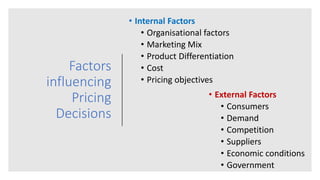
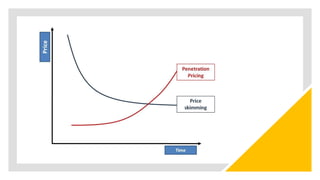
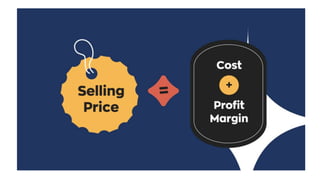
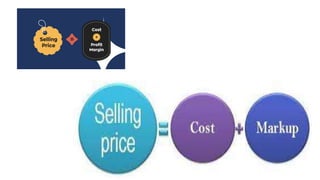
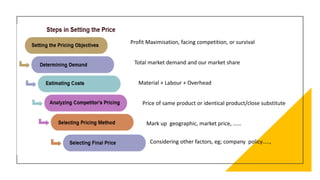
This document discusses pricing decisions and strategies. It outlines several key objectives of pricing including return on investment, market share, profit maximization, and preventing competition. Pricing is influenced by internal factors like costs, product differentiation, and objectives as well as external factors like consumers, demand, competition, suppliers, and economic conditions. Several pricing strategies are described such as price lining, captive pricing, dual pricing, premium pricing, penetration pricing, and skimming pricing. Finally, 11 steps in formulating a pricing strategy are provided.