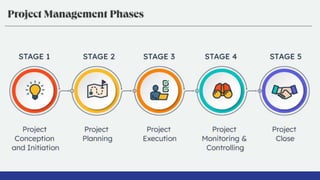
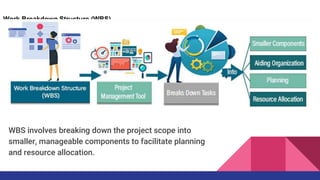
The document explains essential project management concepts, methodologies, and tools, emphasizing the importance of planning, resource allocation, and risk management for successful project delivery. It introduces various methodologies such as Waterfall and Agile, along with techniques like Work Breakdown Structure, Gantt Charts, and SWOT Analysis to facilitate project planning and tracking. Additionally, it highlights the significance of using dashboards and reports for real-time insights and communication with stakeholders.