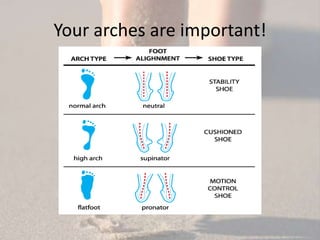
Proper footwear for walking serves three main functions: protection, stability, and shock absorption. Key shoe components include the last, toe break, heel cup, and midsole materials, which vary based on foot type. When shopping, consider factors such as fitting at the end of the day, measuring your size regularly, and consulting professionals, especially if you have medical conditions.