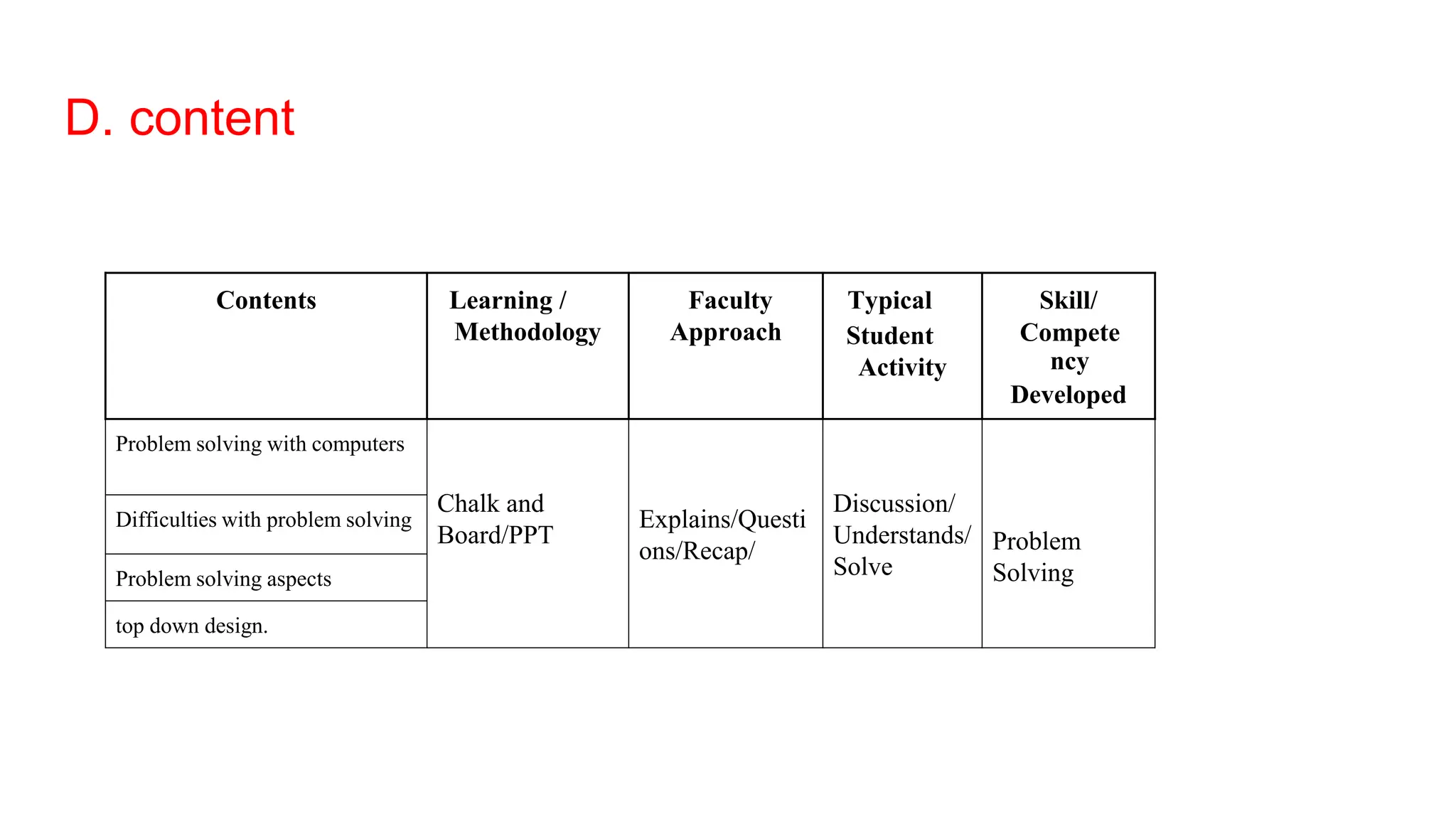
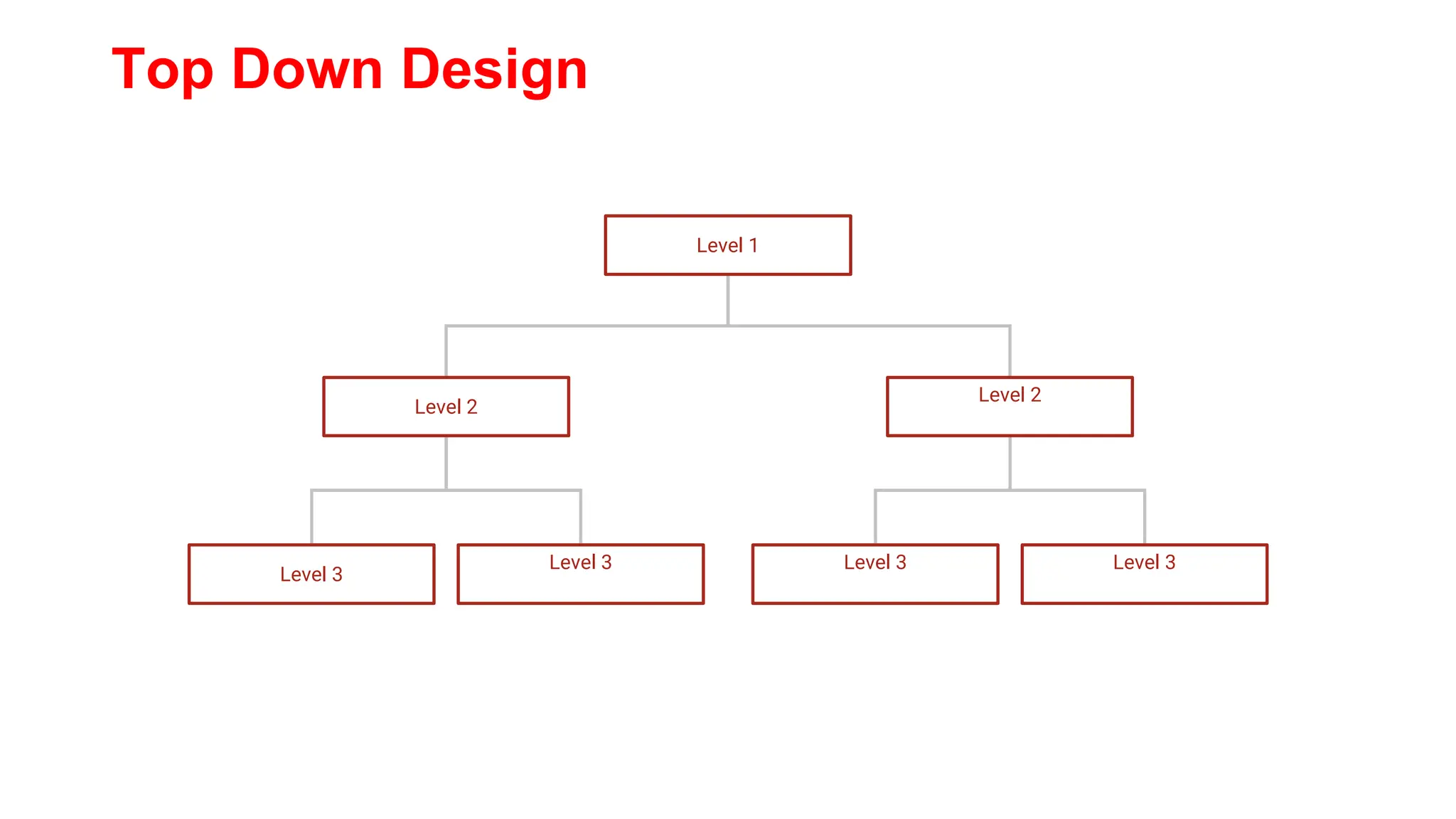
The document discusses problem solving and programming. It outlines the session which includes a review of problem solving steps and learning outcomes related to difficulties in problem solving and problem aspects. It then covers content on problem solving with computers, difficulties in problem solving, problem solving aspects, and top down design. Top down design is explained as breaking a problem down into smaller sub-problems or operations until easily solvable sub-problems are identified.