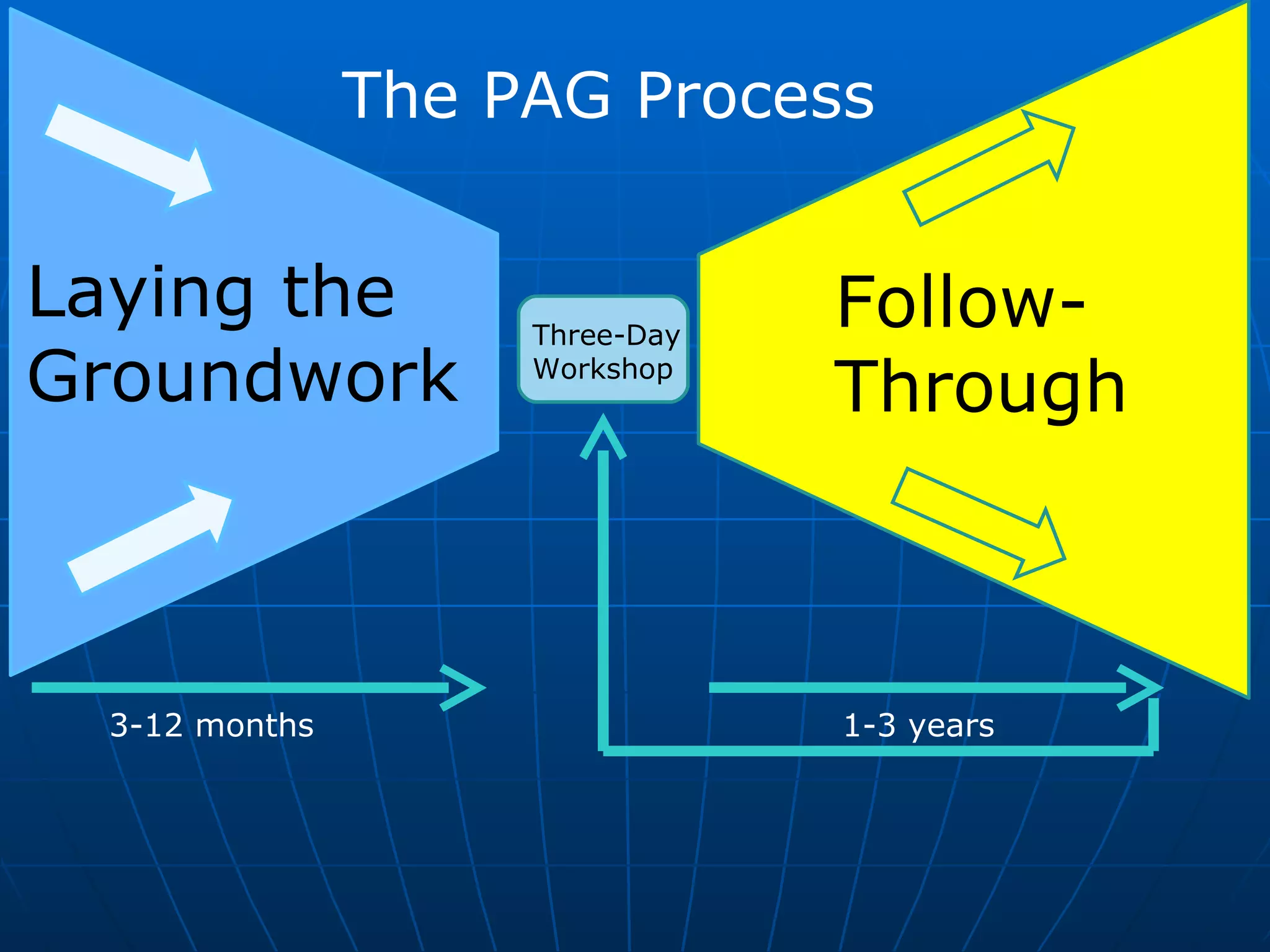
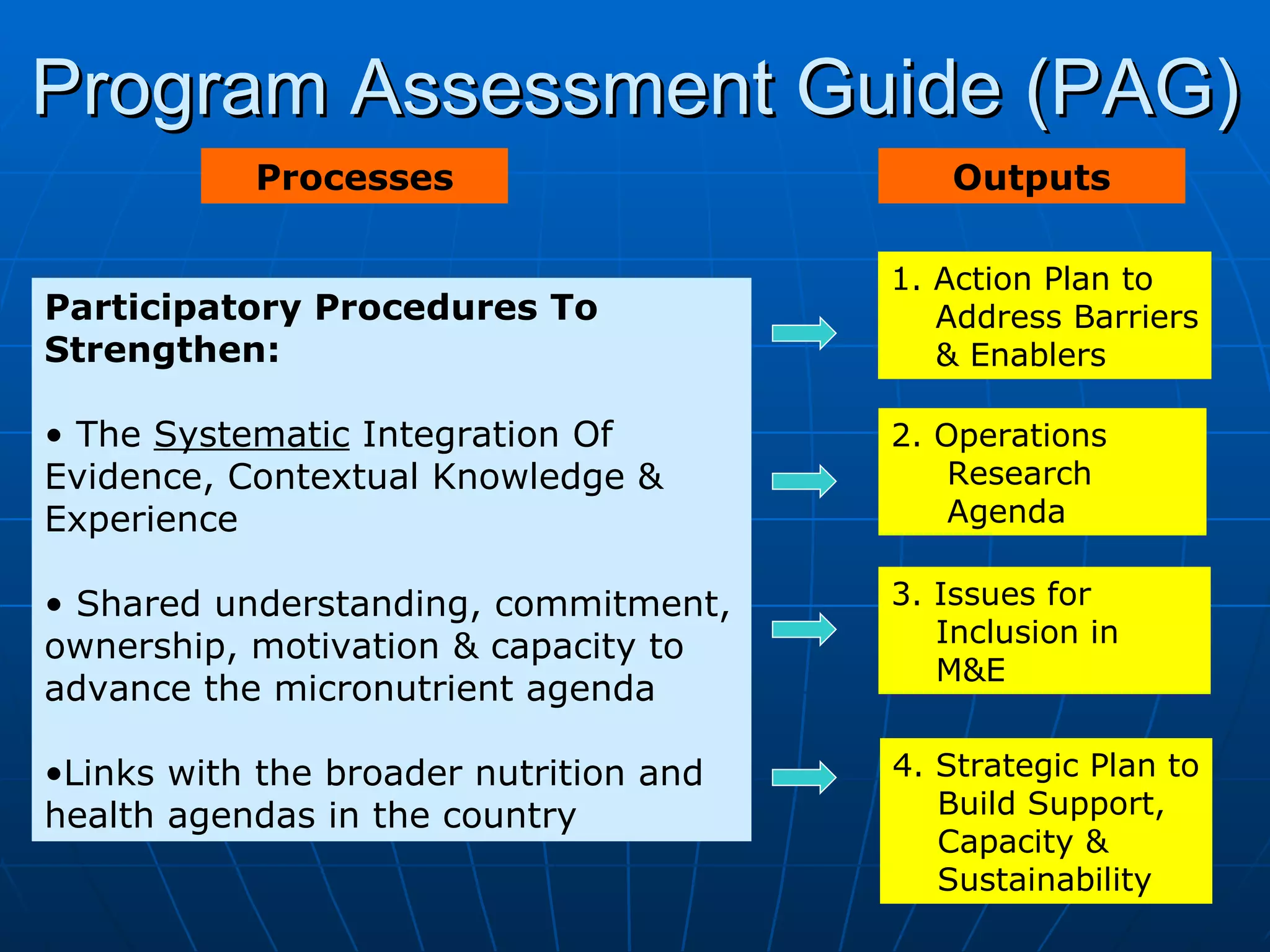
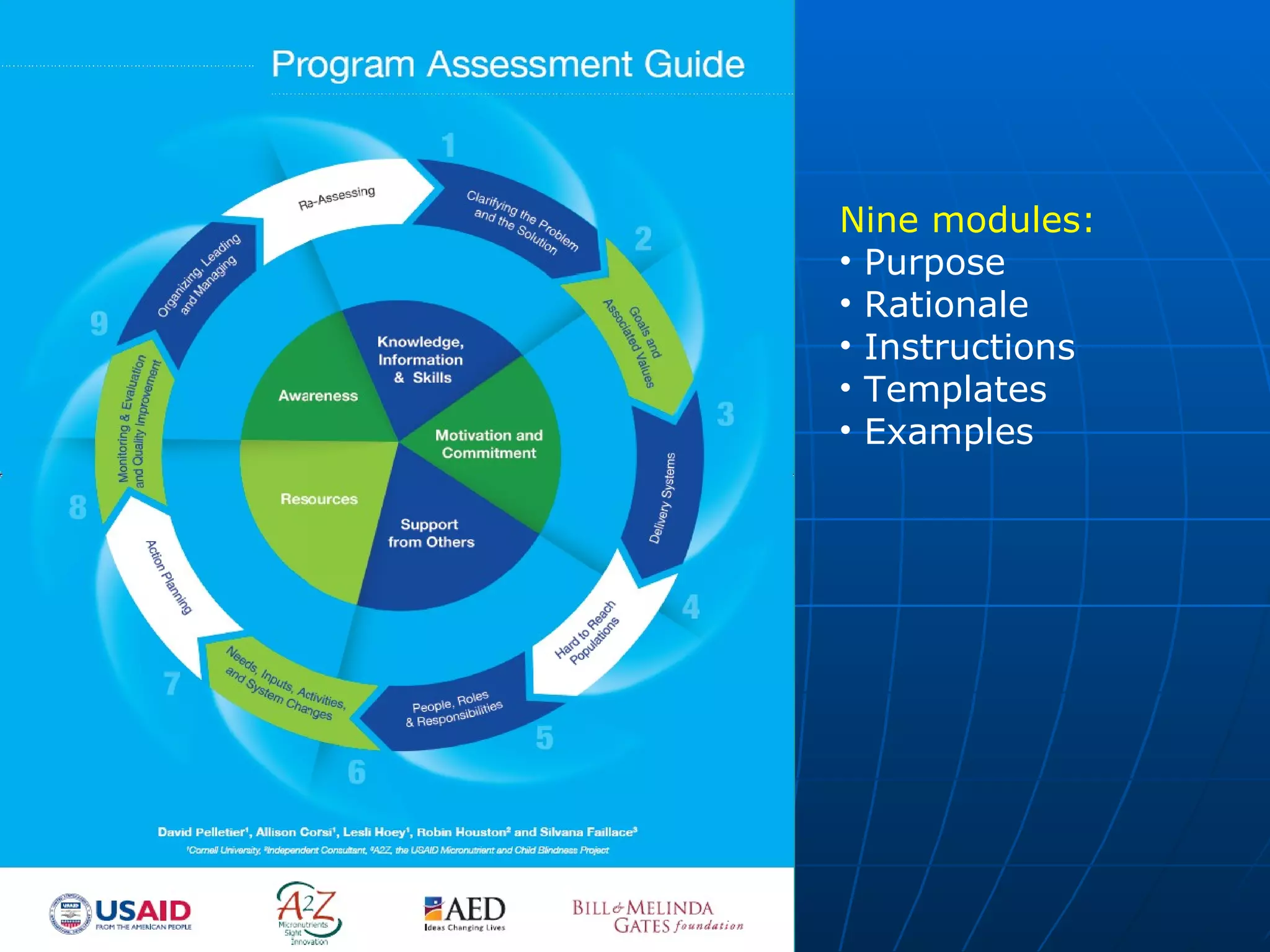
