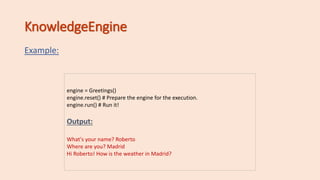
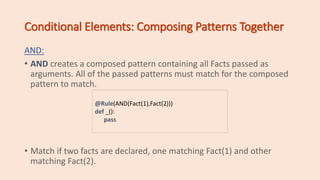
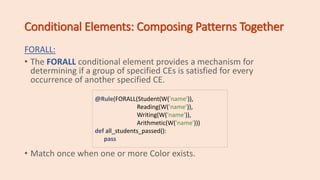
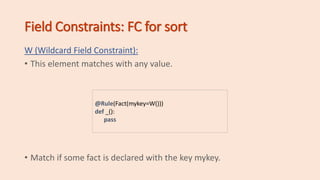
The document introduces fundamental concepts of CLIPS and PyKnow for expert system development, including facts, rules, and the knowledge engine. It covers the syntax and functionality of facts and patterns, the use of conditional elements, and how to create and manage rules within a knowledge engine. Additionally, it explains variable binding, field constraints, and demonstrates examples to illustrate key points.






![Facts
• Facts are the basic unit of information of PyKnow. They are used by
the system to reason about the problem.
Let’s enumerate some facts about Facts:
1. The class Fact is a subclass of dict.
f = Fact(a=1, b=2)
print(f['a’])
# 1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/expertsystemwithpython-2-180417215219/85/Expert-system-with-python-2-7-320.jpg)

![Facts
3. In contrast to dict, you can create a Fact without keys (only values),
and Fact will create a numeric index for your values.
f = Fact('x', 'y', 'z')
print(f[0])
# x](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/expertsystemwithpython-2-180417215219/85/Expert-system-with-python-2-9-320.jpg)
![Facts
4. You can mix autonumeric values with key-values, but autonumeric
must be declared first.
f = Fact('x', 'y', 'z', a=1, b=2)
print(f[0])
# x
print(f['a’])
# 1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/expertsystemwithpython-2-180417215219/85/Expert-system-with-python-2-10-320.jpg)
![Facts
5. You can subclass Fact to express different kinds of data or extend it
with your custom functionality.
class Alert(Fact):
pass
class Status(Fact):
pass
f1 = Alert(color = 'red')
f2 = Status(state = 'critical')
print(f1['color’]) # red
print(f2['state’]) # 'critical](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/expertsystemwithpython-2-180417215219/85/Expert-system-with-python-2-11-320.jpg)




![Rules
Example:
• Match with every Fact which:
• f[0] == 'animal'
• f['family'] == 'felinae'
class MyFact (Fact):
pass
@Rule(Fact('animal', family='felinae’))
def match_with_cats ():
print("Meow!")](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/expertsystemwithpython-2-180417215219/85/Expert-system-with-python-2-16-320.jpg)