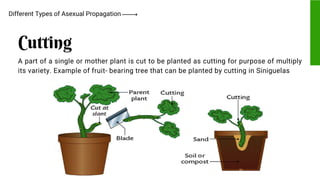
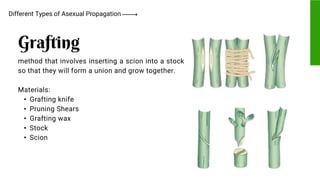
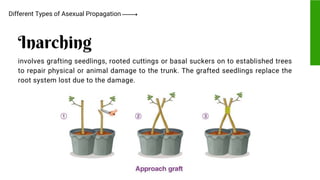
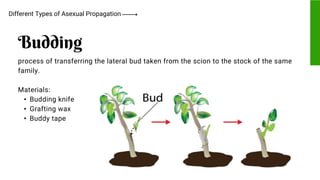
This document provides information on propagating trees and fruit-bearing trees using scientific processes. It discusses the importance of plant propagation and the benefits of using scientific methods. These include ensuring healthy, strong plant growth and increased harvest yields. The document also identifies the appropriate tools used in plant propagation and describes their purposes. Finally, it explains different scientific propagation techniques like sexual propagation using seeds, and asexual propagation methods like cutting, grafting, budding, layering, and inarching. Safety measures for propagating fruit trees are also outlined.