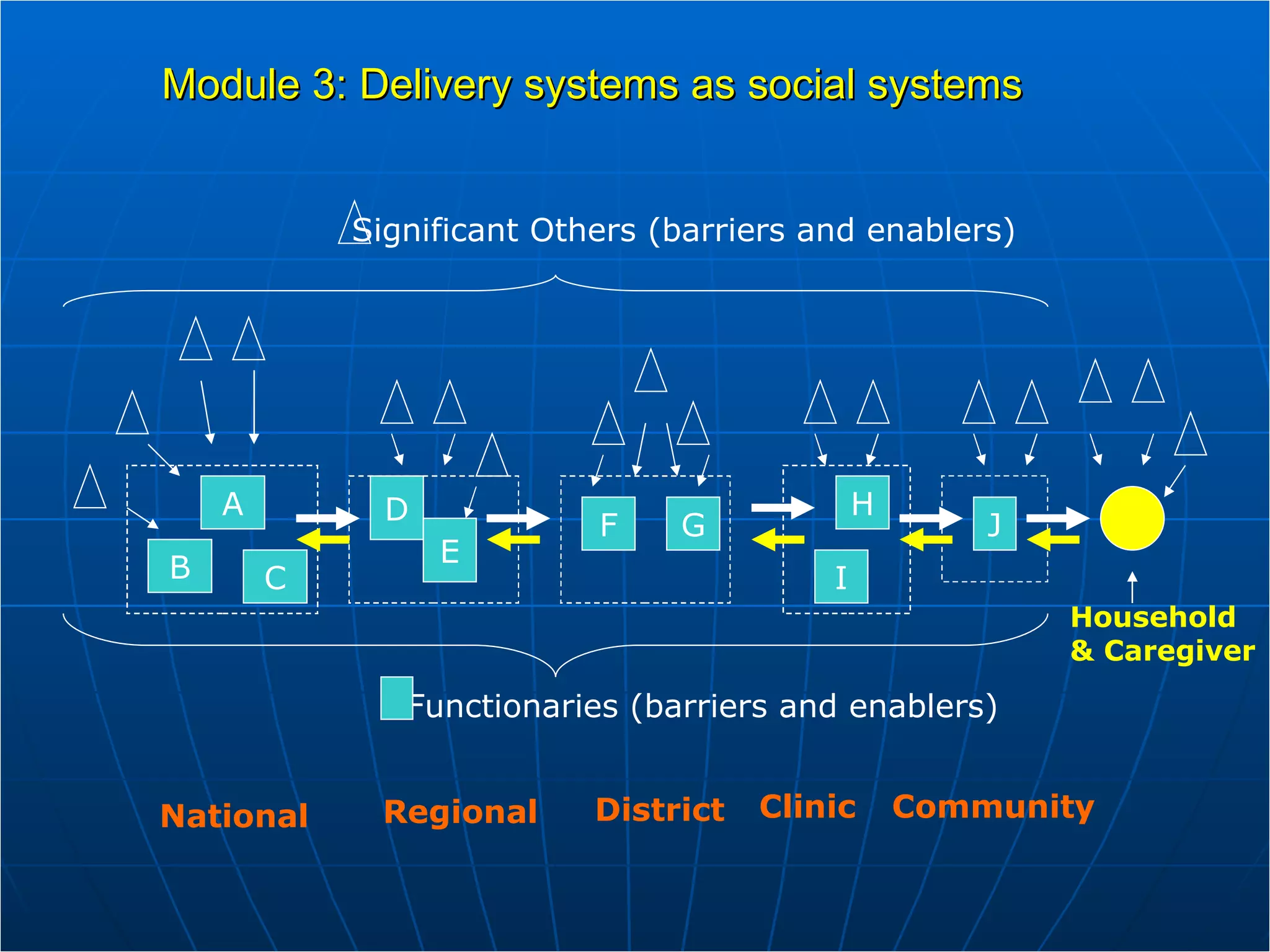
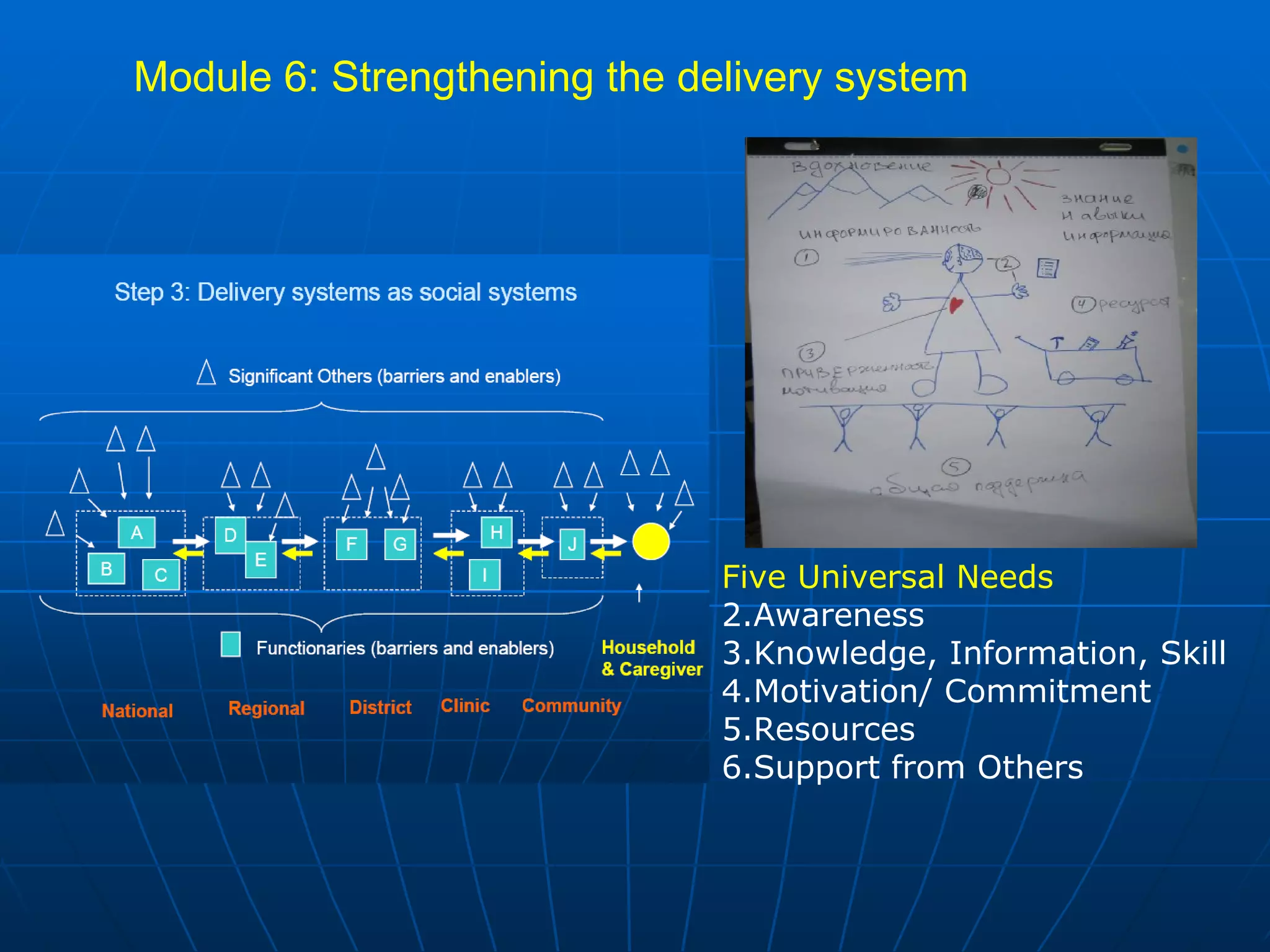
