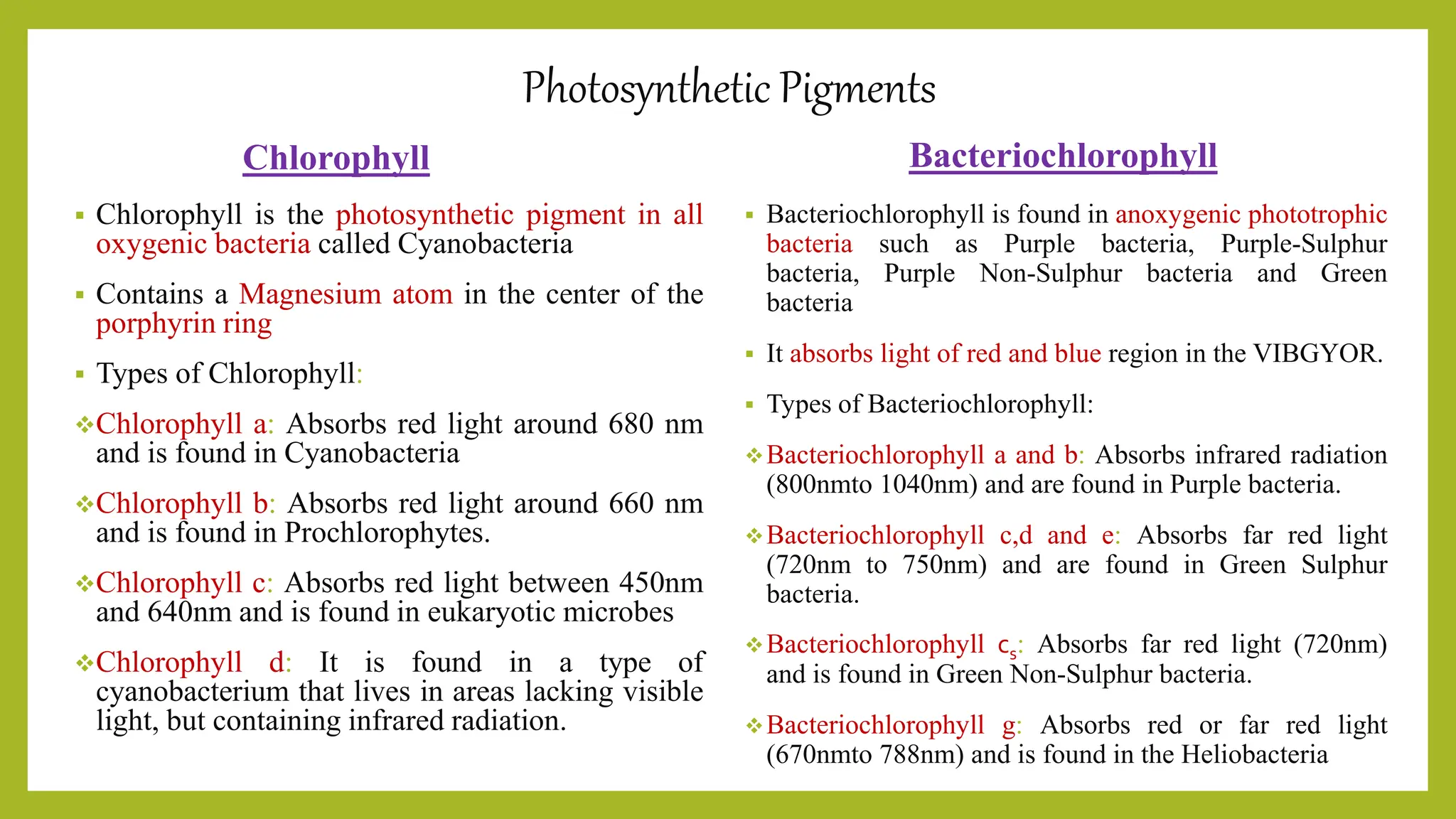
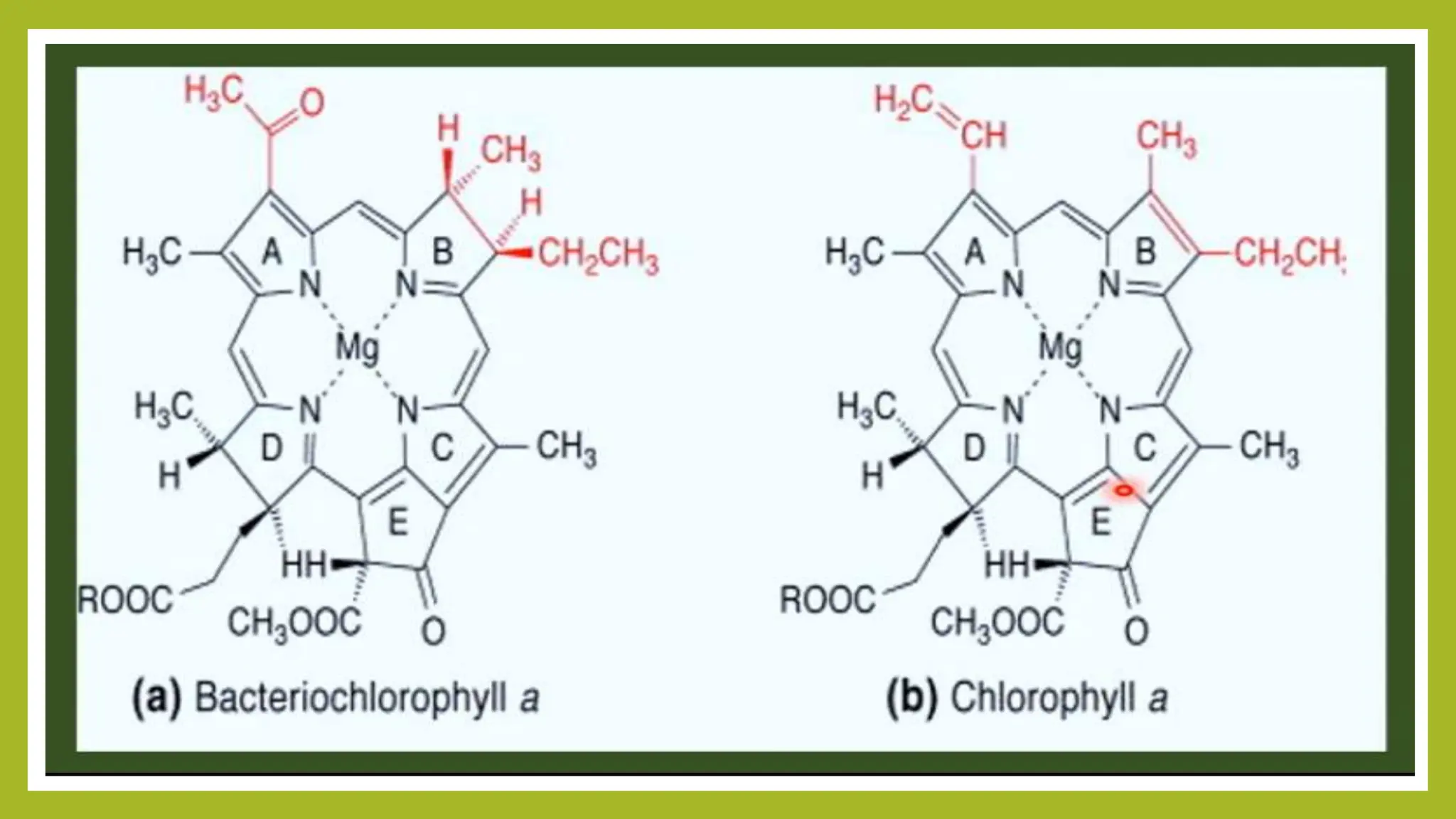
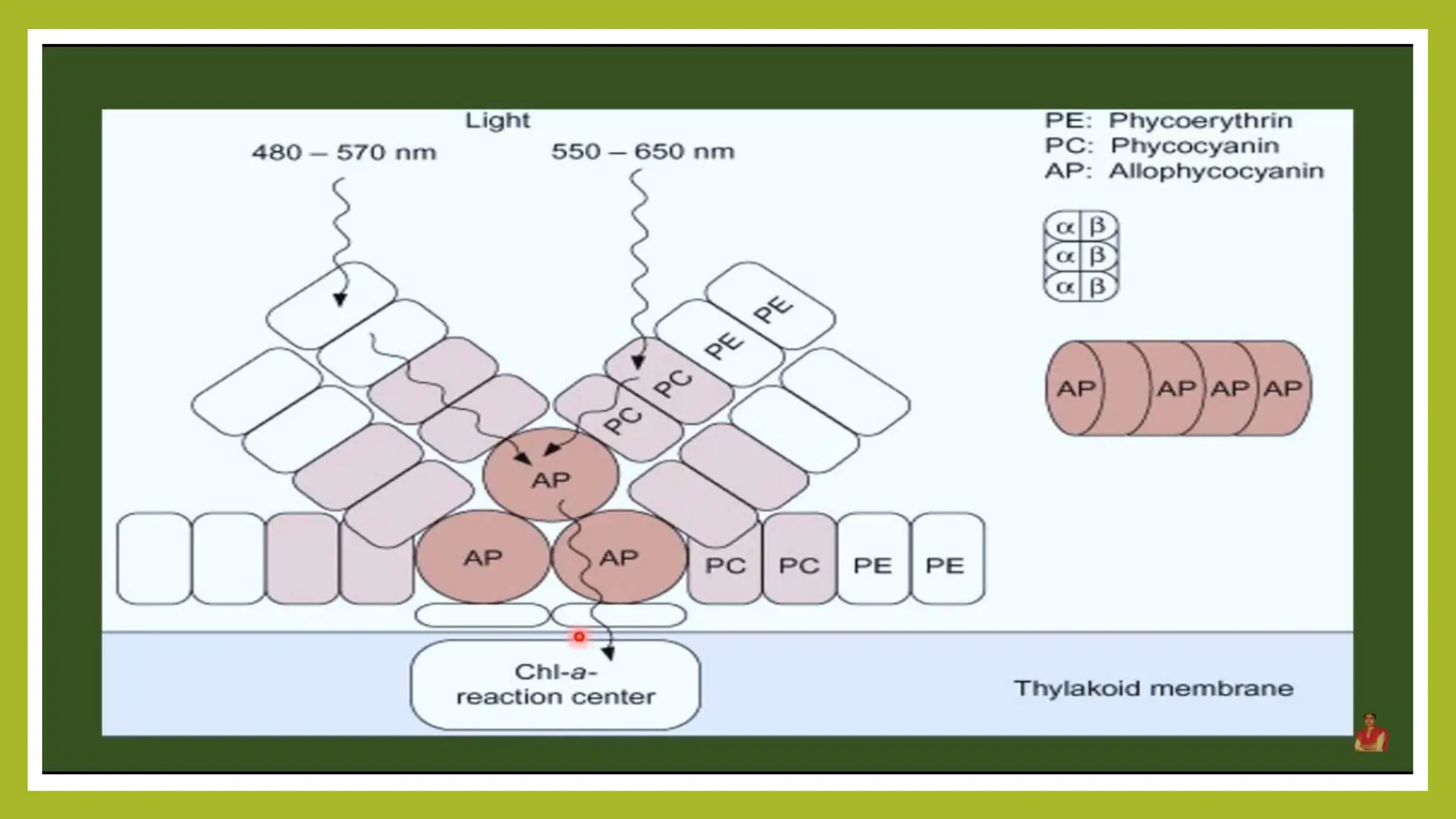
