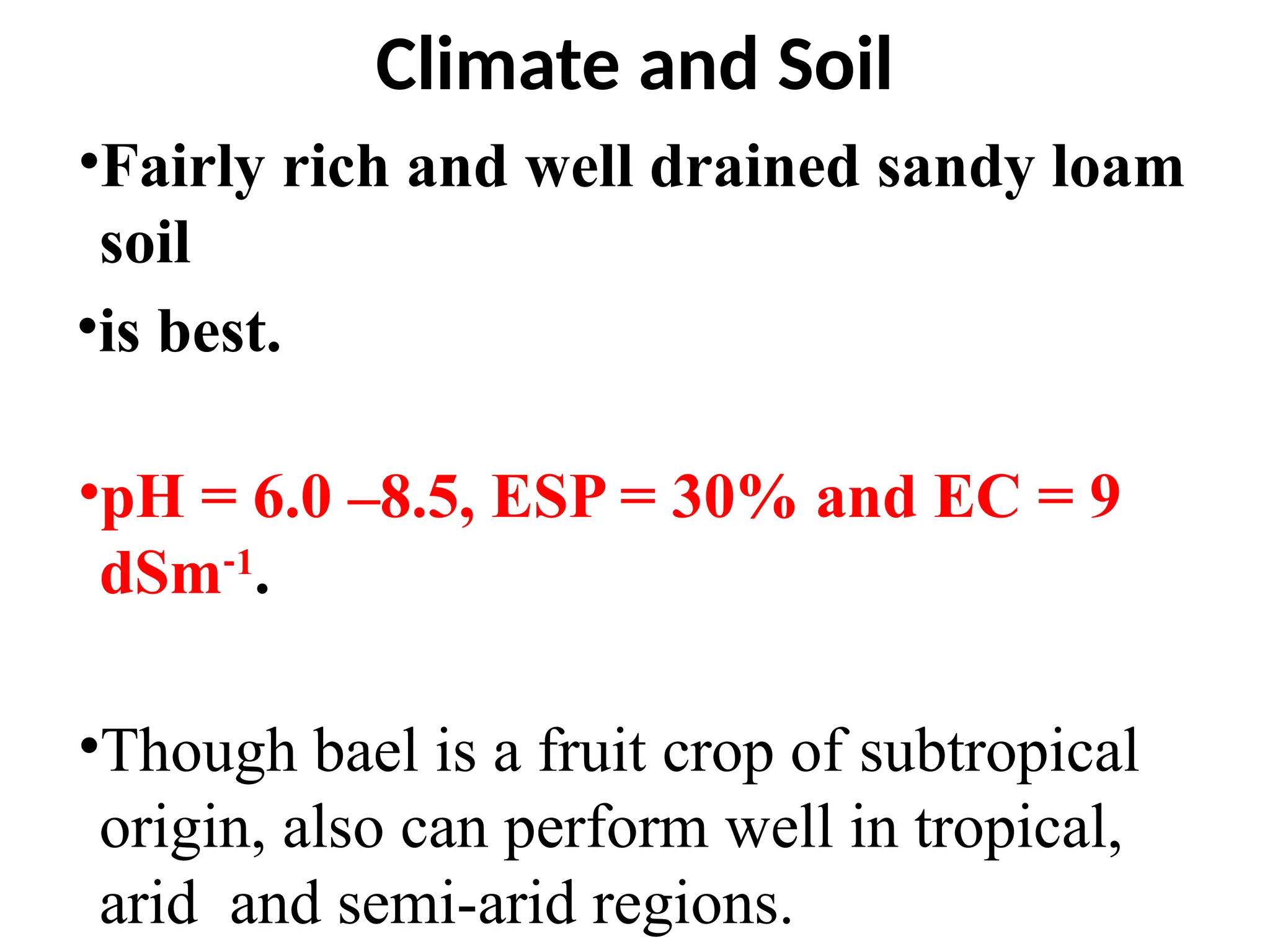
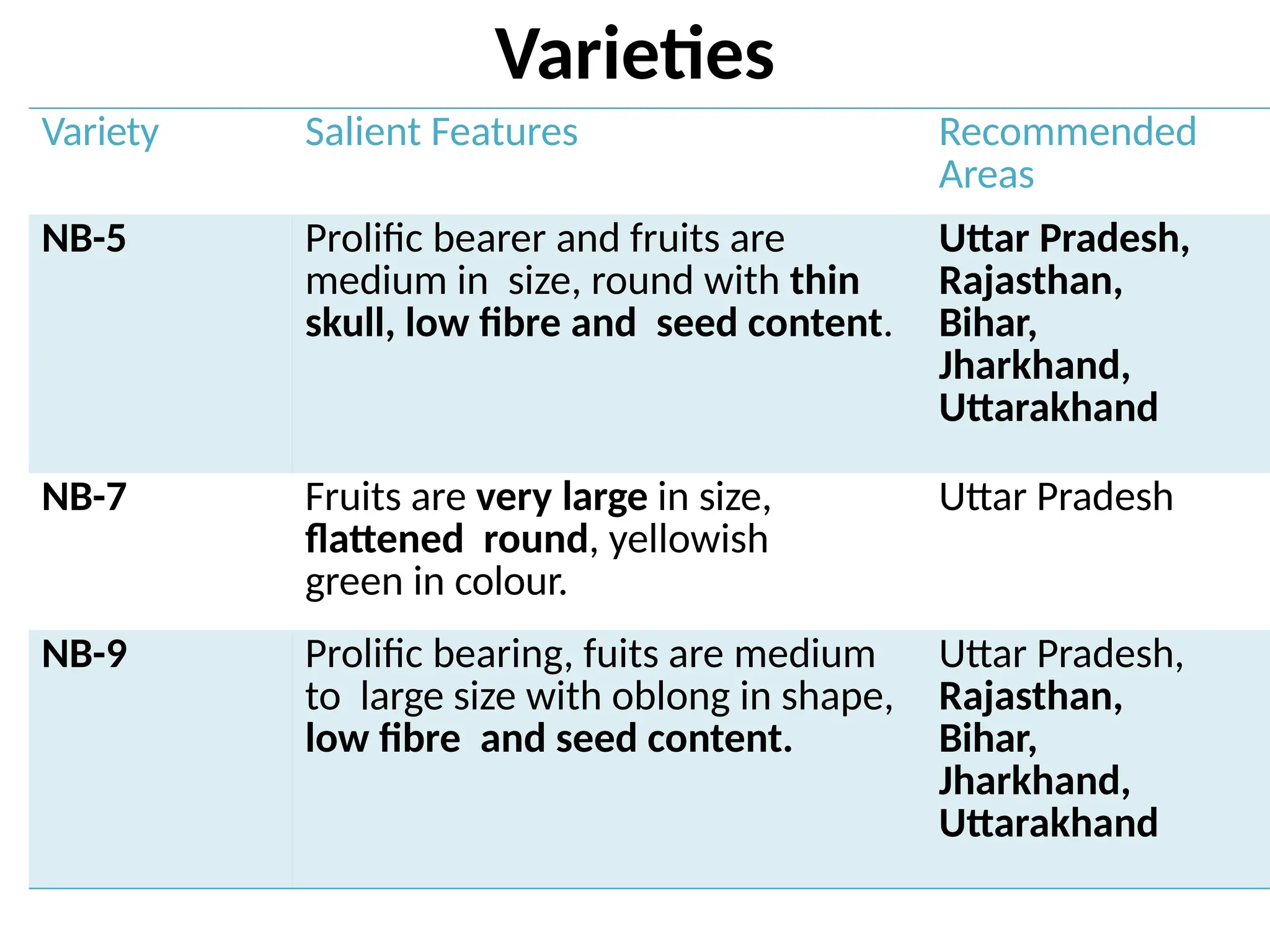
