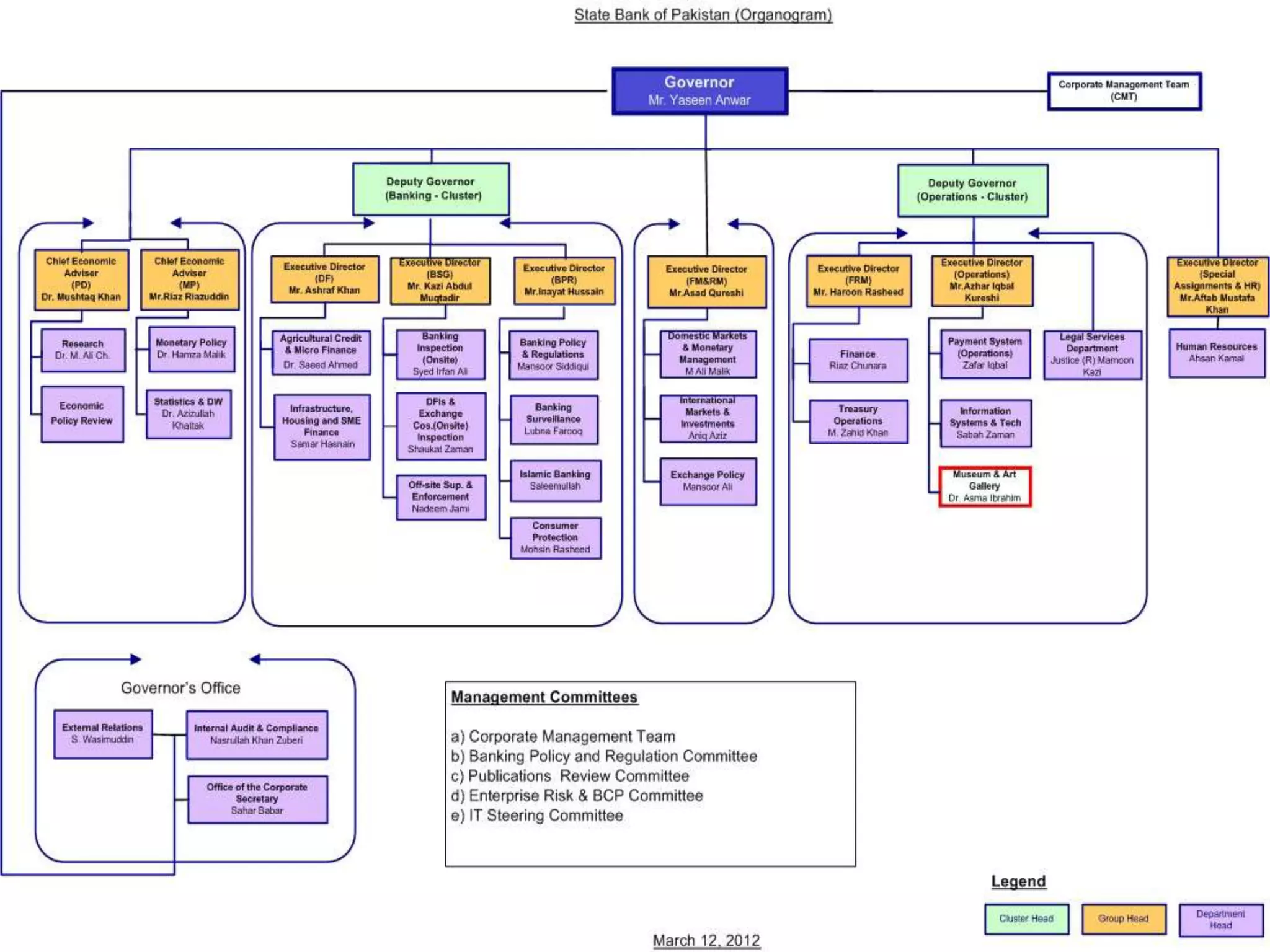
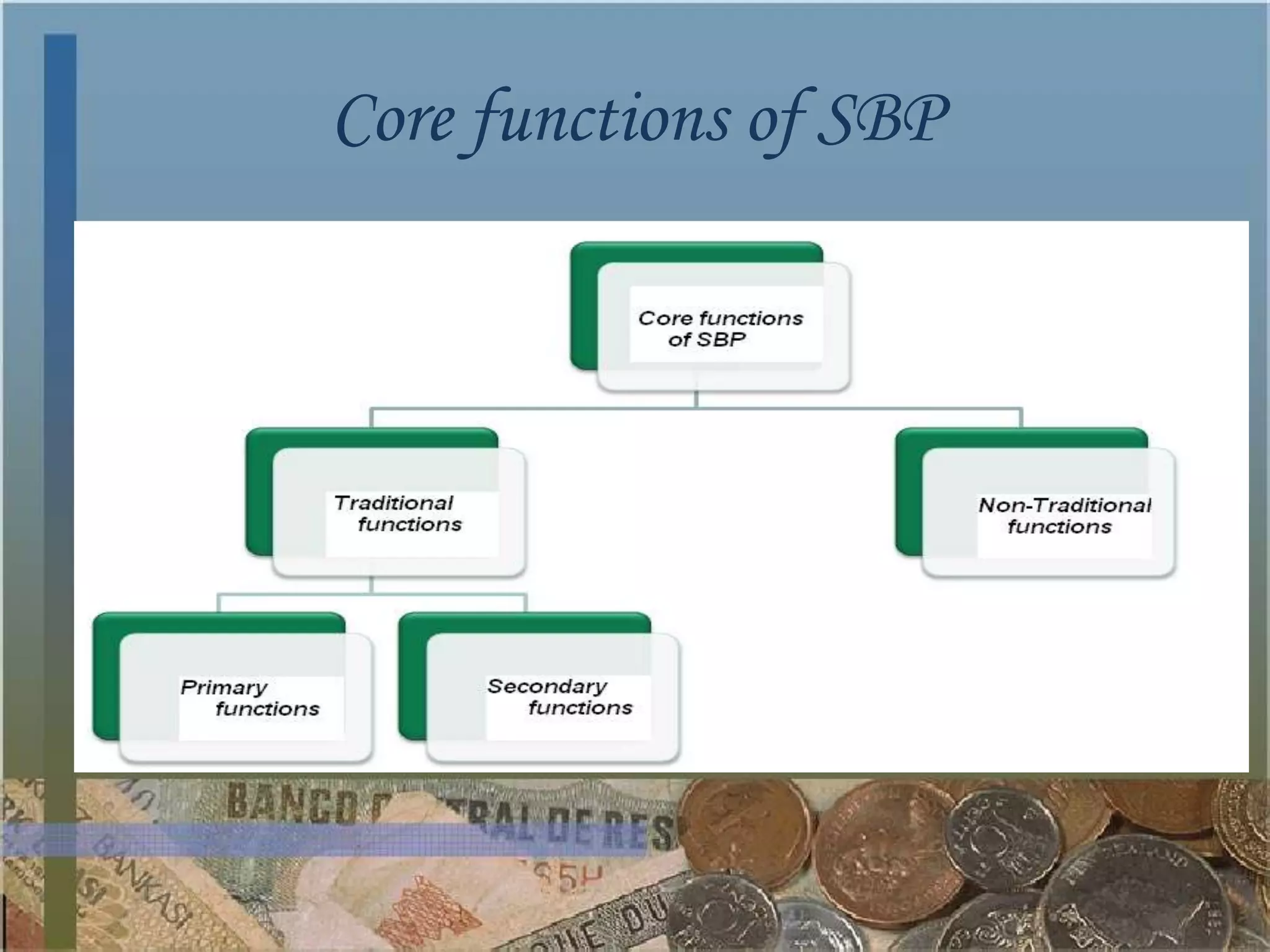
The State Bank of Pakistan (SBP) is the central bank of Pakistan. It was established in 1947 after the partition of India. SBP is responsible for monetary policy, managing foreign exchange reserves, supervising commercial banks, and providing banking services to the government. As an independent institution since 1997, SBP aims to achieve price stability and full employment through tools like interest rates, cash reserve ratios, and open market operations. It also regulates the financial system, acts as the lender of last resort, and advises the government on economic and financial matters.