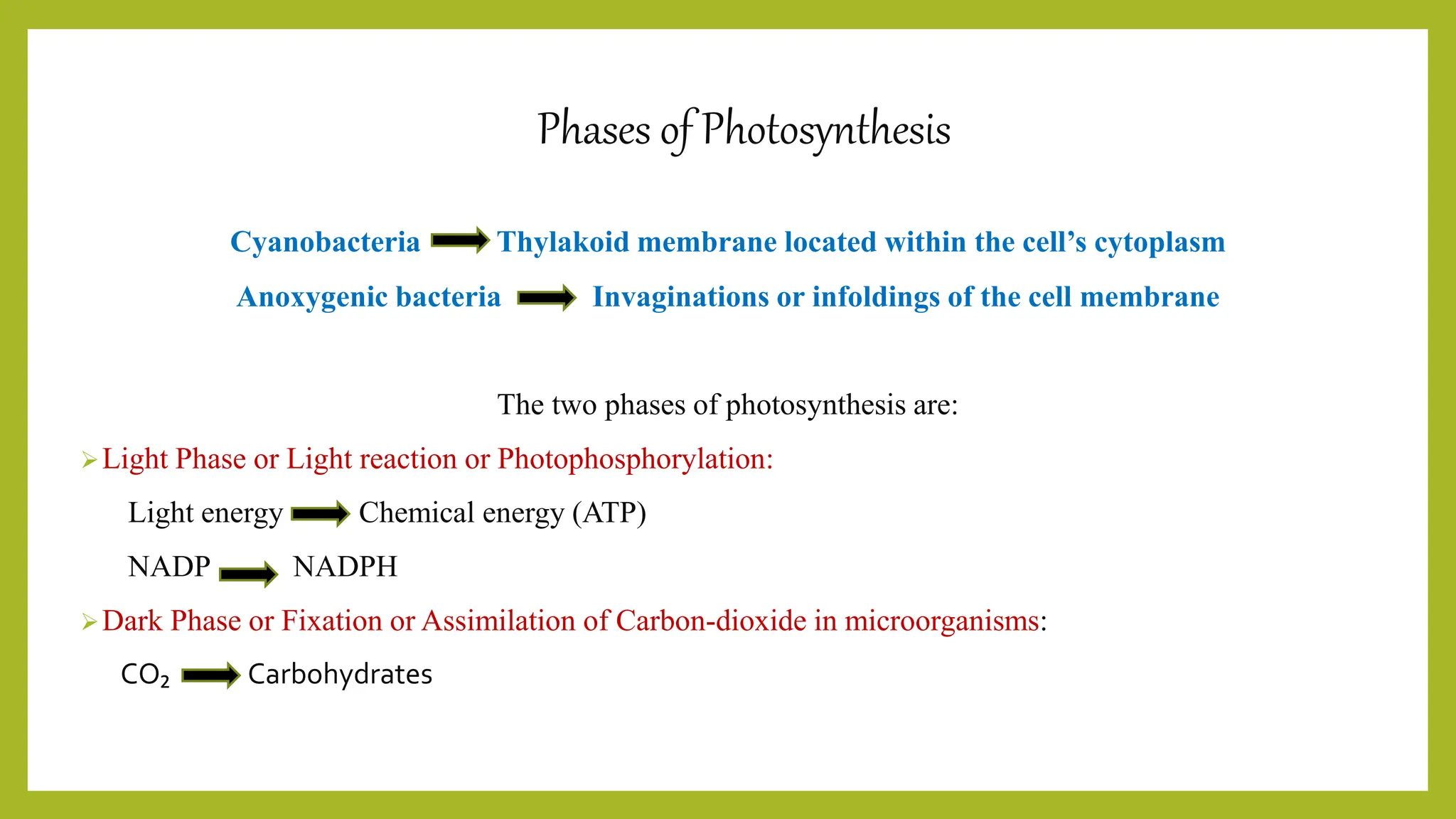
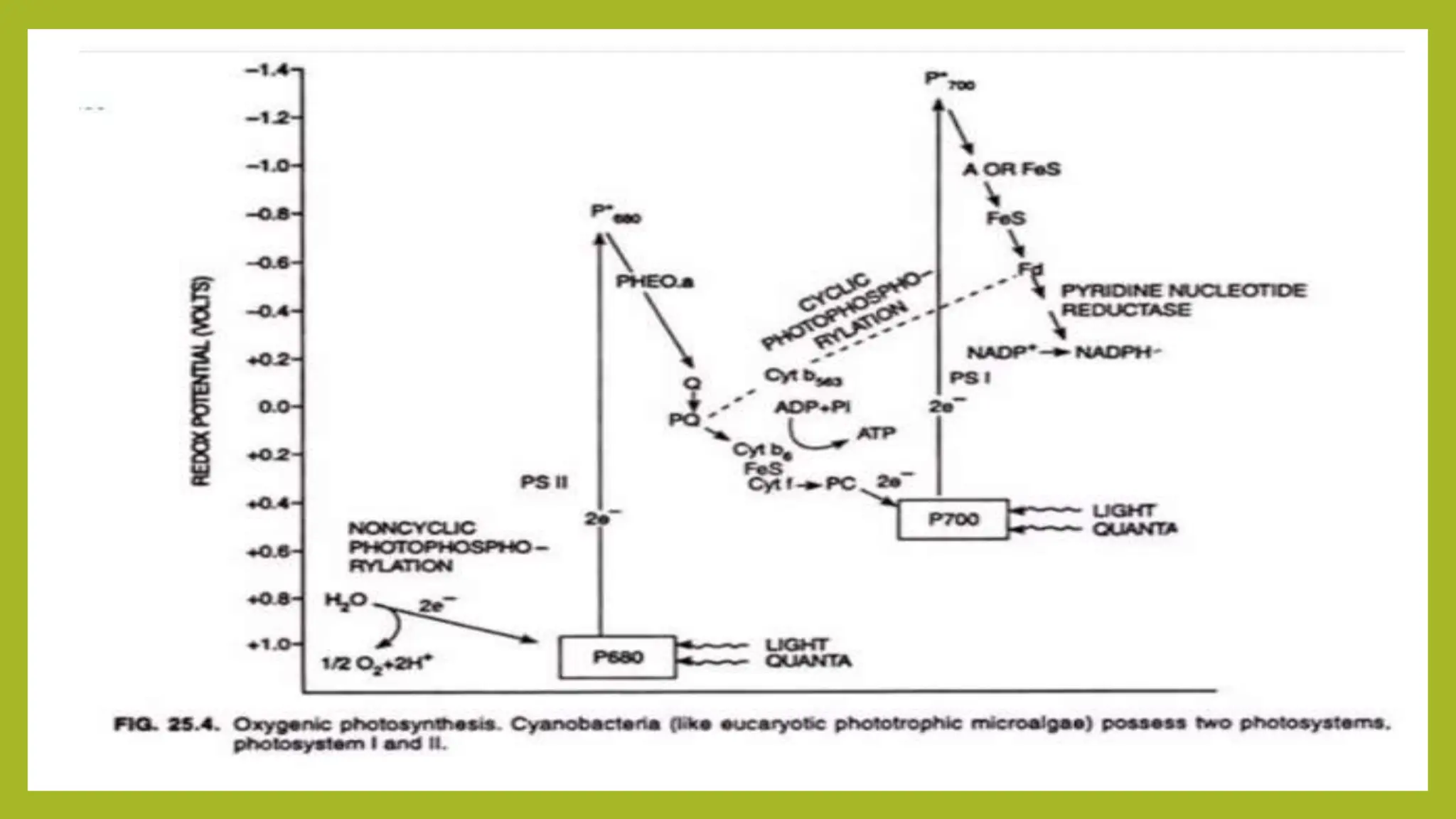
