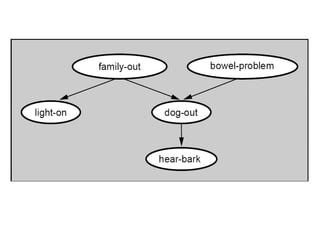
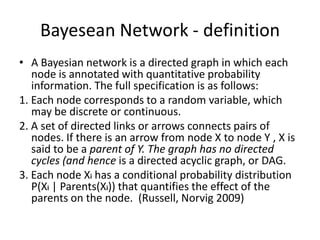
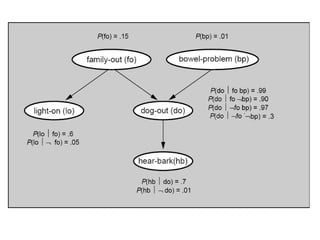
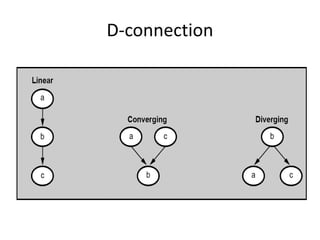
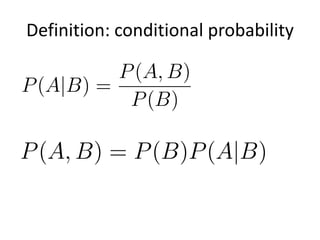
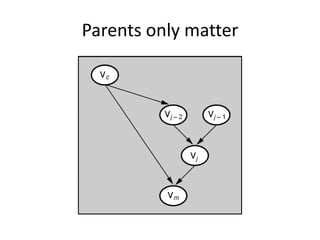
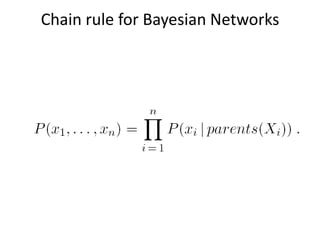
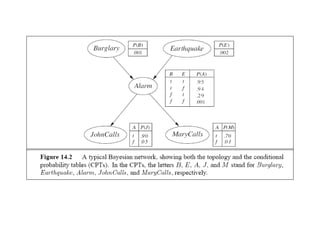
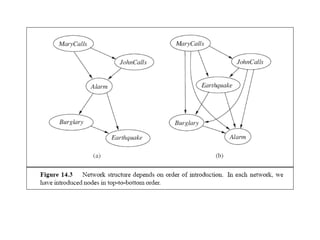
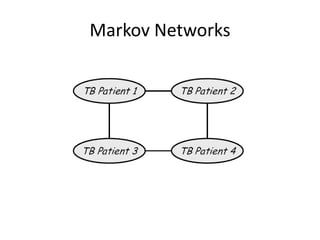
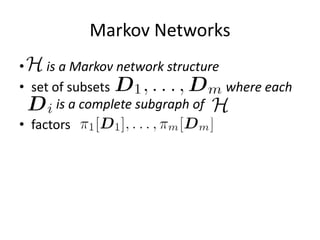
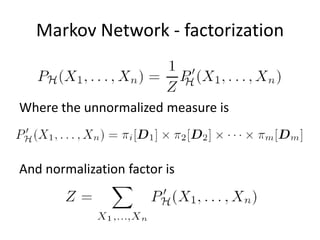
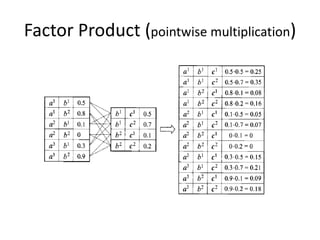
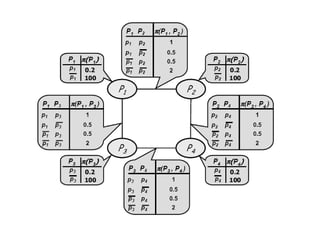
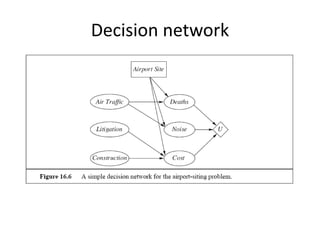
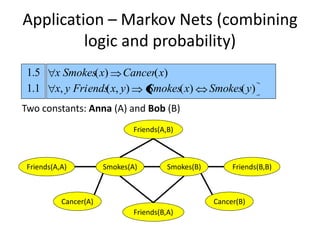
Graphical models provide a framework for combining probabilities and logical structures to compactly represent complex phenomena. Bayesian networks are a type of graphical model that use directed graphs to represent conditional independence relationships between variables. Each node corresponds to a variable with a conditional probability distribution. This factorization allows compressing a full joint distribution into a smaller set of local distributions. Markov networks are another type of graphical model that use undirected graphs and factors to represent relationships without directionality. Graphical models have applications in areas like medical diagnosis, computer vision, and combining logic and probability. Tools exist to help construct and evaluate graphical models.