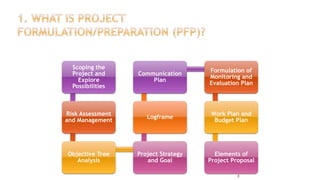
The document explains project formulation/preparation (PFP) within the context of project cycle management (PCM), detailing its importance in establishing a solid foundation for project implementation through systematic analysis. Key components of PFP include scoping, risk assessment, objective analysis, planning, and communication, all aimed at generating a comprehensive project proposal. The document further emphasizes the iterative nature of the analysis process and the significance of stakeholder involvement and effective communication in achieving successful PFP.