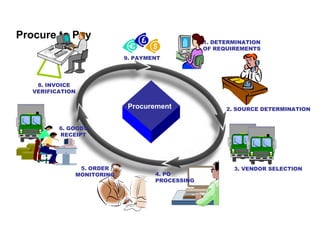
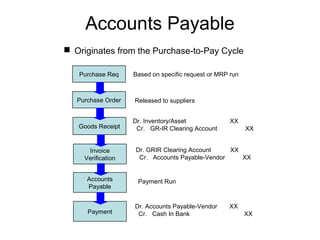
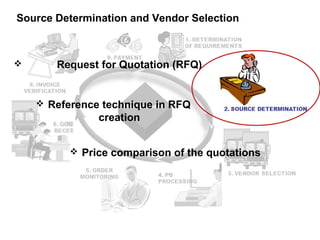
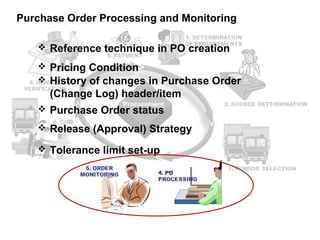
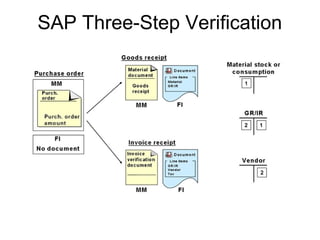
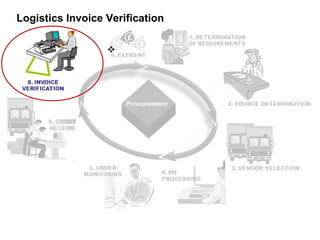
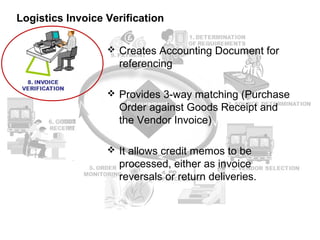
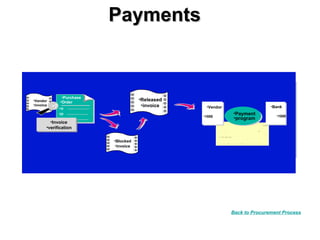
The procure to pay process involves 9 steps: 1) determining requirements, 2) sourcing, 3) vendor selection, 4) purchase order processing, 5) order monitoring, 6) goods receipt, 7) invoice verification, 8) payment verification, and 9) payment. The process tracks requirements and ensures accurate matching between purchase orders, goods receipts, and invoices. It allows efficient payment of vendor invoices and updating of accounting records.