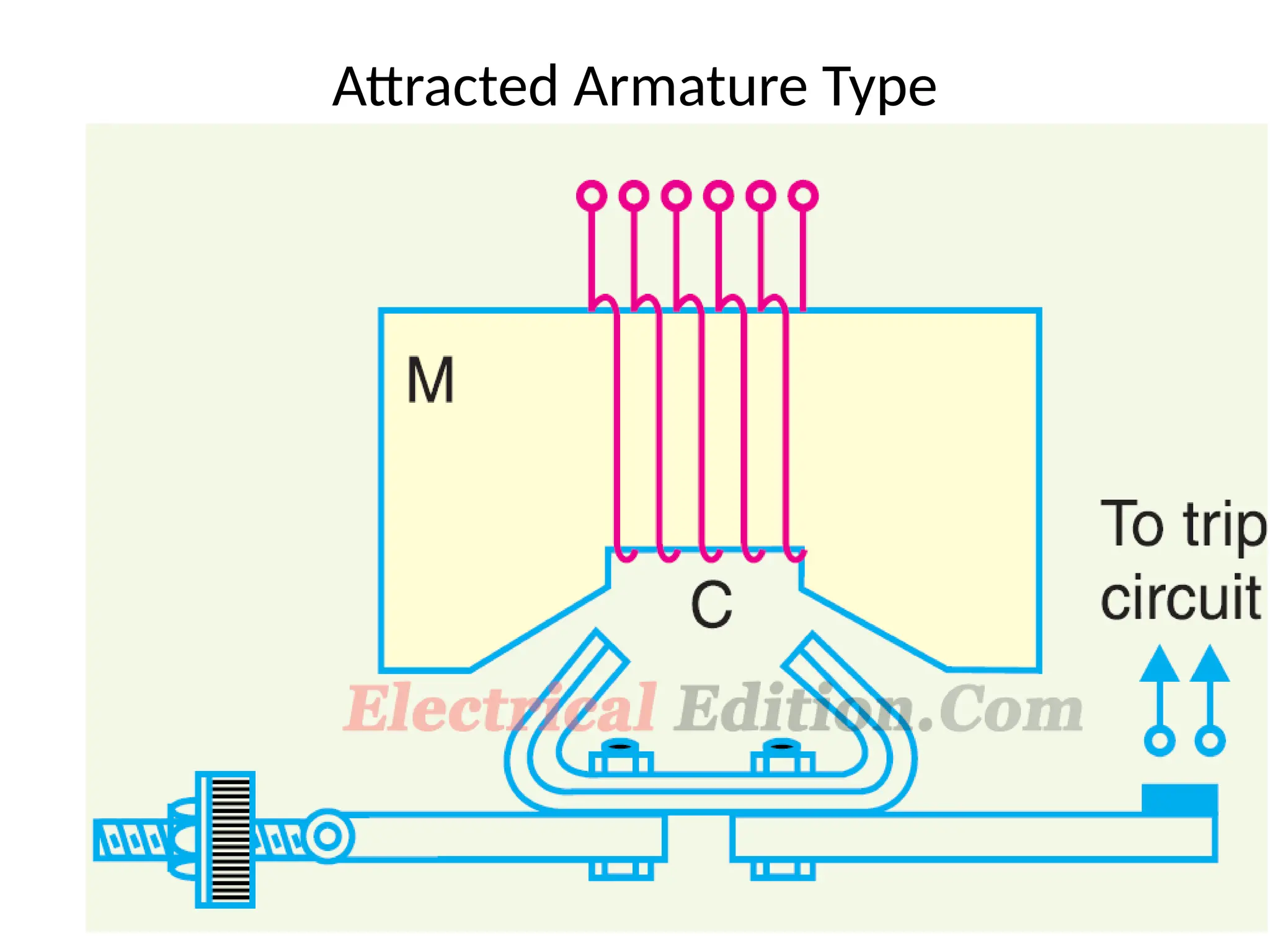
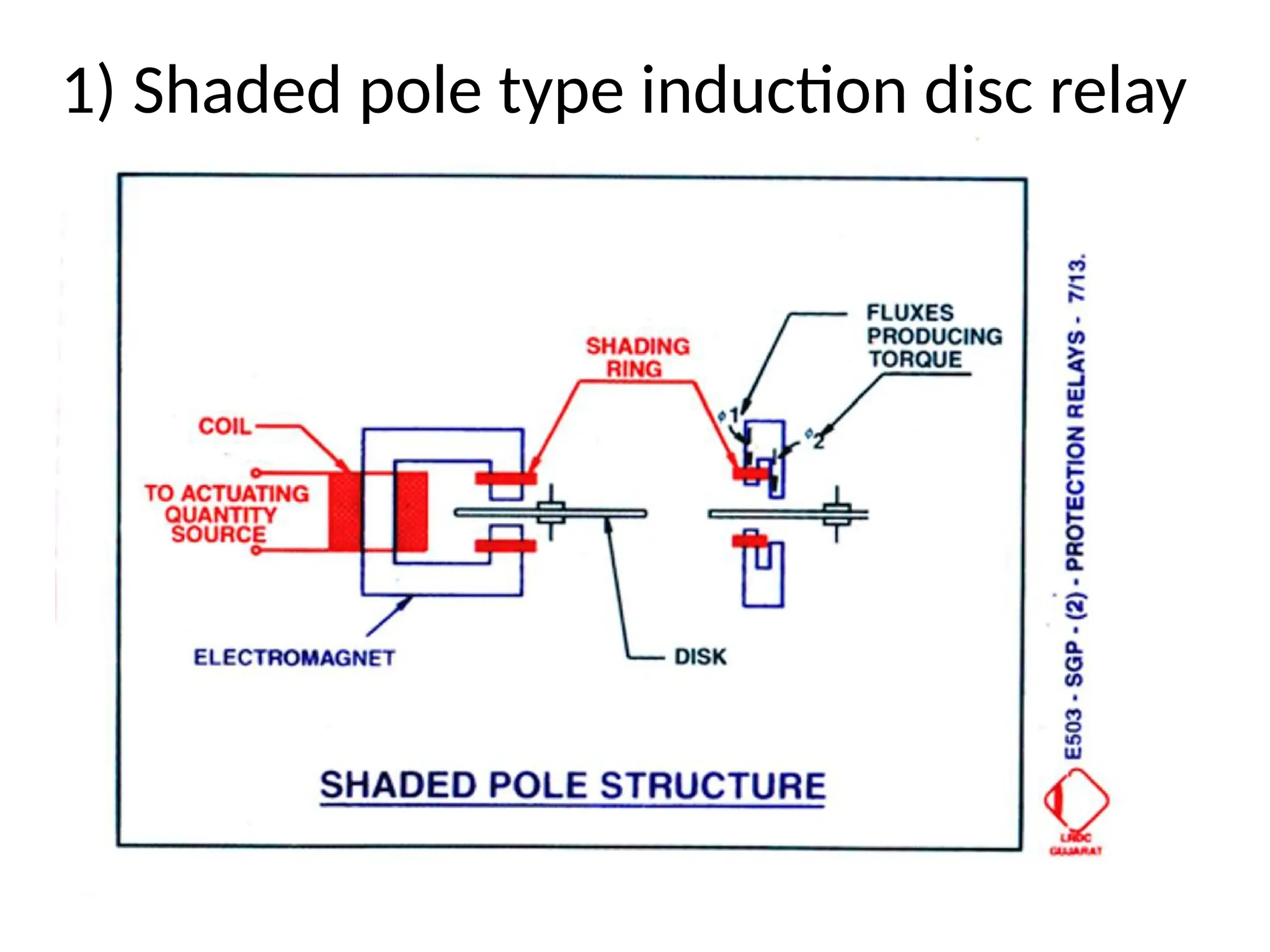
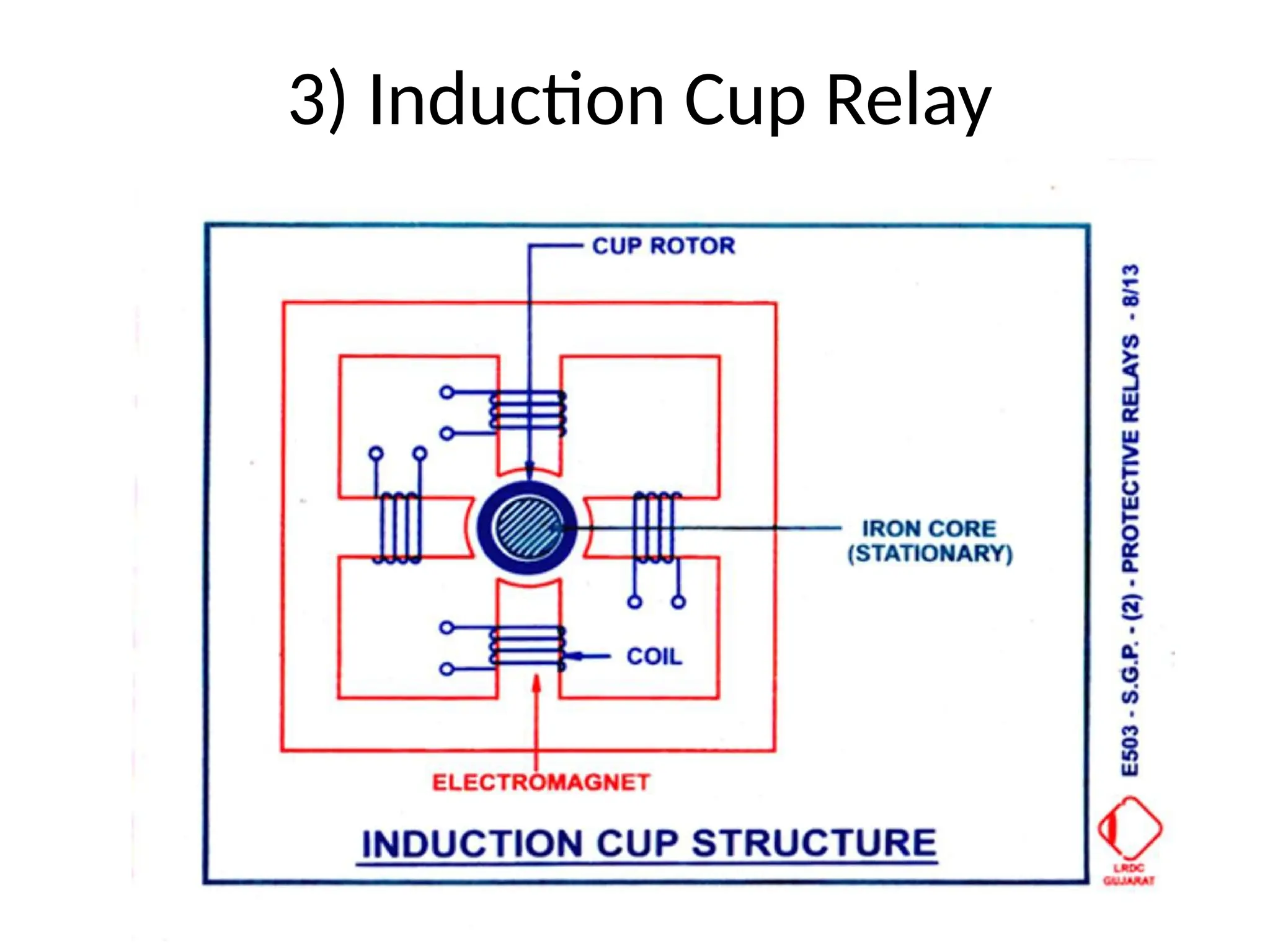
This document outlines various types of protective relays and their principles, including electromagnetic, induction, and balanced beam relays. It also discusses the characteristics and operational time calculations of these relays, emphasizing the importance of current and time settings. Additionally, it highlights the features of directional relays used for protection in high voltage transmission systems.