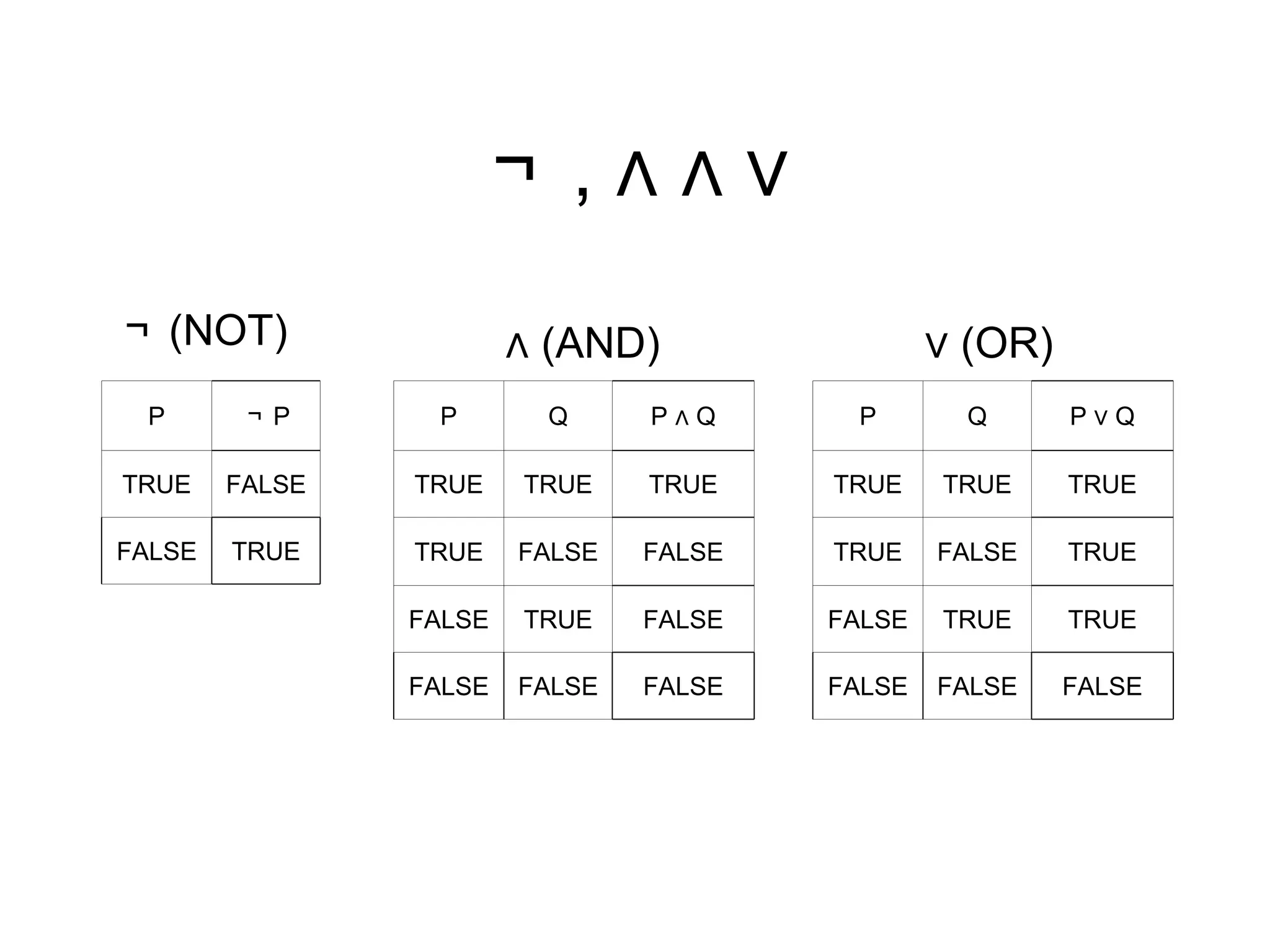
1) Propositional logic uses propositions that can be resolved as true or false and operators like NOT, AND, and OR to combine propositions.
