This document defines key probability concepts and formulas:
1. It defines sample space, trials, and events for a probability problem. A sample space is all possible outcomes, a trial is a single outcome, and an event is a subset of outcomes.
2. It gives the formula for probability of an event as the number of outcomes in the event divided by the total number of outcomes. Expected frequency is the probability of an event times the number of trials.
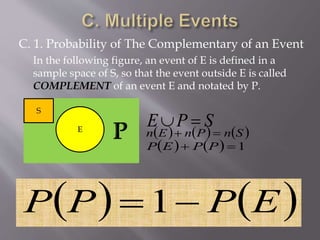
3. It discusses the probability of complementary events, mutually exclusive events, mutually independent events, and conditional events along with the corresponding formulas.