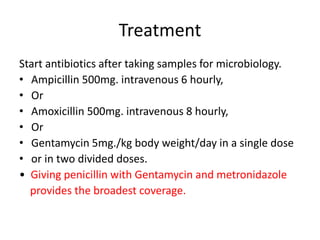
This document discusses puerperal sepsis/infections, providing definitions and guidelines for prevention and treatment. Puerperal sepsis is defined as a genital tract infection occurring between membrane rupture or labor onset through 42 days postpartum, accompanied by at least two symptoms like fever or abnormal discharge. Puerperal infections are a broader term including infections of the genitourinary system or uterus related to labor/delivery. Prevention focuses on identifying/treating infections antenatally, adhering to sterile procedures during labor and delivery, and treating promptly with antibiotics like ampicillin, amoxicillin or gentamycin postpartum.