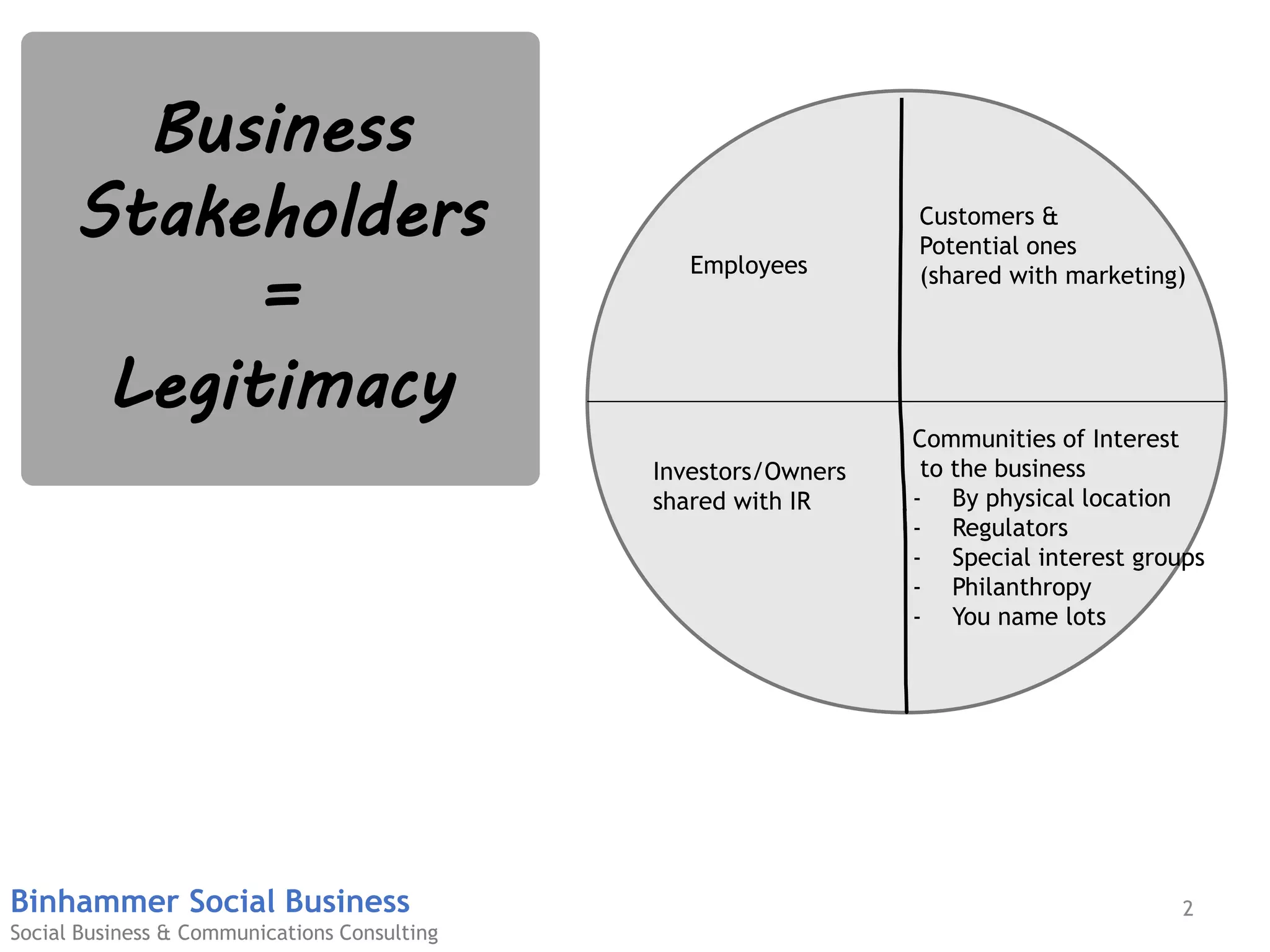
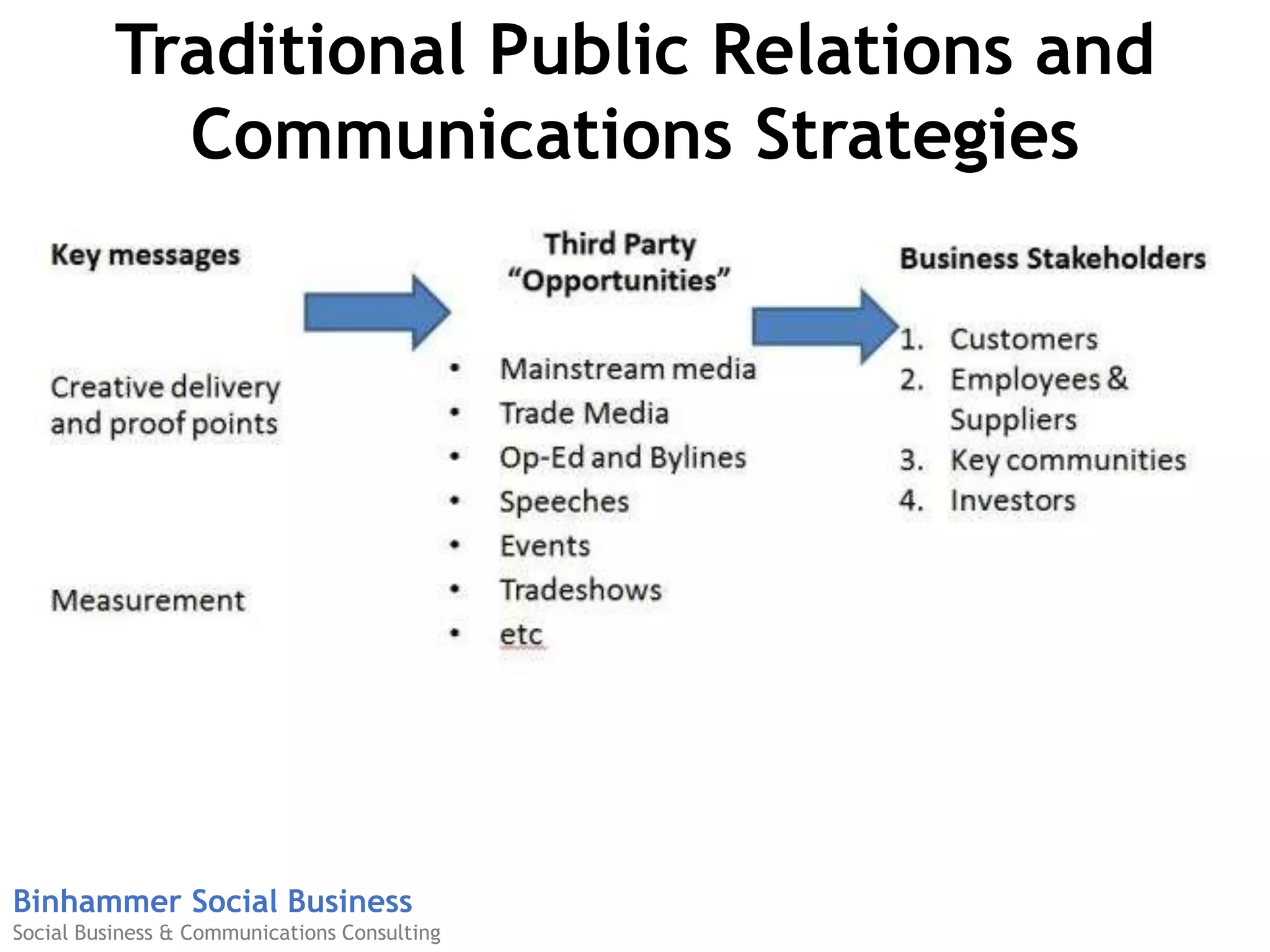
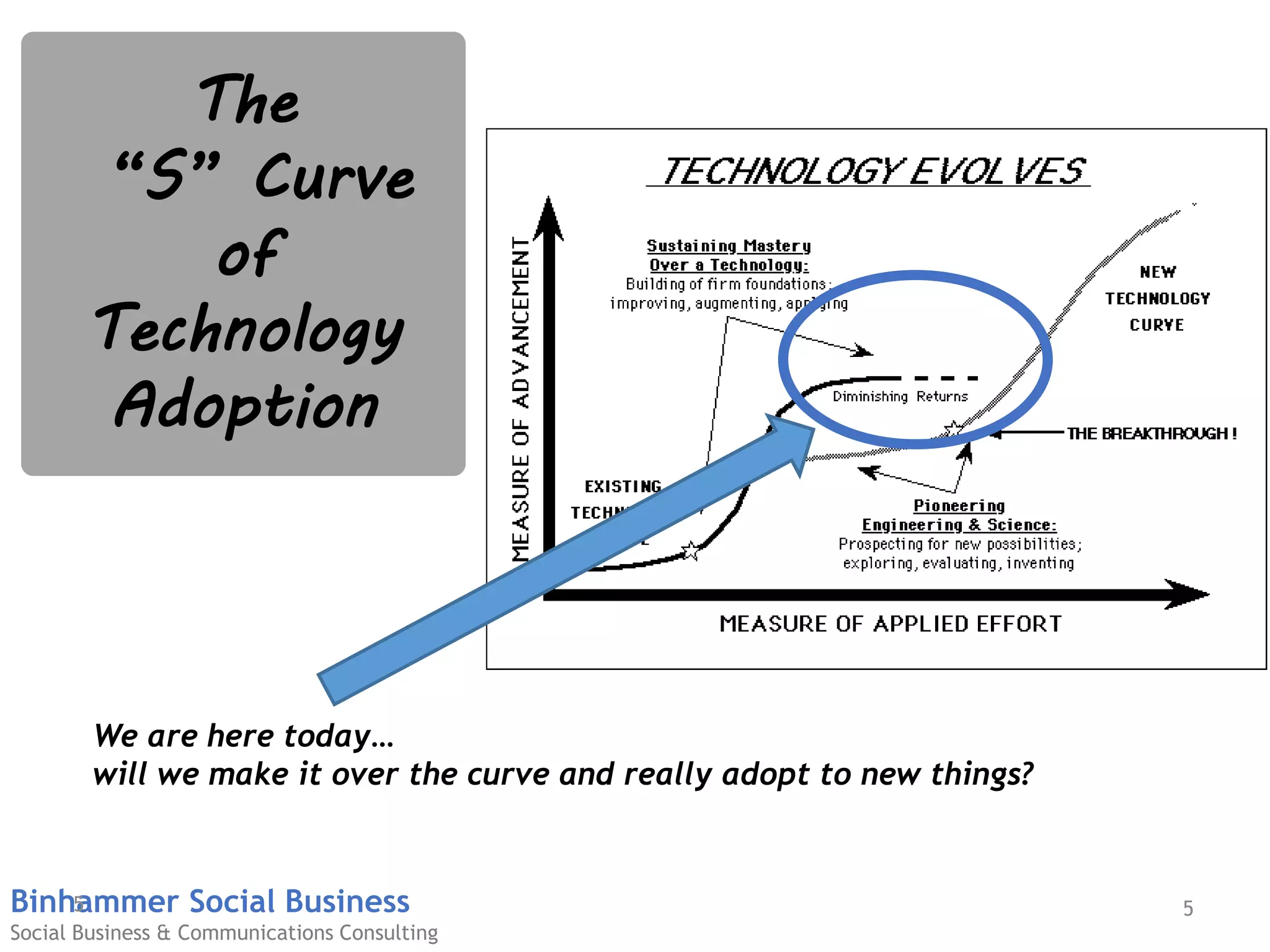
