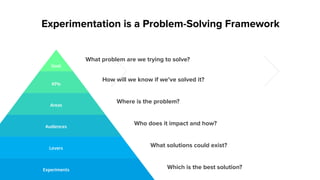
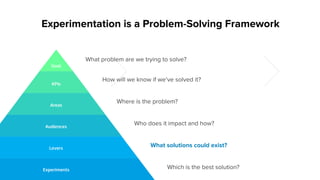
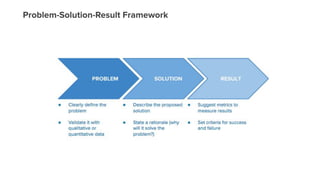
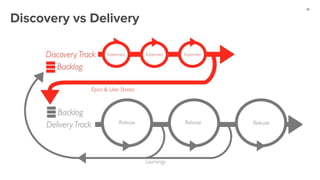
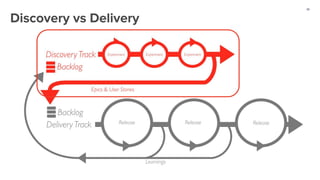
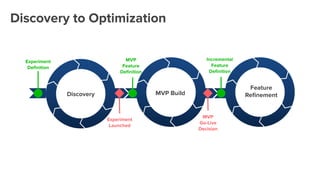
The document outlines a masterclass on forming strong hypotheses for product experimentation, led by Jason G'sell, who has extensive experience in customer education and training. Key points include using direct and indirect data to identify user problems, formulating clear problem statements, and validating these with data. The webinar aims to teach participants how to craft hypotheses that address defined user issues and leverage experimentation as a problem-solving framework.