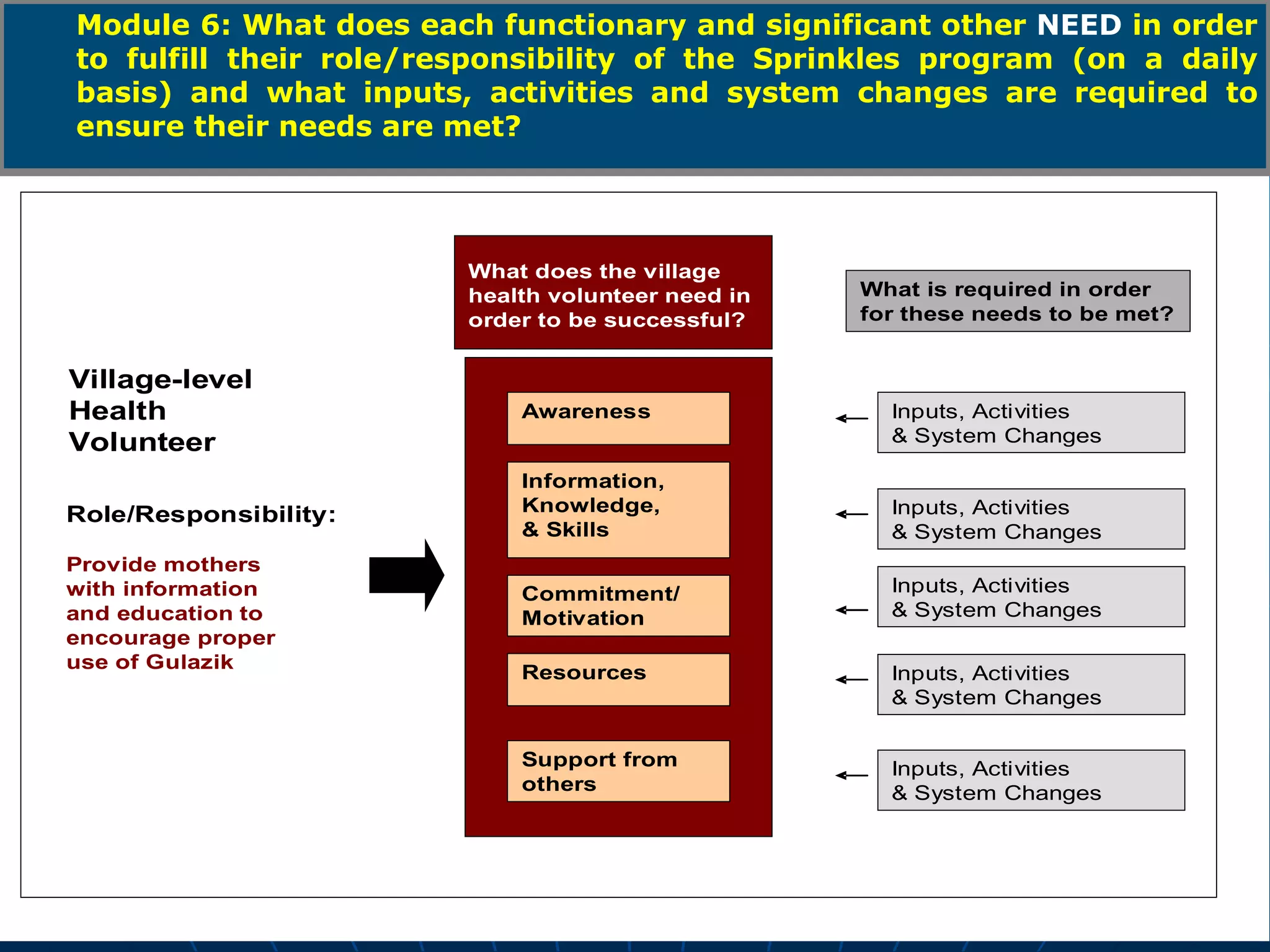
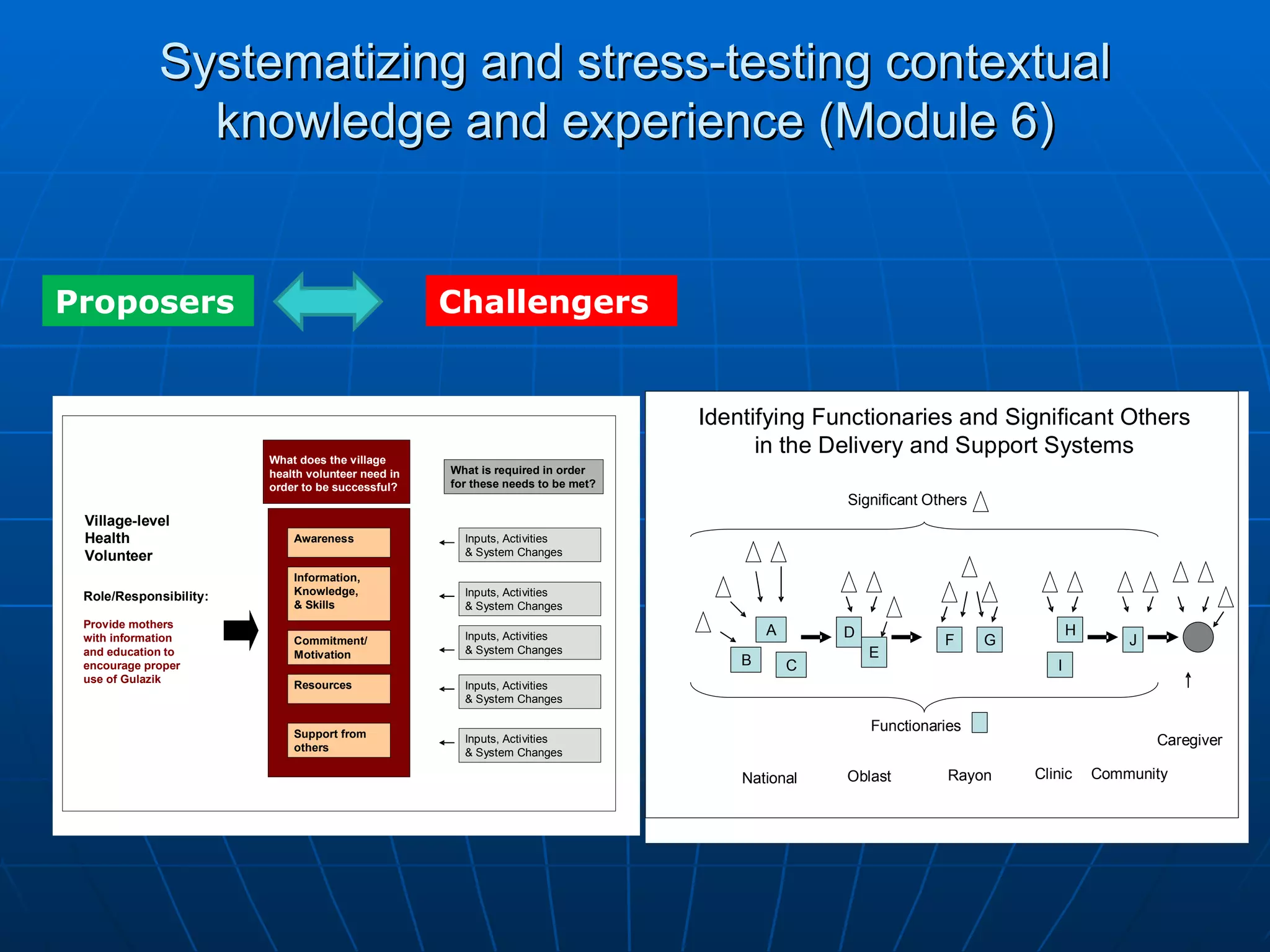
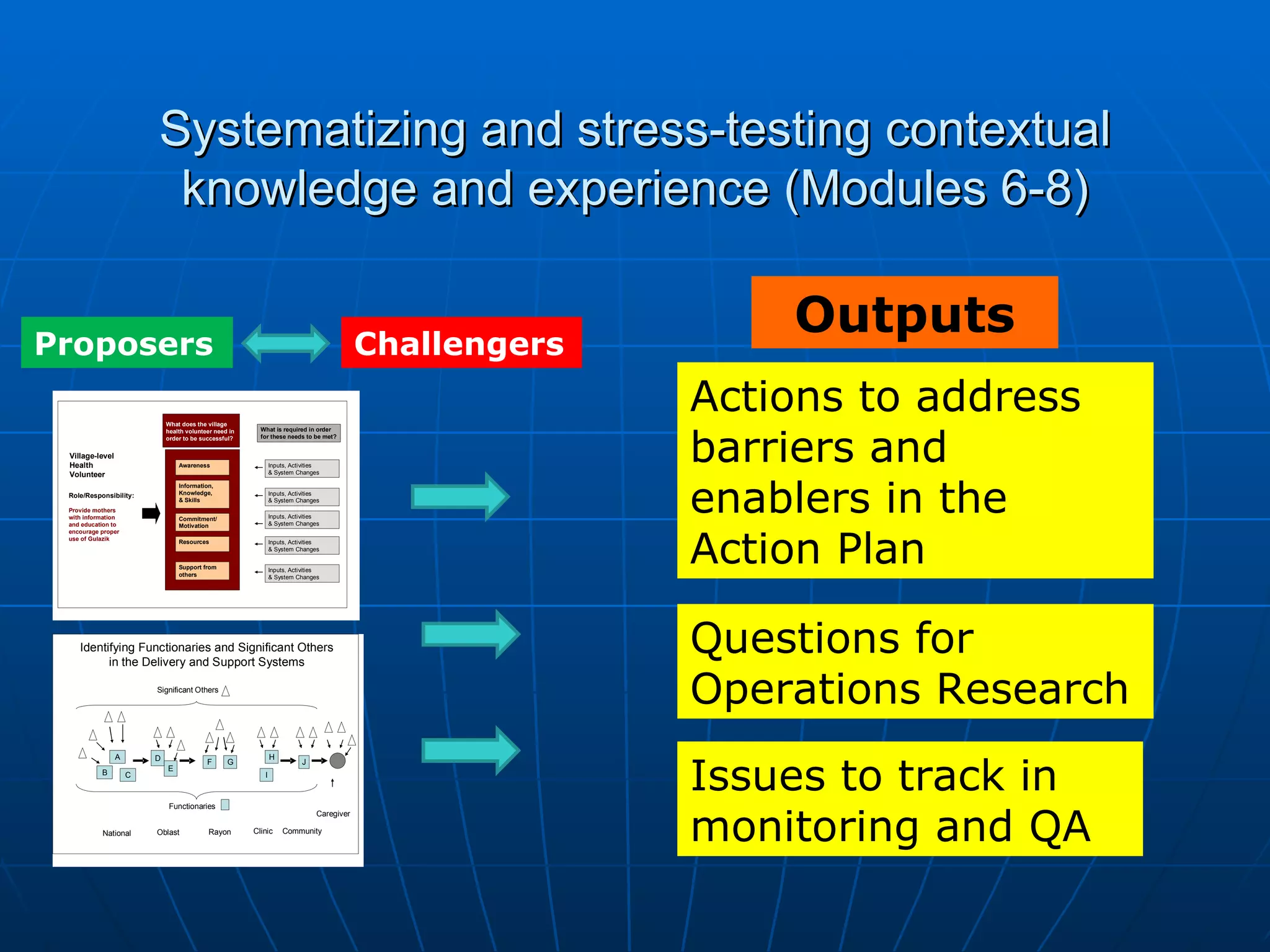
