Most everything else is equivalent to True
These_are_true = True and 1 and 'Text' and {'a' : 'b'} and ['c','d']](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonintroduction-1-180321095455/85/Python-introduction-1-19-320.jpg)


![String Manipulation
animals = 'Cats ' + 'Dogs '
animals += 'Rabbits'
# Cats Dogs Rabbits
fruit = ', '.join(['Apple' , 'Banana' , 'Orange'])
#Apple, Banana, Orange
date = '%s %d %d' % ('Mar' , 20 , 2018)
# Mar 20 2018
name = '%(first)s %(last)s' % {
'first' : 'Ahmad' ,
'last' : 'Hussein'}
# Ahmad Hussein](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonintroduction-1-180321095455/85/Python-introduction-1-22-320.jpg)





![For Loop
for x in range(10):
print(x)
# 0-9
fruits = ['Apple' , 'Orange']
for fruit in fruits:
print(fruit)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonintroduction-1-180321095455/85/Python-introduction-1-28-320.jpg)


![List comprehensions
• Useful for replacing simple for-loops.
odds = []
for x in range(50):
if x % 2 :
odds.append(x)
odds = [x for x in range(50) if x % 2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonintroduction-1-180321095455/85/Python-introduction-1-31-320.jpg)
