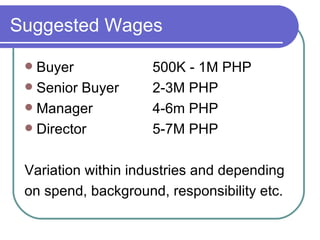
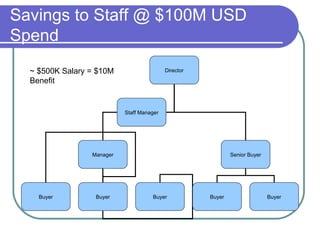
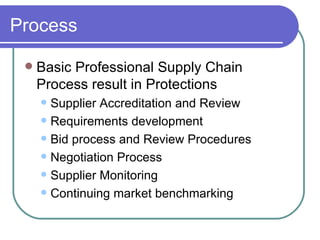
This document discusses procurement fraud and provides definitions, frameworks, and strategies for organizations to prevent and detect fraud. It outlines that procurement fraud involves intentional deception to obtain an unlawful advantage. It then discusses how fraud occurs at the organizational, personal, and process levels and provides warning signs. Finally, it recommends professionalizing the procurement process through training, compensation, and establishing standard procedures while also conducting periodic reviews and using outside help to detect potential fraud.