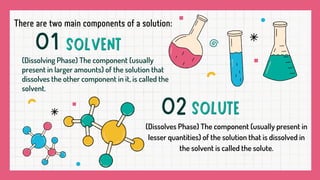
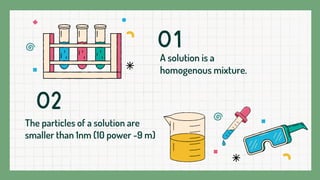
A solution is a homogeneous mixture composed of a solvent and a solute, where the particles are evenly distributed and indistinguishable at the particle level. Examples include lemonade and soda water, with various states such as gas in liquid and solid solutions like alloys. Solutions are stable, do not scatter light, and the solute cannot be separated by filtration.