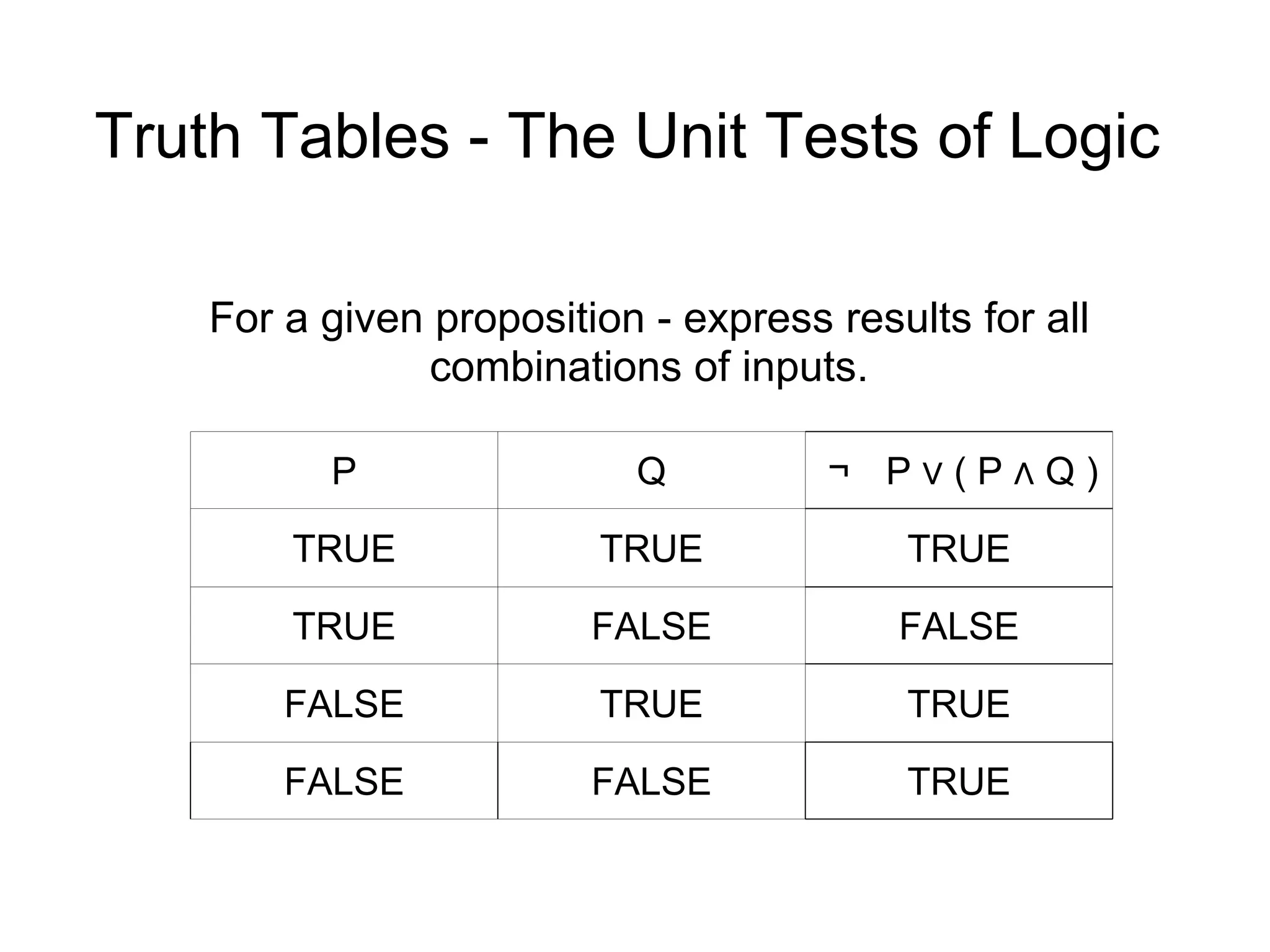
2) Truth tables express all combinations of inputs to determine if a proposition is a tautology (always true) or contradiction (always false).
