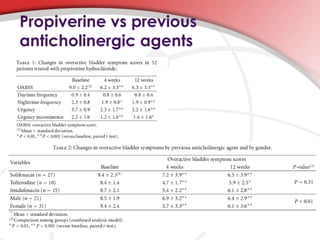
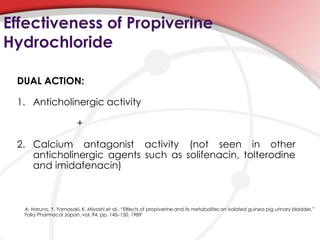
This document discusses overactive bladder and compares the drug propiverine hydrochloride to previous anticholinergic agents for treating overactive bladder symptoms. It summarizes that propiverine has dual action as both an anticholinergic and calcium channel blocker. A clinical study of 73 patients compared propiverine to previous anticholinergic treatments and found that patients who completed the study on propiverine saw significant improvements in nighttime urinary frequency, urgency, and urgency incontinence. The document concludes that propiverine may be more effective than previous anticholinergic agents for some patients with overactive bladder.
![What is an Overactive Bladder?
Overactive bladder
(also known as
Overactive Bladder
Syndrome) is a
urological condition
related to problems
with urination. [1]
1. Abrams, P; Cardozo, L; Fall, M; Griffiths, D; Rosier, P; Ulmsten, U; Van Kerrebroeck, P; Victor, A; Wein, A;
Standardisation Sub-Committee of the International Continence, Society (January 2003). "The standardisation of
terminology in lower urinary tract function: report from the standardisation sub-committee of the International
Continence Society.". Urology 61 (1): 37–49. PMID 12559262](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/propiverinehydrochloridevspreviousanticholinergicagents-140501140254-phpapp02/85/Propiverine-hydrochloride-vs-previous-anticholinergic-agents-For-Overactive-Bladder-2-320.jpg)
![Causes of Overactive Bladder
Causes of overactive bladder: [1]
Age
Diabetes
Certain Medications (diuretics)
Lifestyle Choices
Excessive consumption of Caffeine or
Alcohol
1. "DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT OF OVERACTIVE BLADDER (Non-Neurogenic) IN ADULTS: AUA/SUFU GUIDELINE".
American Urological Association. Retrieved 25 Aug 2013](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/propiverinehydrochloridevspreviousanticholinergicagents-140501140254-phpapp02/85/Propiverine-hydrochloride-vs-previous-anticholinergic-agents-For-Overactive-Bladder-3-320.jpg)


![Propiverine Hydrochloride vs
Oxybutynin Hydrochloride
A double blind randomized control study
demonstrated that propiverine was superior to
oxybutynin hydrochloride in terms of improvement of
pollakisuria and urinary incontinence associated with
neurogenic bladder and unstable bladder. [1]
1. M. Stohrer, G. Murtz, G. Kramer, F. Schnabel, E. P. Arnold, and J. J. Wyndaele, “Propiverine compared
to oxybutynin in neurogenic detrusor overactivity: results of a randomized, double-blind, multicenter
clinical study,” European Urology, vol. 51, no. 1, pp. 235–242, 2007.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/propiverinehydrochloridevspreviousanticholinergicagents-140501140254-phpapp02/85/Propiverine-hydrochloride-vs-previous-anticholinergic-agents-For-Overactive-Bladder-9-320.jpg)