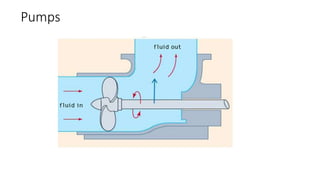
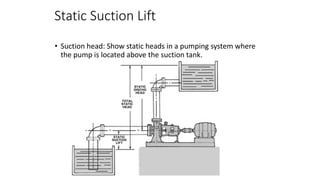
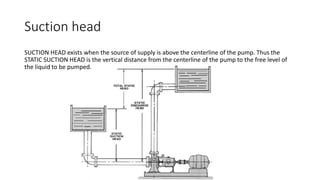
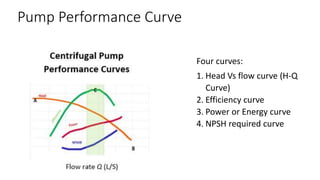
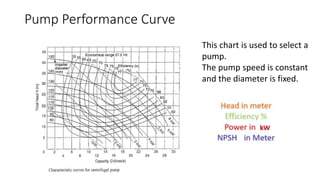
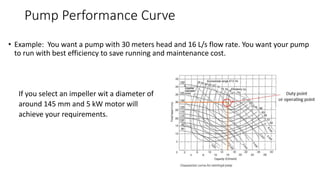
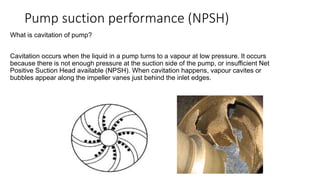
Pumps require energy to move fluids from one location to another by overcoming resistance. The amount of energy needed depends on factors like the height fluid must be lifted, pressure at the delivery point, pipe dimensions, flow rate, and fluid properties. Proper pump selection involves considering the total static head, friction head, velocity head, and pressure head. Pump performance is illustrated by curves showing relationships between head, flow rate, efficiency, power, and net positive suction head (NPSH) required to prevent cavitation. Cavitation can damage pumps and reduce performance, so sufficient NPSH must be provided.