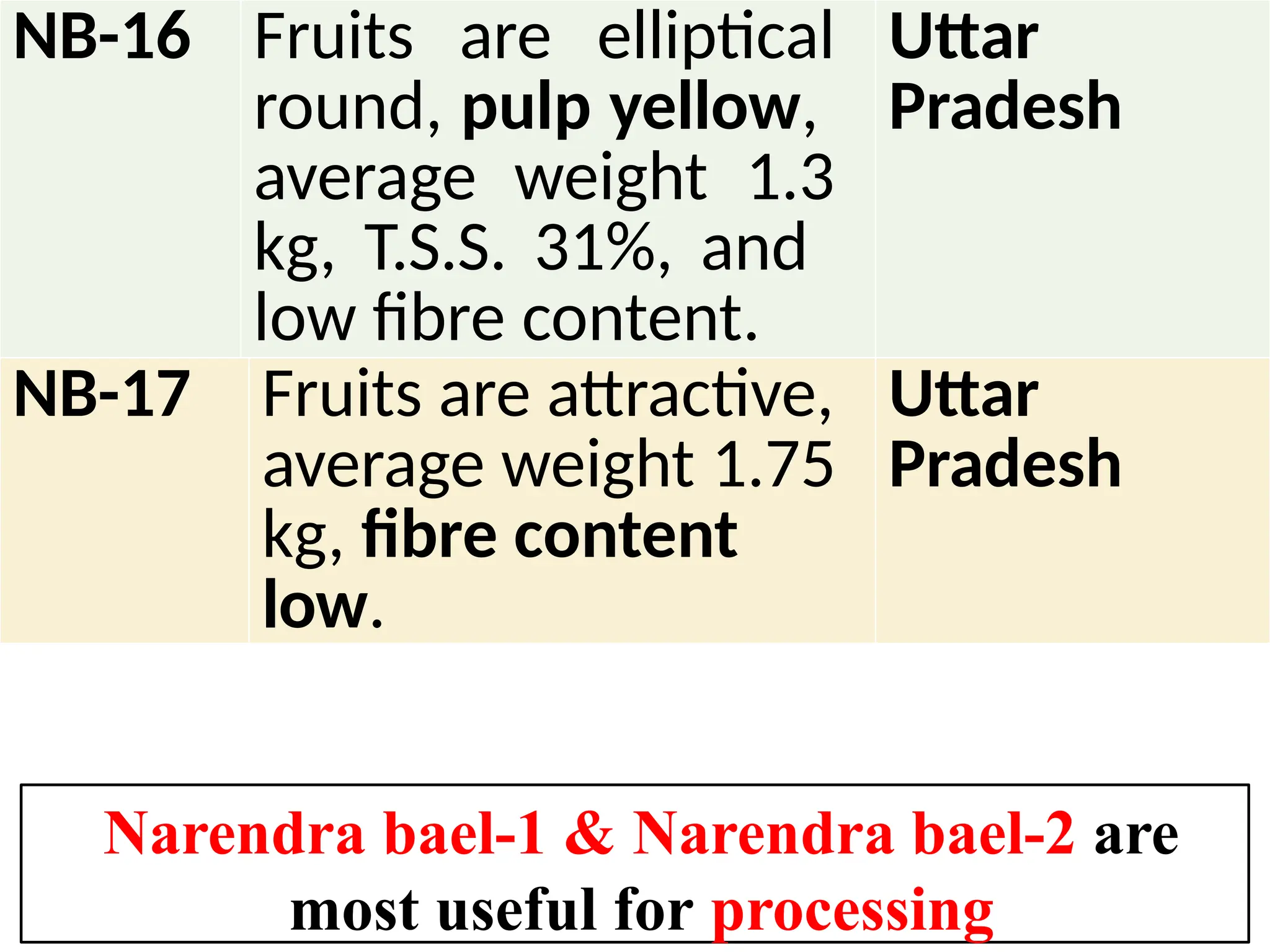
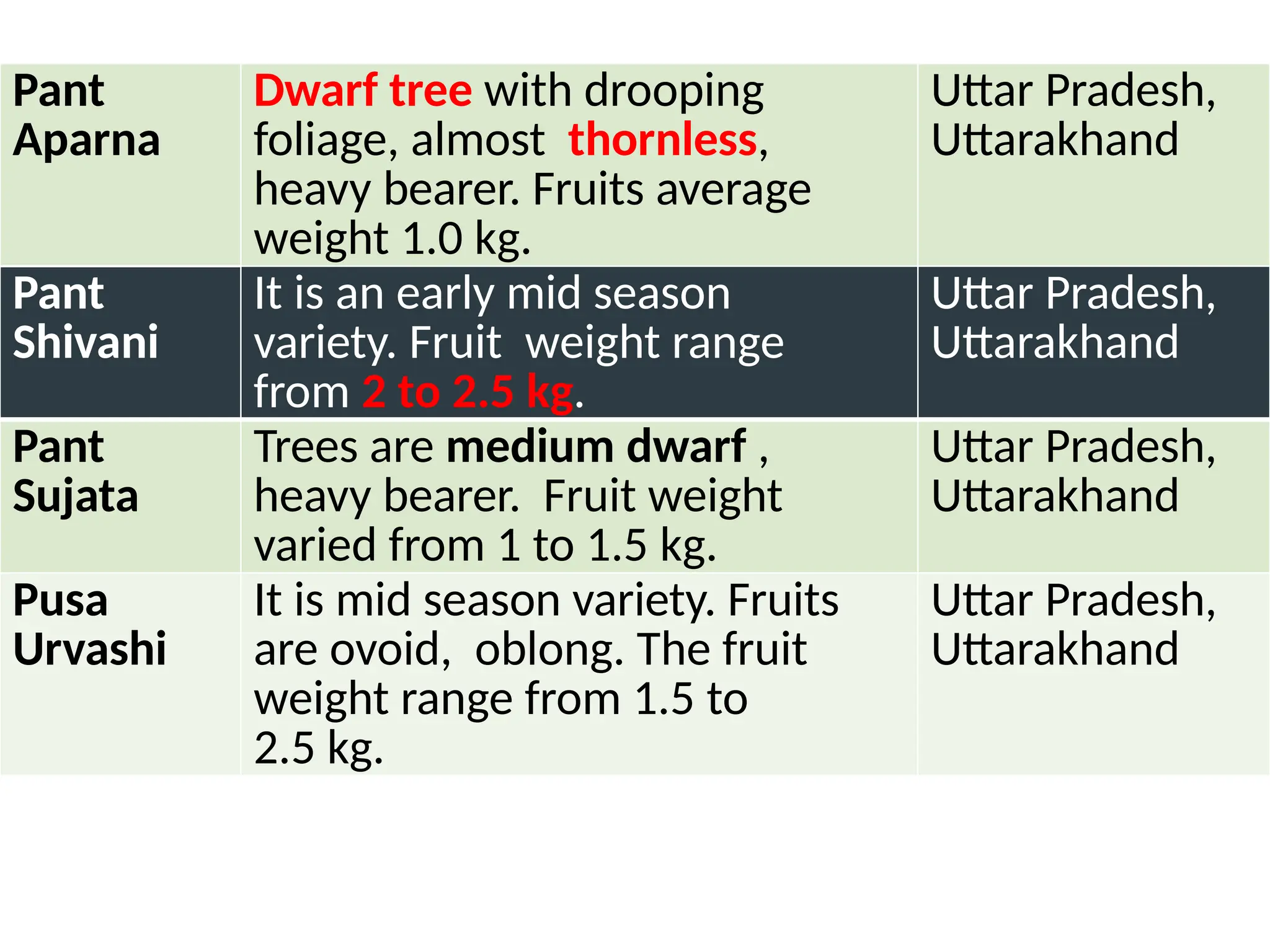
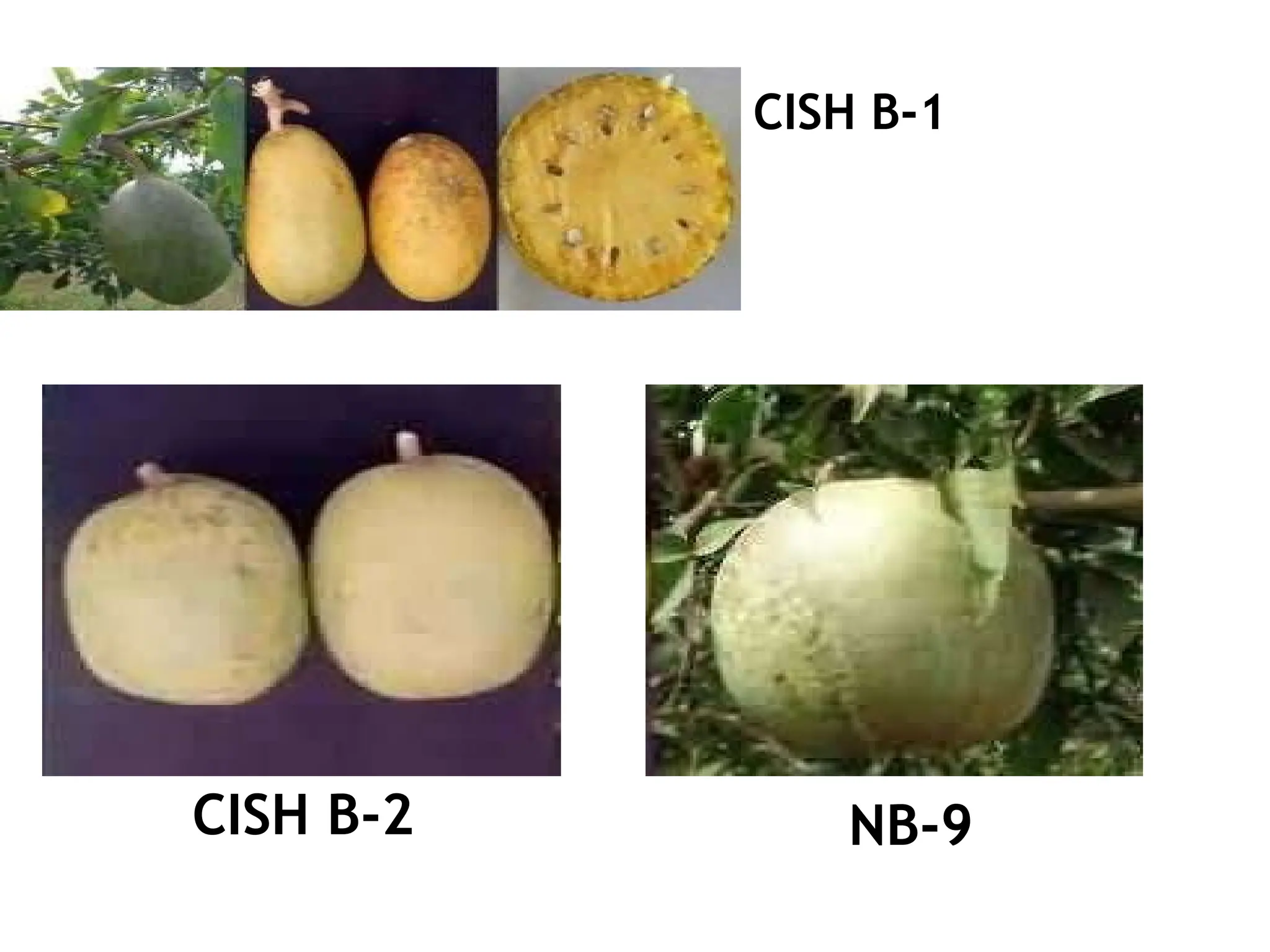