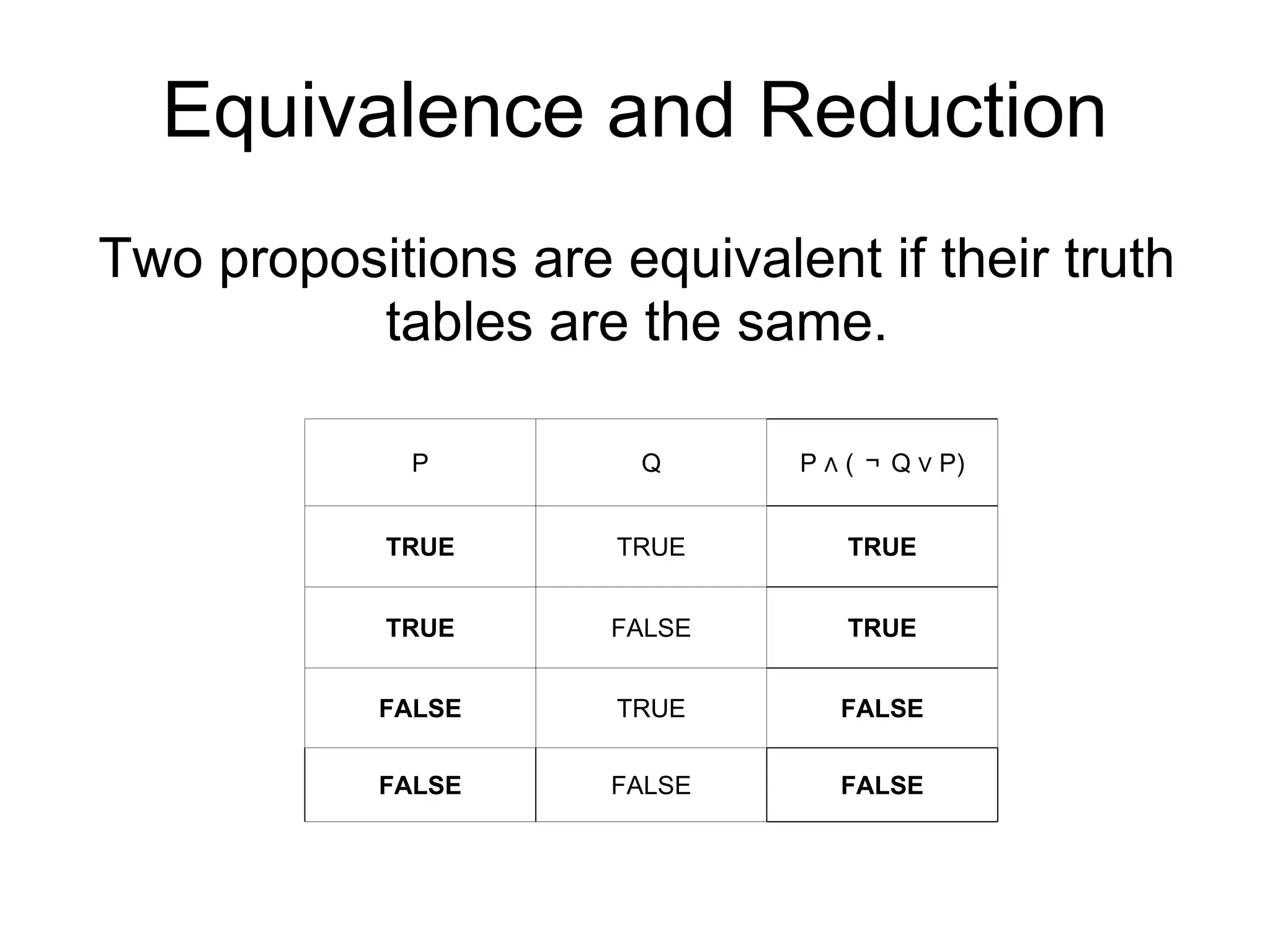
3) Equivalent propositions have the same truth values and De Morgan's laws can be used to transform expressions.