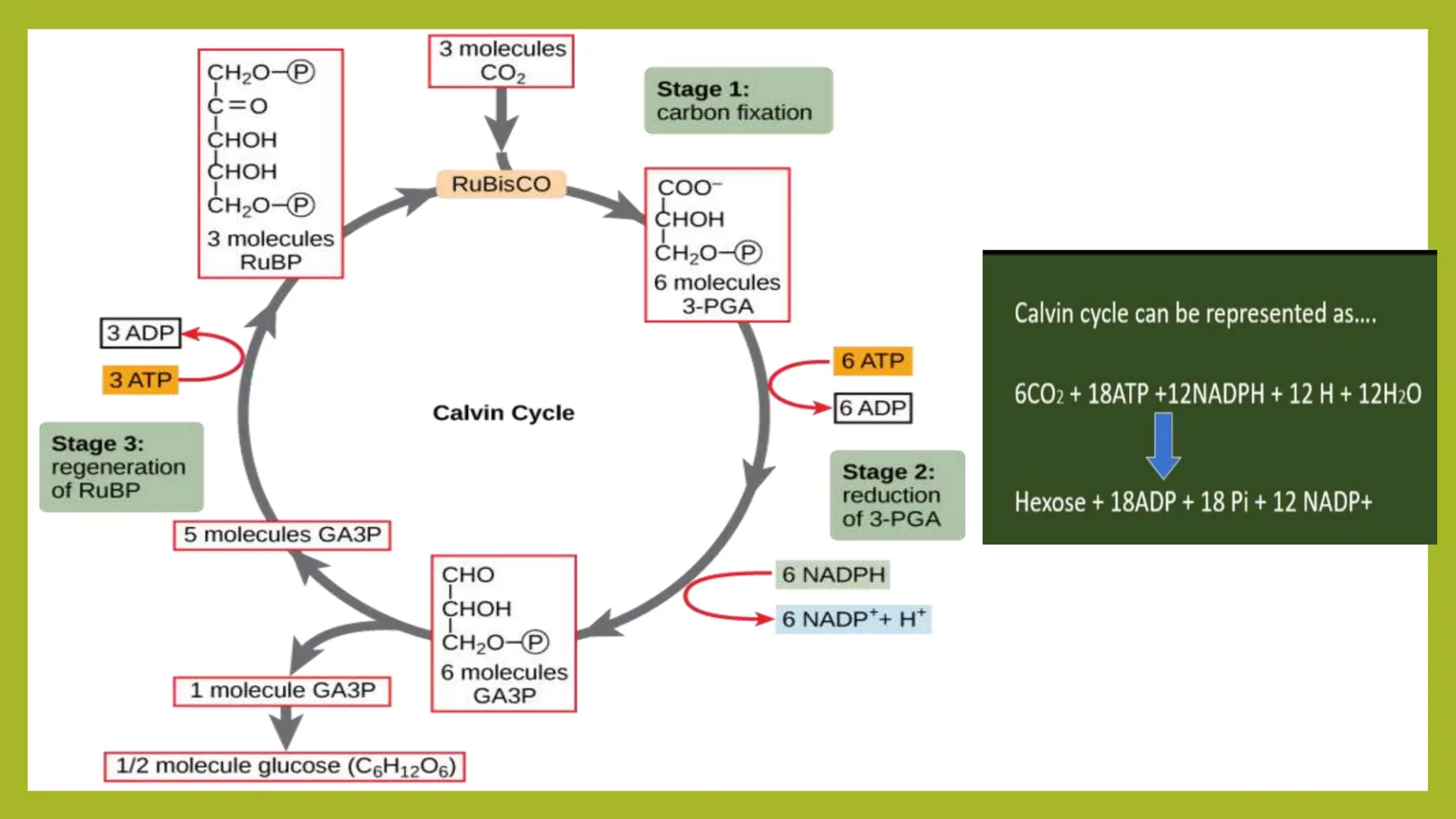
The document provides an overview of bacterial photosynthesis, detailing its types, pigments, and phases. It distinguishes between oxygenic and anoxygenic photosynthesis, highlighting the different pigments involved such as chlorophyll and bacteriochlorophyll. The text also outlines the light and dark phases of photosynthesis and references key literature on the subject.