Embed presentation
Download to read offline









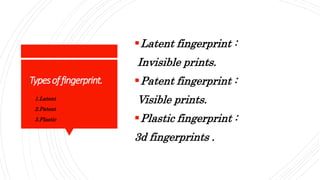
This document discusses the basic principles of forensic science. It outlines seven principles: 1) Locard's exchange principle that every contact leaves a trace, 2) individuality that every piece of evidence has unique characteristics, 3) comparison that only similar evidence can be compared, 4) progressive change that evidence degrades over time, 5) analysis that evidence must be analyzed based on observations, 6) probability that there is always some probability associated with evidence, and 7) circumstantial facts that facts don't lie but people can. It also briefly discusses types of fingerprints including latent, patent, and plastic fingerprints.









