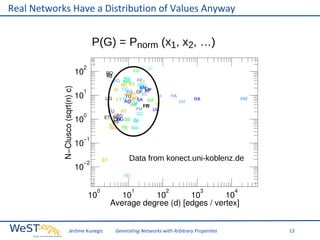
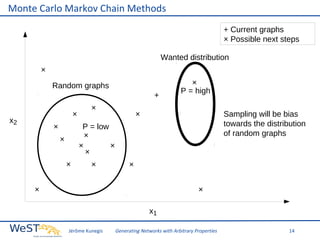
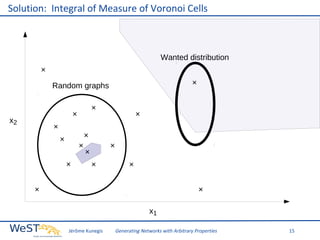
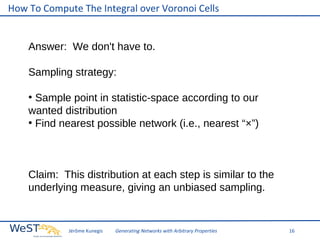
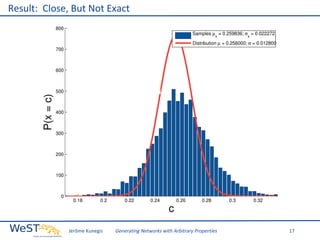
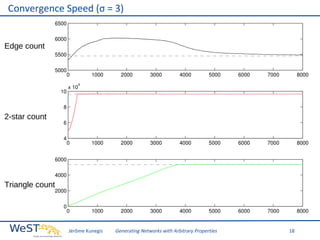
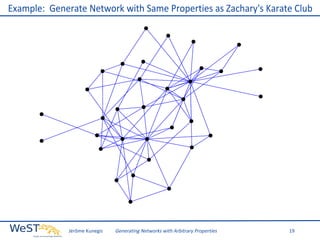
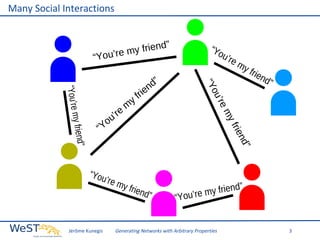
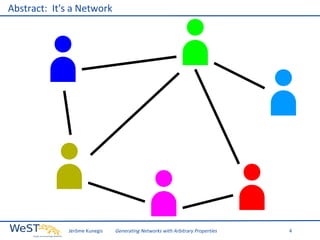
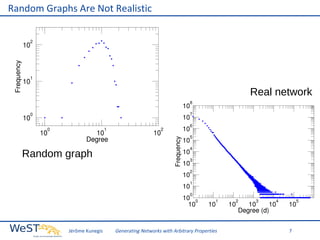
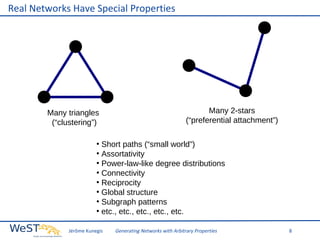
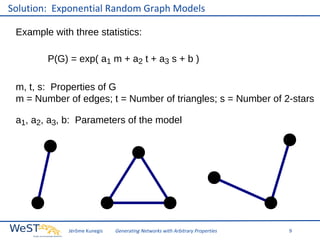
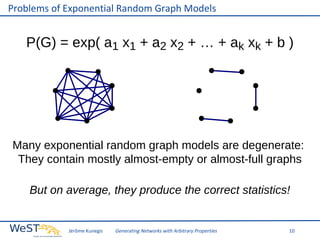
This document discusses generating networks with arbitrary properties. It begins by explaining the limitations of random graphs in capturing properties of real-world networks. Exponential random graph models are then introduced as a way to generate graphs with specific properties, but these models often produce degenerate graphs. The document proposes using a normal distribution over graph properties rather than just expected values. It describes using Monte Carlo Markov chain methods and integrating over Voronoi cells to sample graphs from this distribution. Finally, it shows an example of generating a network with the same properties as the real-world Karate Club network.

![Explanation of Degeneracy
Consider a variable x between 0 and 1
with expected value 0.3.
An exponential random model for it is given by:
P(x) = exp( ax + b )
P(x)
We get
Mode[x] = 0
!!
0
Jérôme Kunegis
0
0.3
Generating Networks with Arbitrary Properties
1
x
11](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation-131219045225-phpapp01/85/Generating-Networks-with-Arbitrary-Properties-11-320.jpg)
![Idea
Require not that E[x] = c, but that x follow a normal distribution
P(x)
0
0
0.3
1
x
P(G) = Pnorm (x1, x2, …; μ1, μ2, …, σ1, σ2, …)
Jérôme Kunegis
Generating Networks with Arbitrary Properties
12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation-131219045225-phpapp01/85/Generating-Networks-with-Arbitrary-Properties-12-320.jpg)