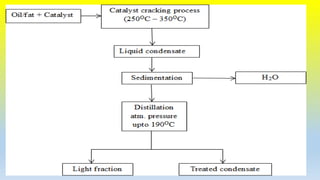
There are four main methods to produce biodiesel from vegetable oils and animal fats: direct use and blending, transesterification, pyrolysis, and microemulsions. Transesterification is the most common process, which uses a catalyst like sodium hydroxide to react triglycerides with alcohol, producing biodiesel and glycerin. Pyrolysis involves thermal cracking of oils at 250-350°C to reduce viscosity. Microemulsions create a stable mixture of oil, water, and surfactant to improve properties. Biodiesel has benefits over petroleum diesel like being renewable, having lower emissions, and similar fuel characteristics.