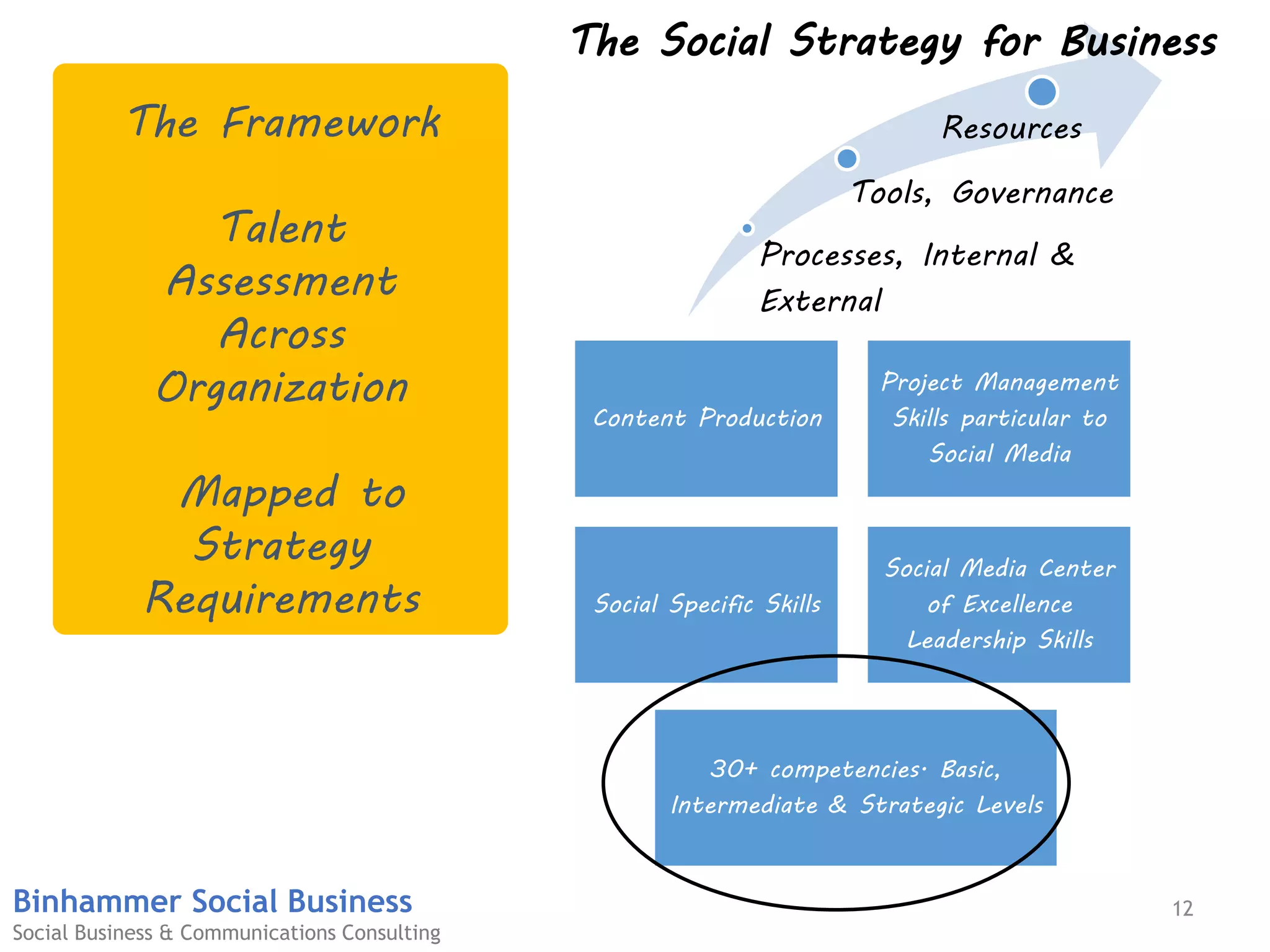
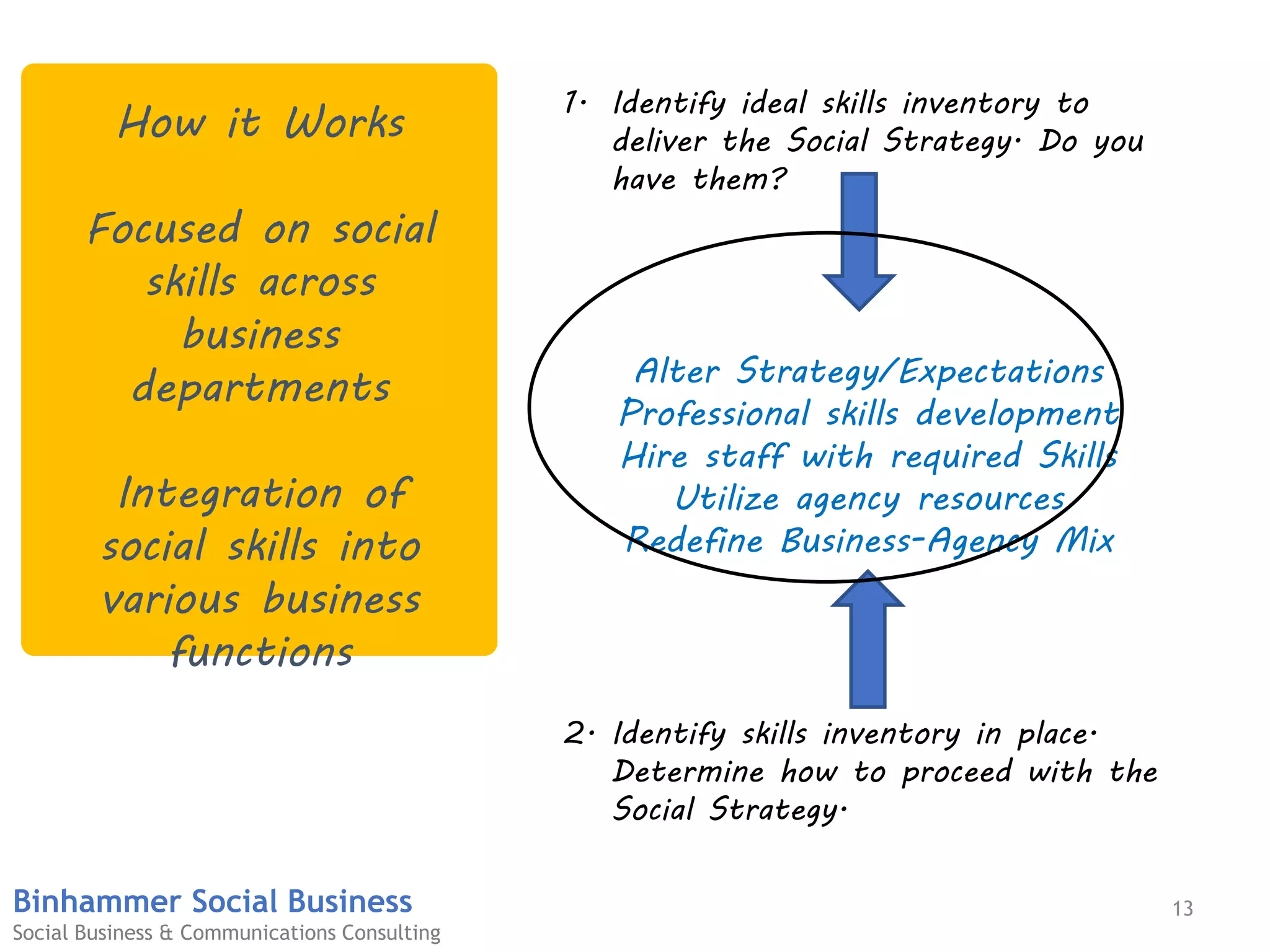
