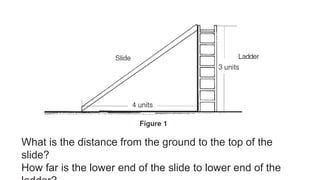
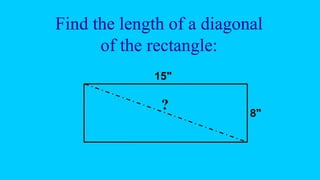
The document explains how to use the Pythagorean theorem to solve problems involving right triangles. It provides examples of using the theorem to calculate the length of a ladder/slide, the distance a diver must swim, the length of a kite string, and the distance traveled from driving directions. The theorem states that for any right triangle, the square of the hypotenuse (the side opposite the right angle) equals the sum of the squares of the other two sides. The document walks through setting up and solving examples using the formula a2 + b2 = c2, where a and b are the legs and c is the hypotenuse.