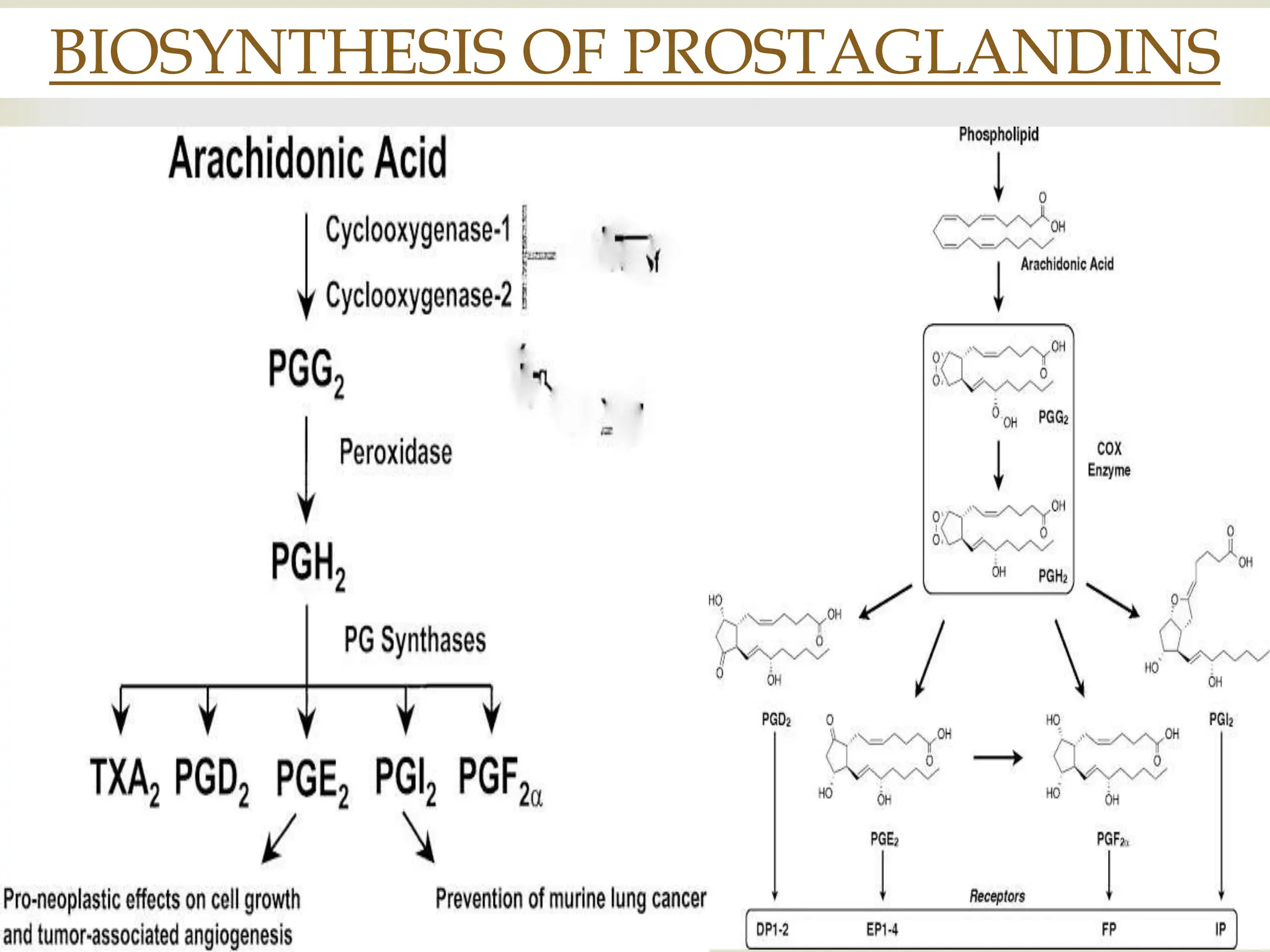
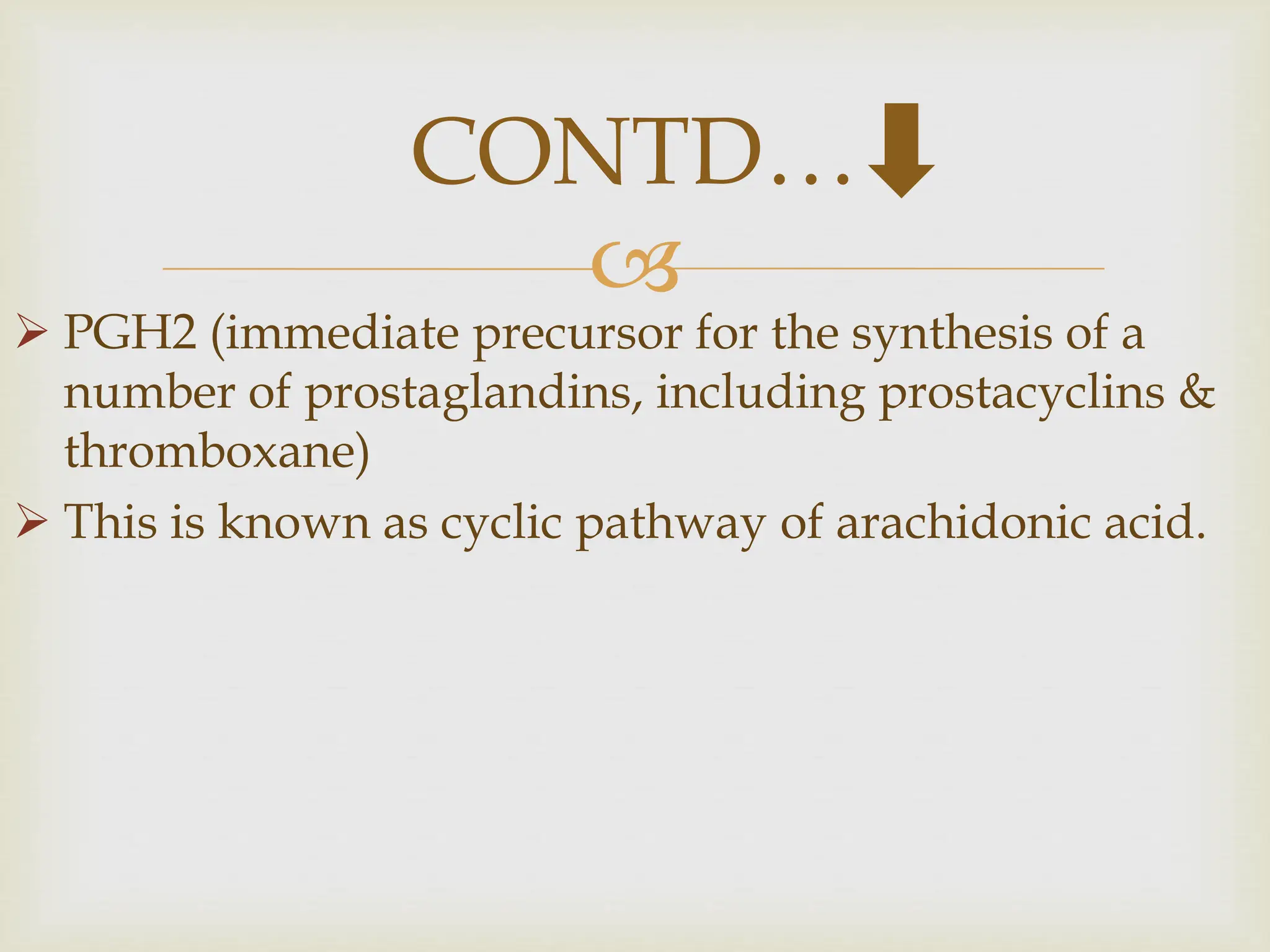
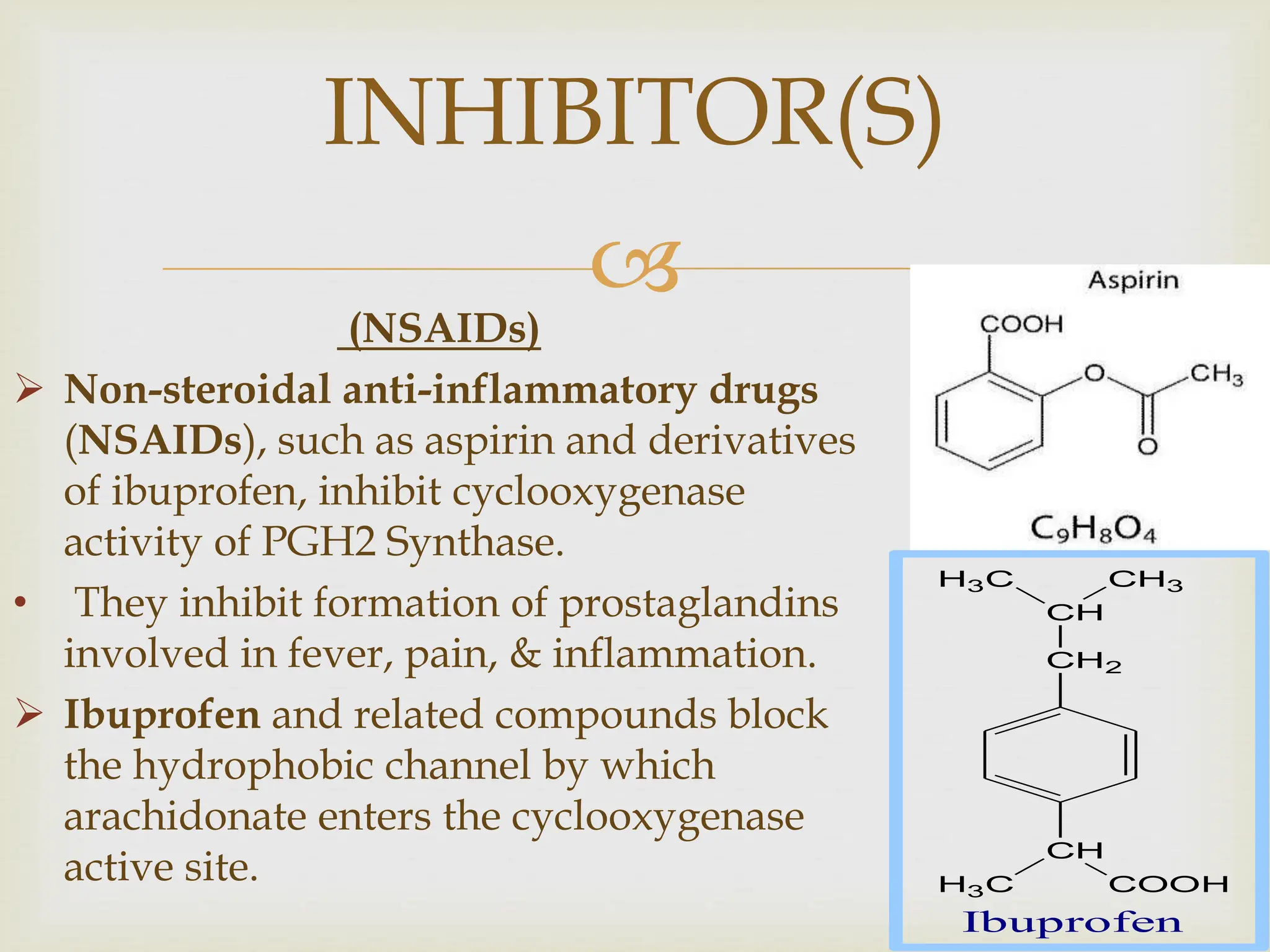
Prostaglandins are eicosanoids containing a 20-carbon cyclopentane ring that are produced by cells and act as local hormones. They are produced from arachidonic acid through a cyclic pathway involving prostaglandin H2. Prostaglandins perform various functions like regulating blood pressure, inflammation, reproduction, and gastric secretion. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs like aspirin and ibuprofen inhibit prostaglandin production by blocking cyclooxygenase. Aspirin irreversibly acetylates cyclooxygenase, while ibuprofen blocks the channel for arachidonic acid entry.