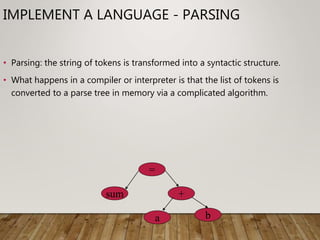
This document provides an introduction to programming languages. It discusses the different generations of programming languages from machine language to high-level languages like C++ and Java. It also covers the differences between interpreters and compilers and the basic steps involved in implementing a programming language which are scanning, parsing, and code generation.