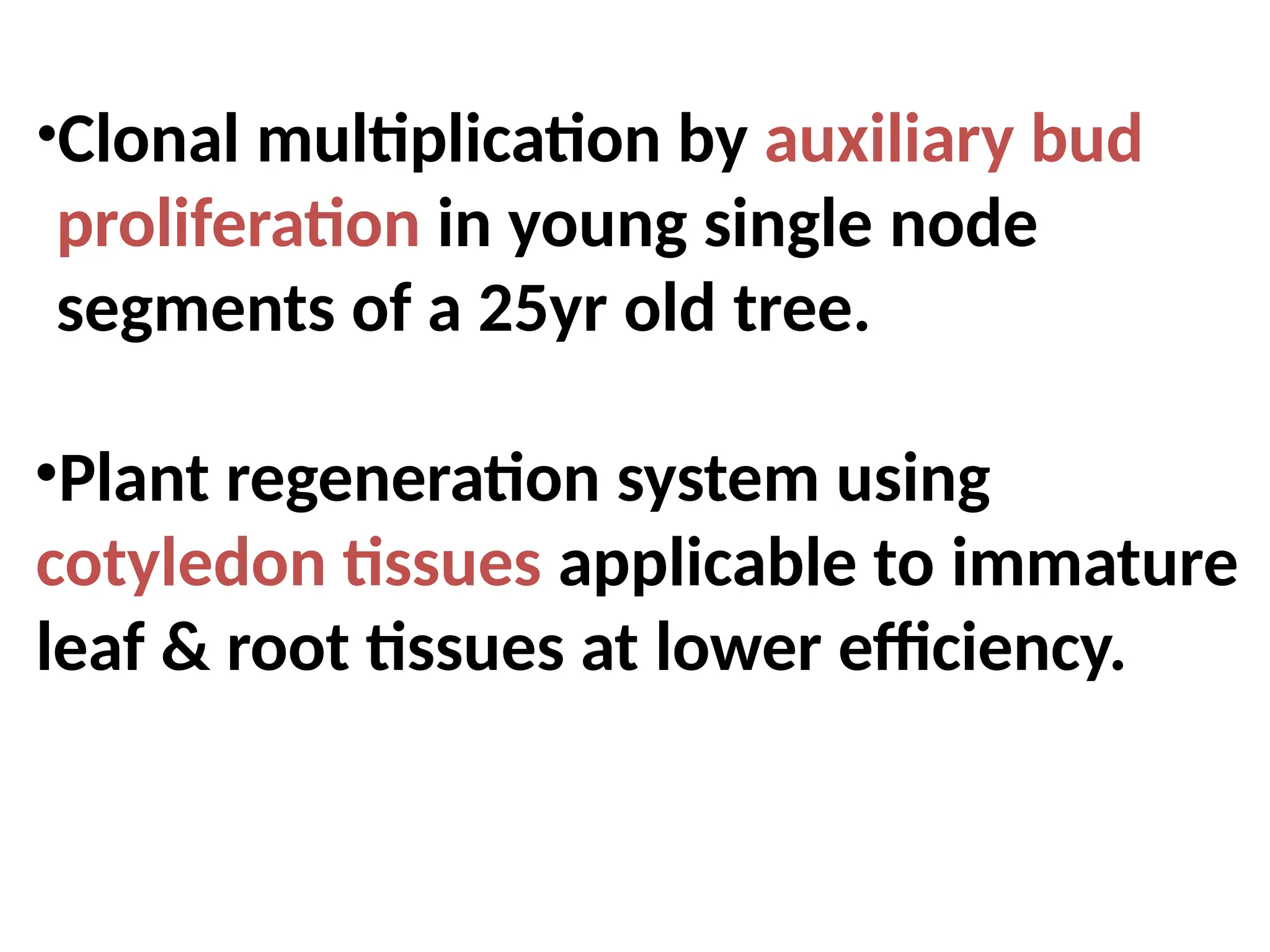
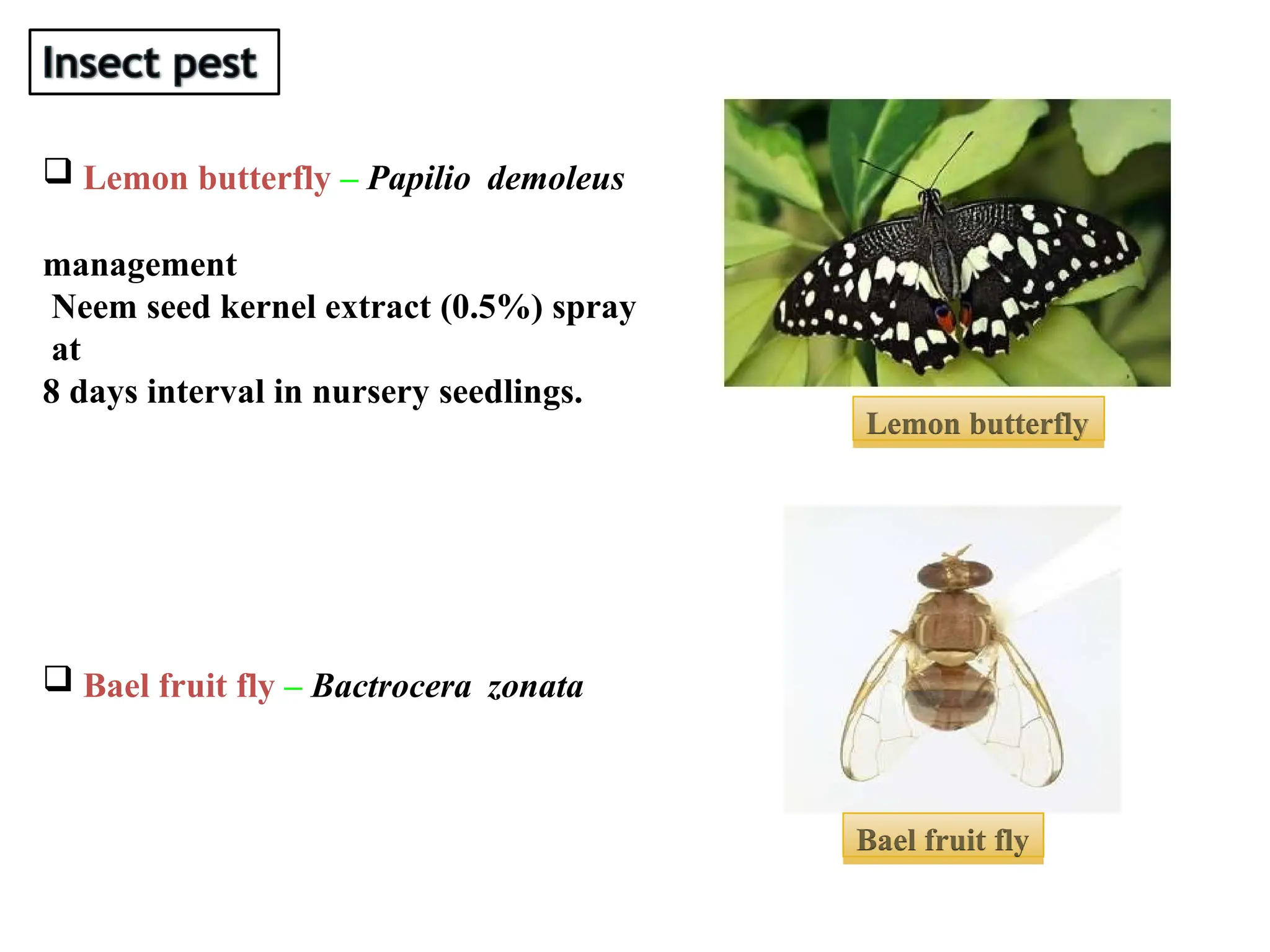
The document discusses the production technology of the bael fruit, including its botanical characteristics, climate requirements, and various medicinal uses. It outlines different varieties, propagation methods, nutrient and water management practices, and aftercare for cultivation. Additionally, it addresses potential issues like fruit drop, cracking, and diseases, along with management strategies.