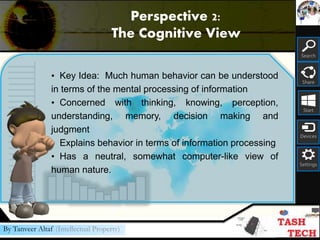
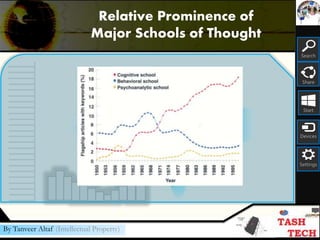
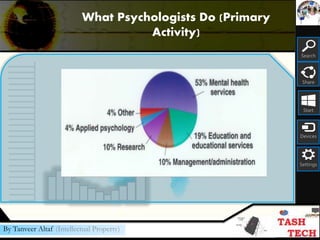
This document provides an overview of psychology as a science. It discusses that psychology is the study of behavior and mental processes. It also outlines the major perspectives in psychology, including psychodynamic, biological, cognitive, behavioral, and sociocultural approaches. Additionally, it describes the different types of psychologists and their specialties, including where they work and their primary activities. The document aims to introduce some of the key concepts and fields within the study of psychology.