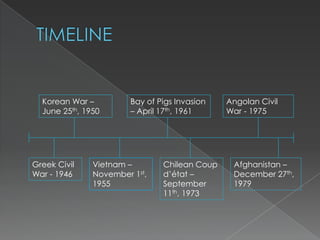
The document discusses several proxy wars that occurred during the Cold War between the US and USSR. These include the Korean War, Vietnam War, Angolan Civil War, and war in Afghanistan. In each conflict, one superpower backed a local ally against a rival backed by the other superpower. This led to an expansion of influence for the supporting power and increased tensions between the US and USSR as they fought to spread their competing political ideologies around the world through proxy allies rather than direct military conflict.