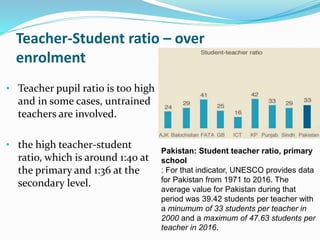
There are several problems with curriculum implementation in Pakistan. Economic problems are a major issue, as Pakistan only spends 2.4% of its GDP on education, which is not enough to fund teaching resources, teacher training, and other necessities. Political instability also hinders curriculum implementation, as different political parties have varying education policies. Additionally, teachers are often not properly trained or reluctant to accept changes to the curriculum. Other issues include a lack of sequencing in curriculum, uncertainty among parents regarding changes, and outdated curriculum that does not match students' current needs and skills. Proposed solutions include developing comprehensive implementation plans, increasing funding and resources, providing quality teacher training, and improving monitoring and evaluation of teachers.