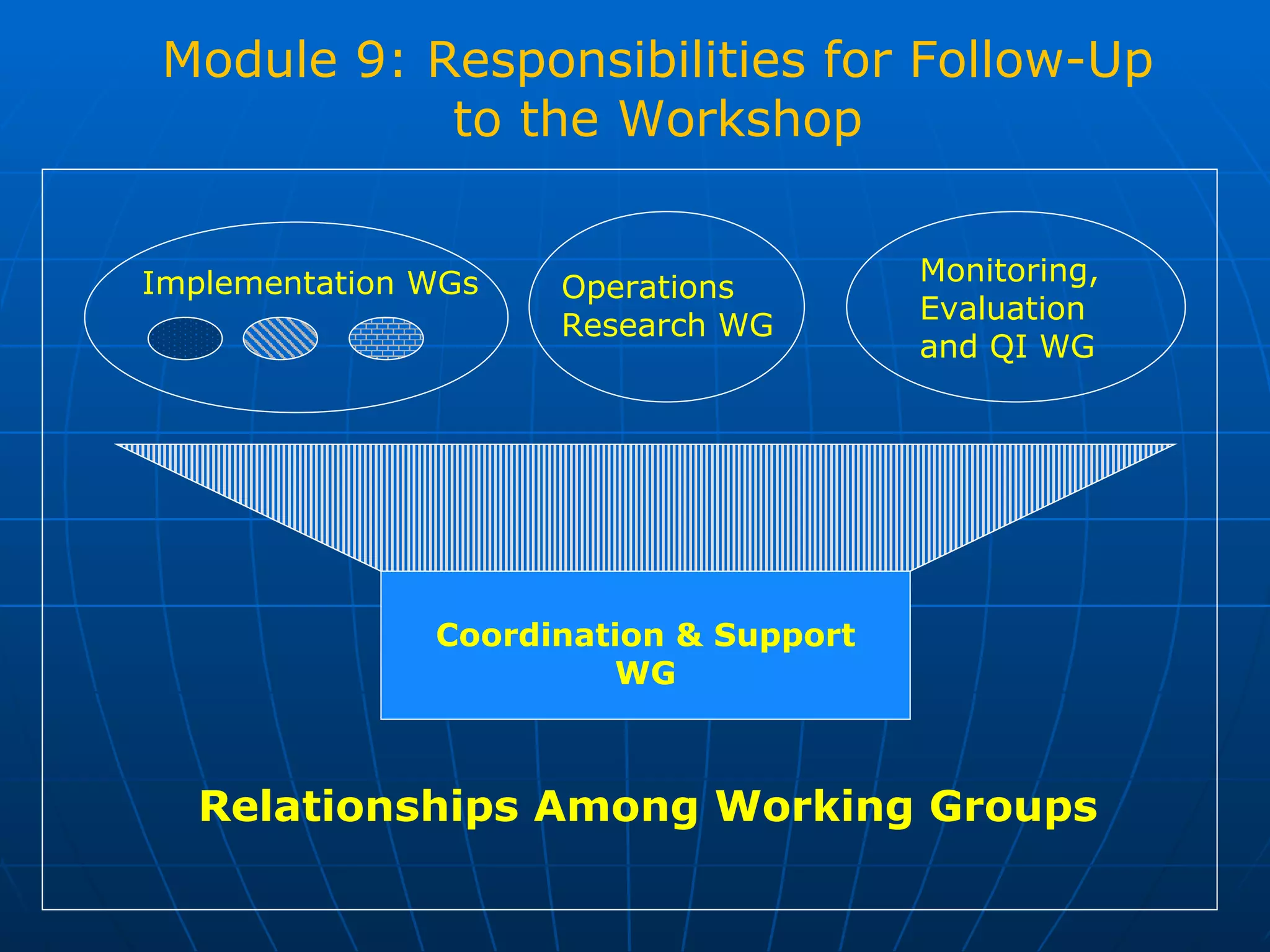
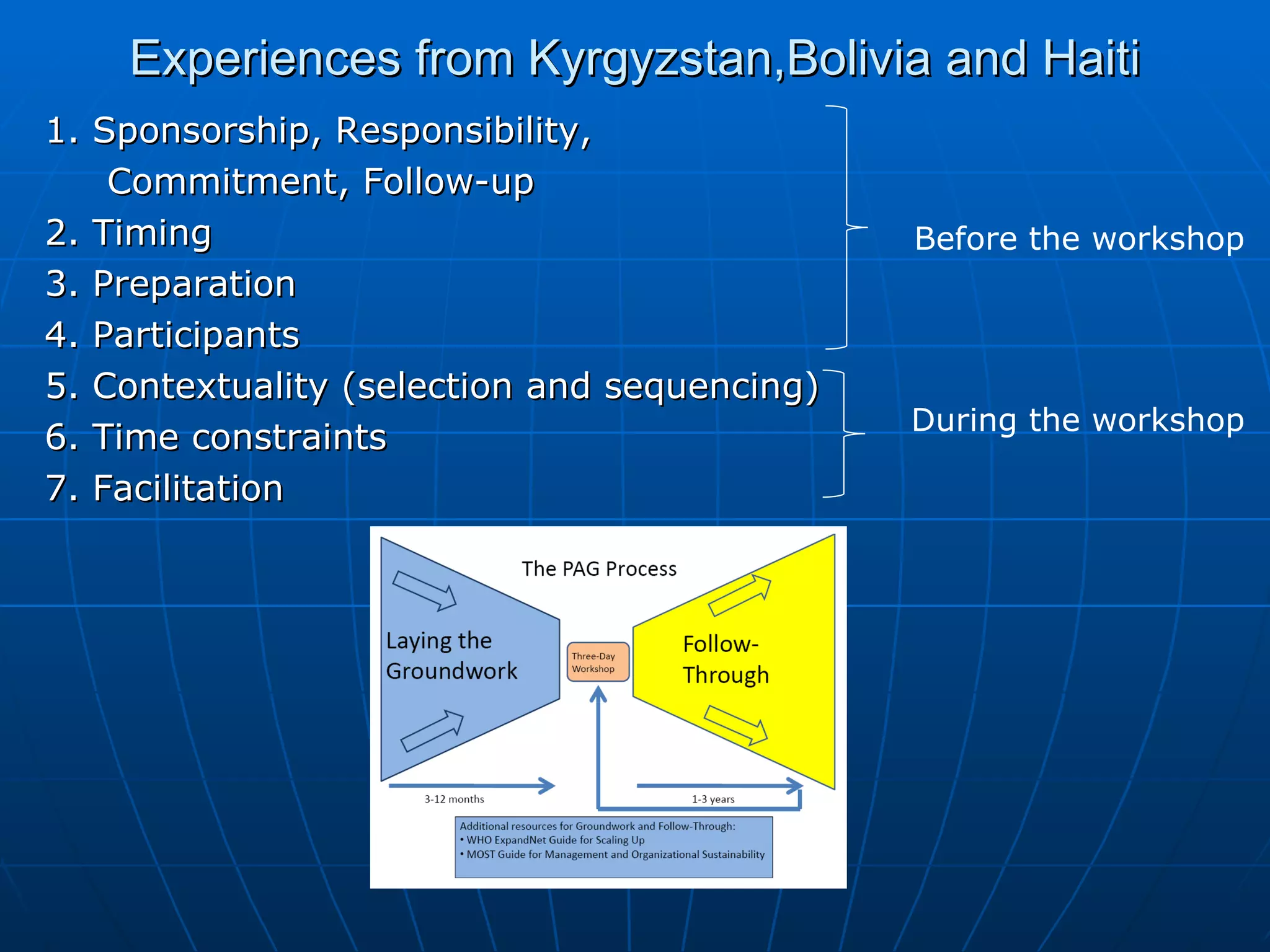
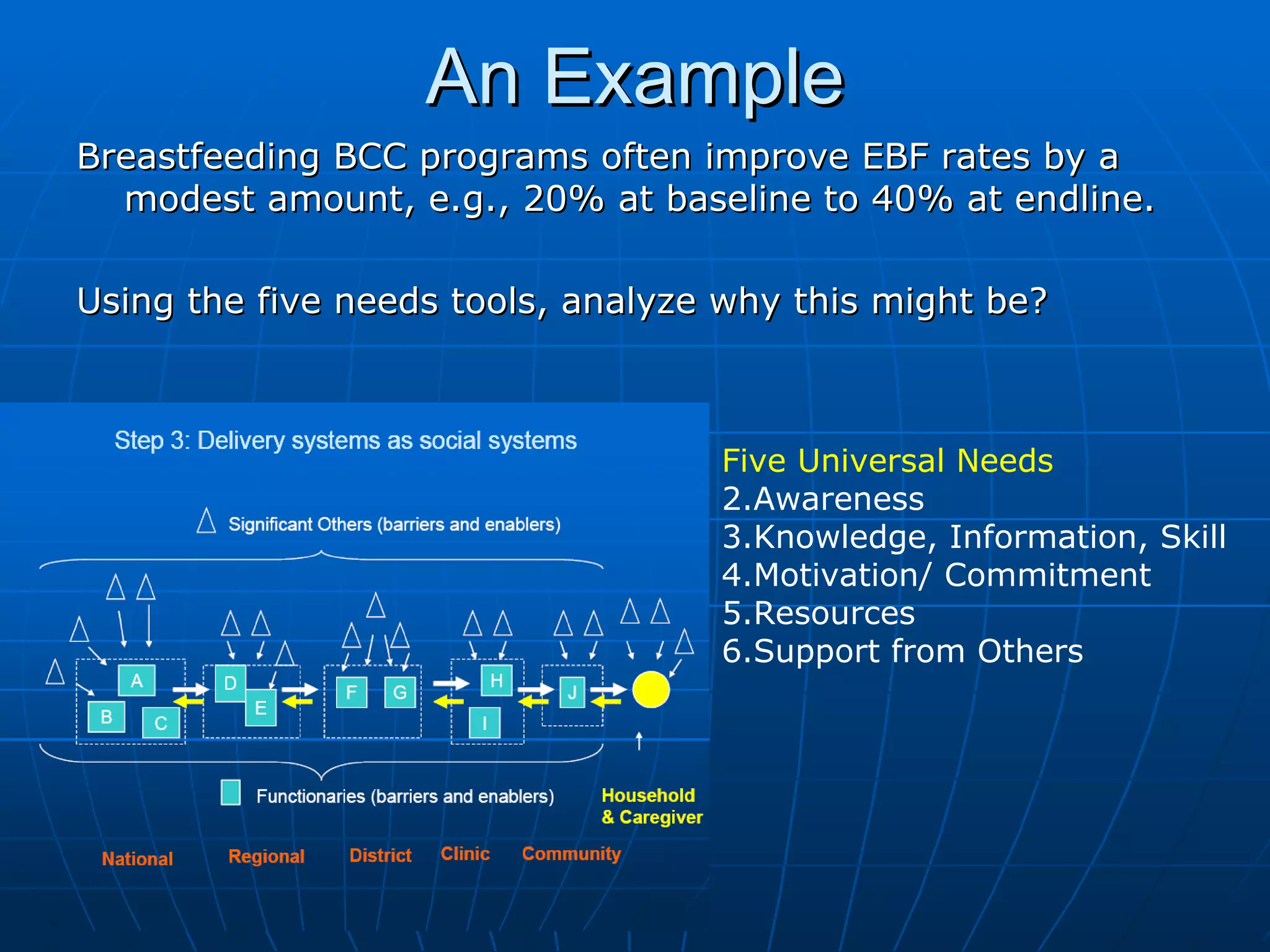