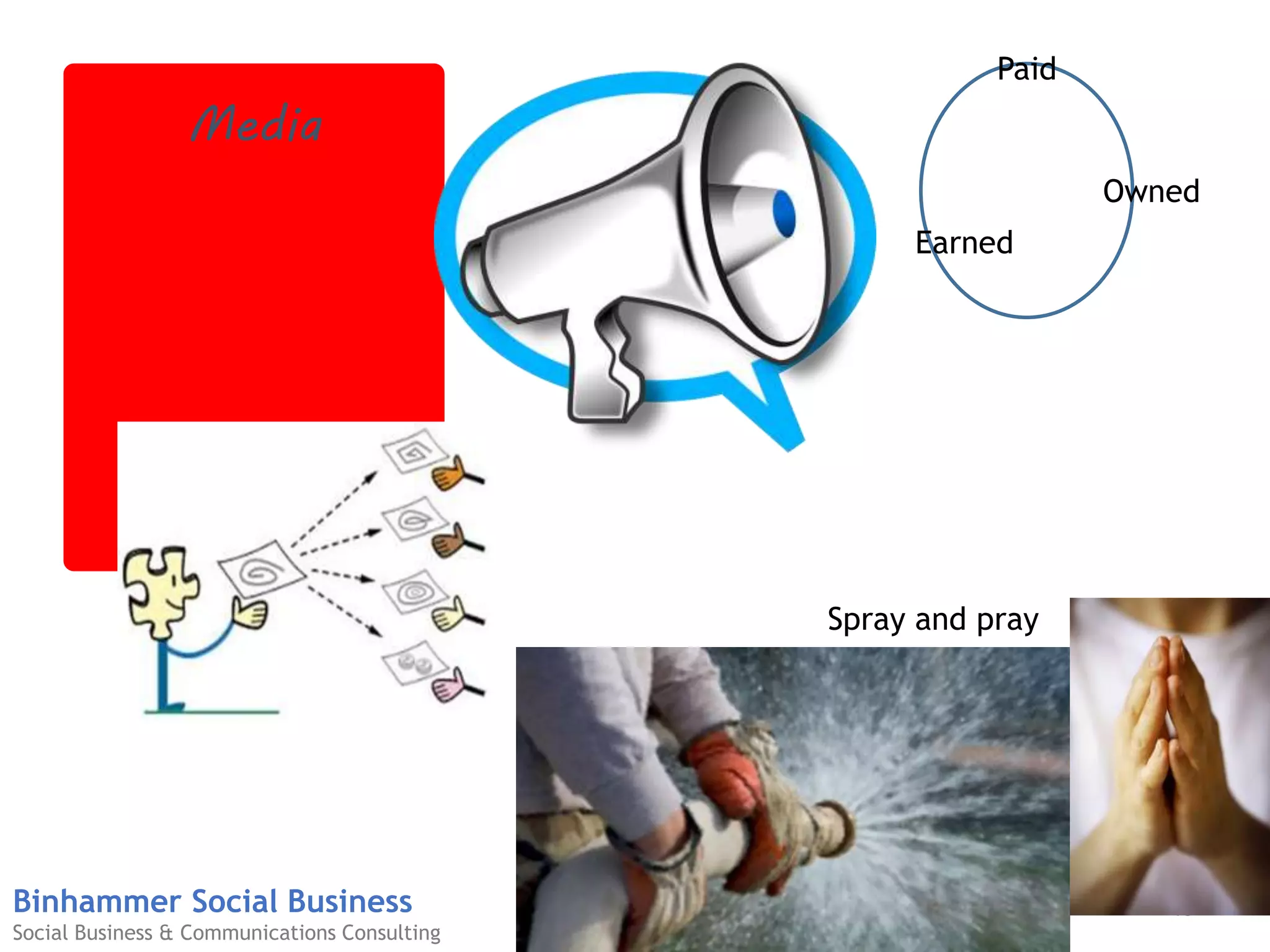
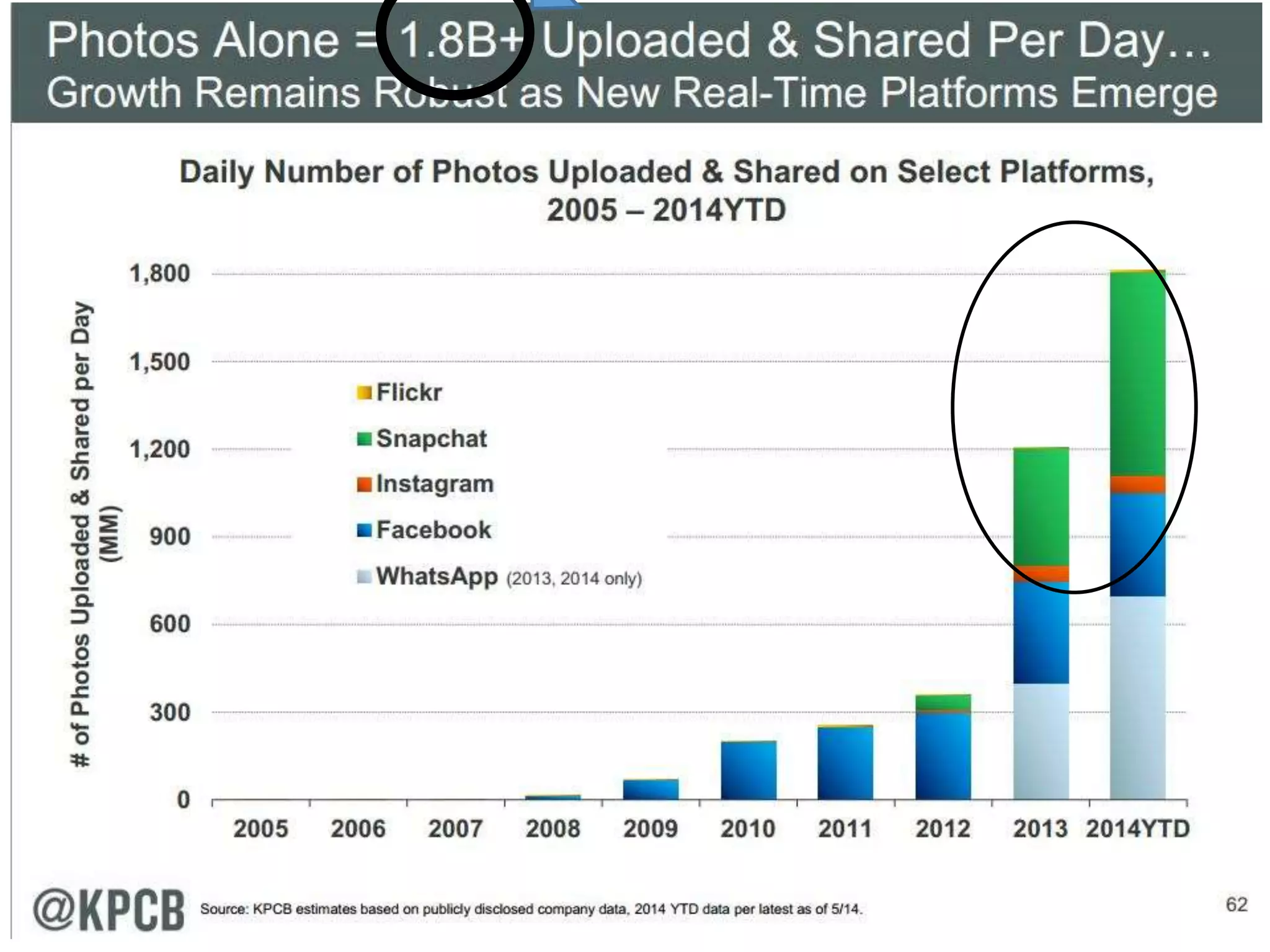
The document discusses the challenges businesses face in adopting digital strategies and social media due to a significant skills gap among employees. It highlights that while many executives recognize the importance of digital initiatives, a substantial number feel their organizations lack the necessary capabilities and resources. It emphasizes the urgent need for companies to develop talent and integrate social skills across various functions to succeed in a rapidly changing digital landscape.