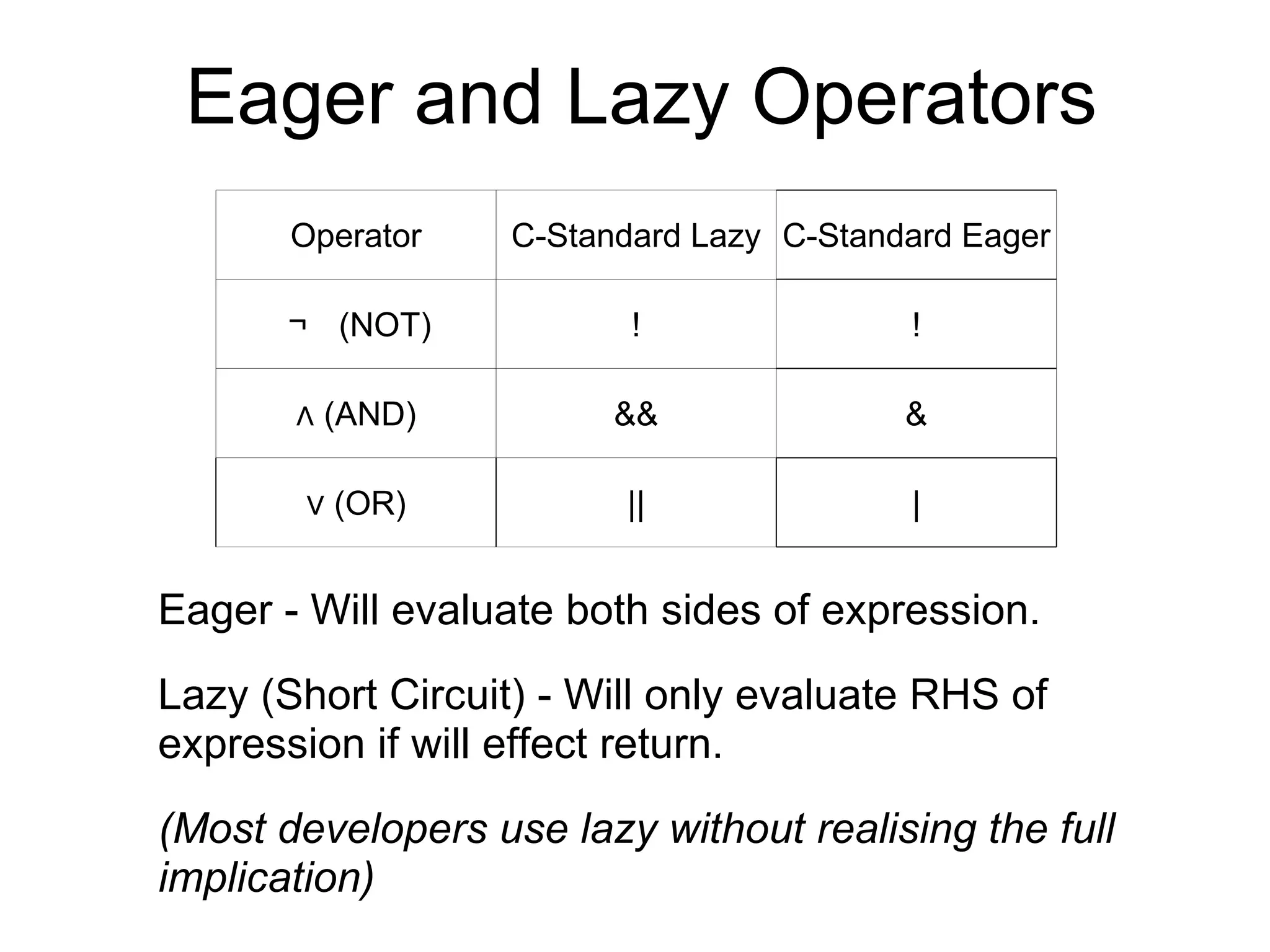
4) Some logical operators are "lazy" and short-circuit evaluation to improve efficiency by reducing unnecessary computations.

![Propositions Functions/Statements which can be resolved to True or False. P – Do you like Sausage Butties? Q – Do you like Bacon Butties[1]? [1] Technically Q is a tautology.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/propositionallogic-111017103214-phpapp02/75/Propositional-logic-for-Beginners-2-2048.jpg)