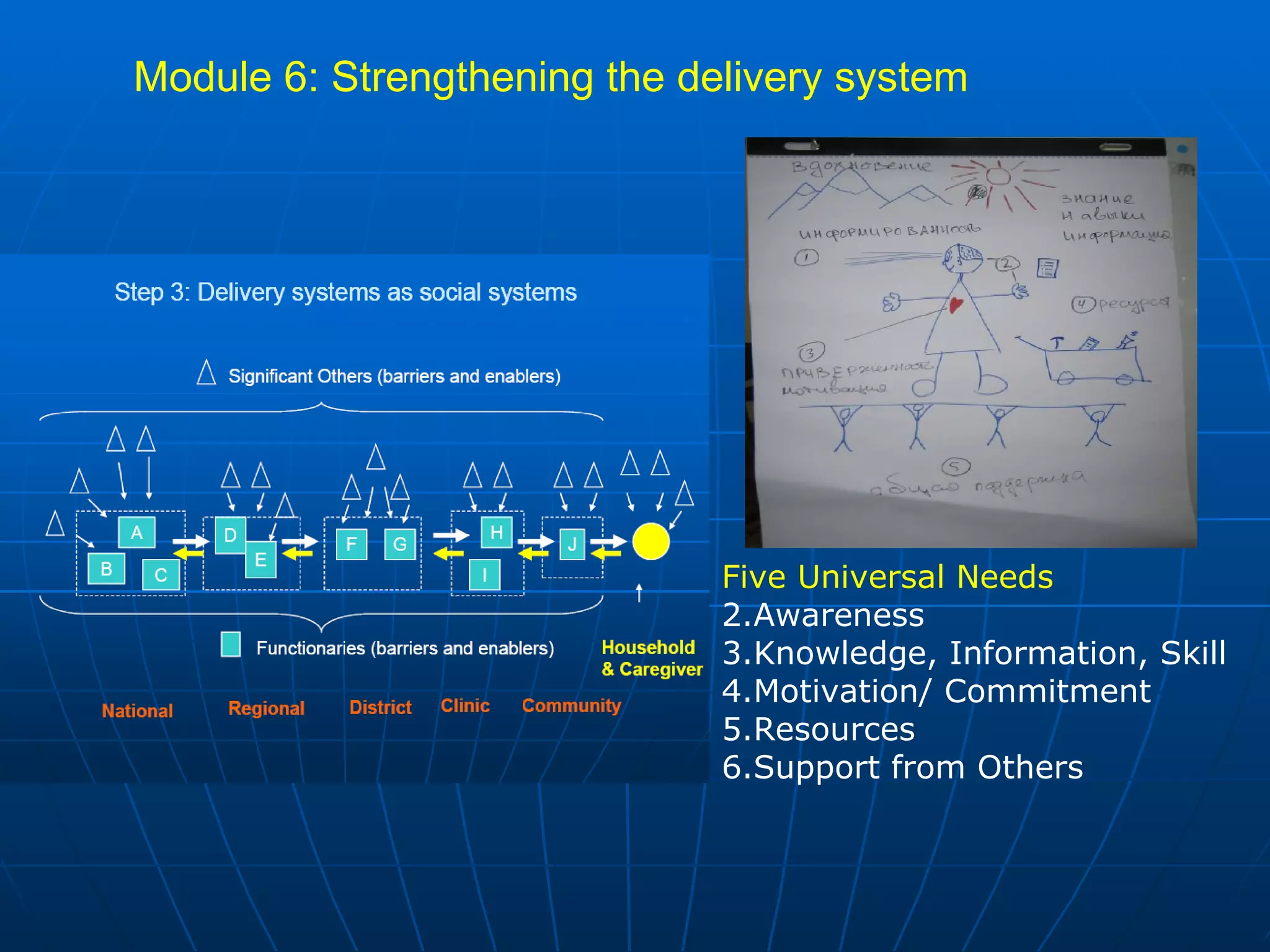
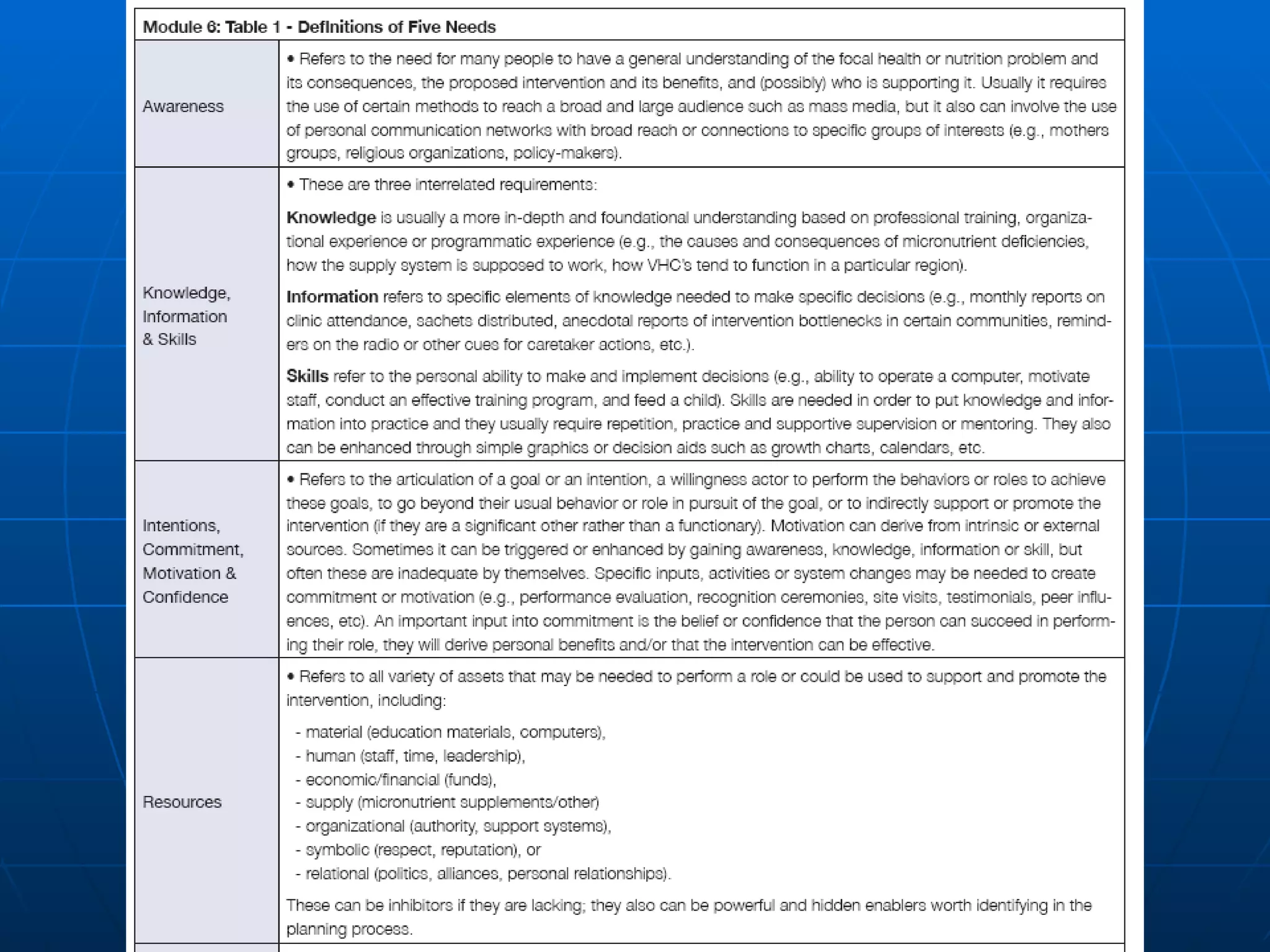
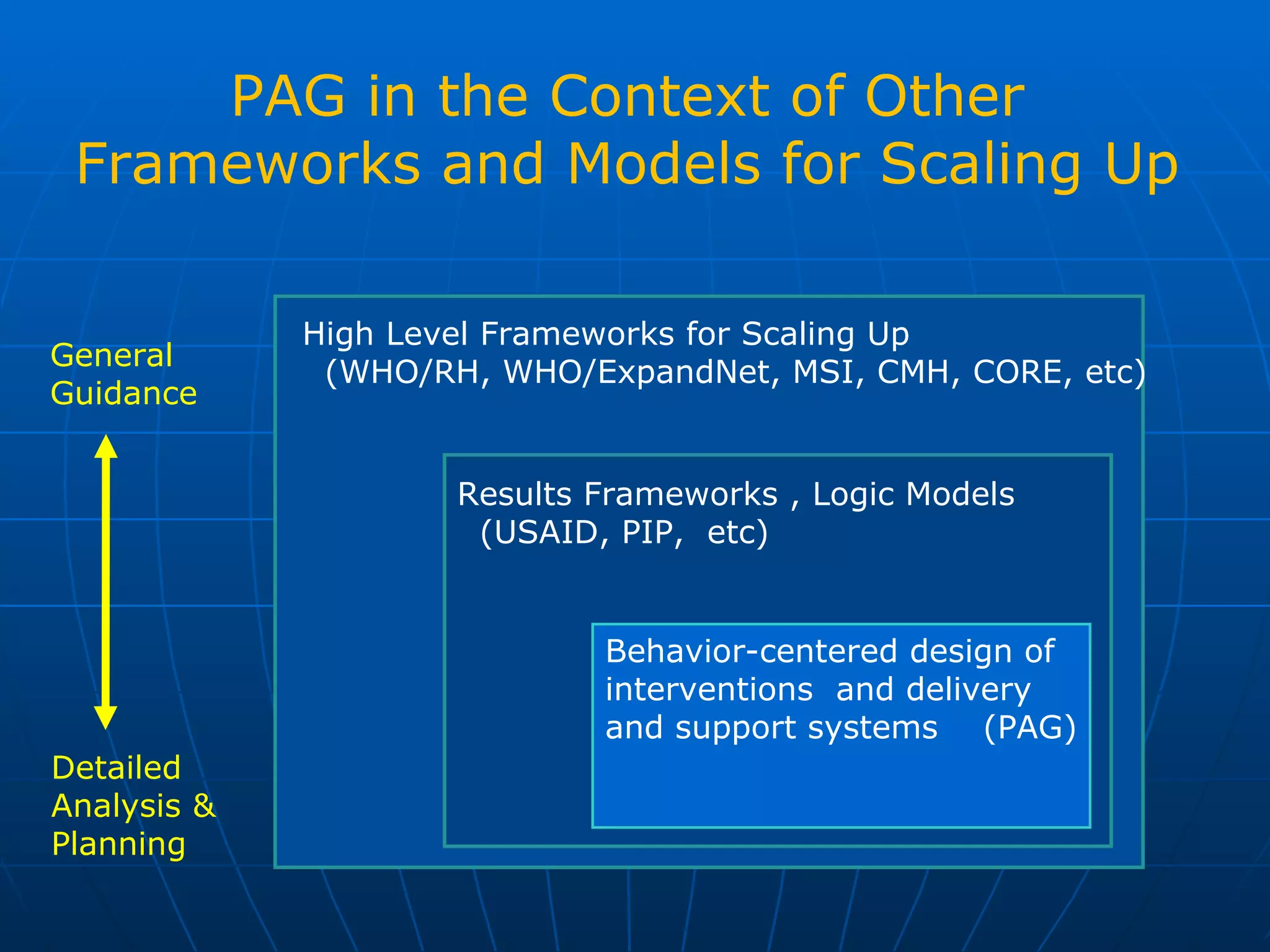
The PAG consists of nine modules that guide users through assessing problems and solutions, goals, delivery systems, populations, roles and responsibilities, strengthening interventions, building support systems, monitoring and evaluation, and management. Key features include analyzing delivery systems as social